Abstract
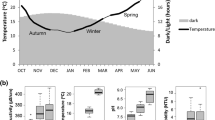
Seasonal changes in water temperatures, embracing periods of low, rising, high and declining temperatures, were recorded in both a temperate and a tropical pond. In the course of a year, the range between the lowest and highest average weekly temperatures was greater in the temperate pond. The spans between the average minimum and the average maximum weekly water temperatures in the warmest months of the year in the tropical pond were greater than those found at any time of the year in the temperate pond. The average weekly air and water temperatures showed the same pattern of seasonal fluctuations; in the tropical pond the average weekly air temperatures were always less than the average minimum weekly water temperatures, whereas they were below, within or above the spans between the average minimum and average maximum weekly aquatic temperatures, according to the time of year, in the temperate pond.
In both ponds, diurnal fluctuations were absent during the cooler months; the amplitudes of the fluctuations in the warmer months varied according to the time of year, and were greater, during the warmest months, in the tropical pond. In both ponds lowest temperatures were recorded sometime between 0200 and 1000 hours and highest between 1200 and 2000 hours.
The influence of temperature on the life-cycles of invertebrates in both ponds is discussed briefly.
Zusammenfassung
Jahreszeitlich bedingte Schwankungen in der Wassertemperatur, welche Perioden mit niedriger, ansteigender, hoher und abfallender Temperatur einschlossen, wurden in einem gemäßigten und in einem tropischen Teich festgestellt. Im Laufe eines Jahres war der Unterschied zwischen den tiefsten und höchsten wöchentlichen Durchschnittstemperaturen im gemäßigten Teich größer. Hingegen war der Abstand zwischen Mindest- and Höchsttemperatur des Wassers im Wochendurchschnitt während der warmsten Monate des Jahres im tropischen Teich größer als zu irgendeiner Jahreszeit im gemäßigten Teich. Der Wochendurchschnitt der Luft- und Wassertemperaturen wies das gleiche jahreszeitlich bedingte Schwankungsmuster auf. In dem tropischen Teich war die wöchentliche Durchschnittstemperatur der Luft stets niedriger als die Mindestdurchschnittstemperatur des Wassers in einer Woche. Jedoch lag sie — je nach Jahreszeit — unterhalb, auf gleicher Höhe oder oberhalb der Spannweite der niedrigsten and der höchsten wöchentlichen Dutchschnittstemperaturen des Wassers im gemäßigten Teich.
In beiden Teichen traten die taglichen Schwankungen während der kÜhleren Monate nicht auf. Der Umfang der Schwankungen in den wärmeren Monaten variierte je nach Jahreszeit and war in den wärmsten Monaten in dem tropischen Teich größer. In beiden Teichen wurden die tiefsten Temperaturen zwischen 2.00 and 10.00 Uhr and die höchsten zwischen 12.00 and 20.00 Uhr gemessen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buschkiel, A. L. - 1939 - Stoffwechsel im tropischen Teich, fischereibiologisch betrachtet. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 6: 156–206.
Chodorowski, A. - 1961 - Some chemical and thermal properties of the small pools in the Kampinos Forest in the spring-time. Polskie Arch. Hydrobiol. 9: 287–317.
George, M. G. - 1961 - Diurnal variations in two shallow ponds in Delhi, India. Hydrobiologia 18: 265–273.
Klimowicz, H. - 1961 - Daily temperature variations in a small water pool in Cairo. Polskie Arch. Hydrobiol. 9: 195–202.
Macan, T. T. - 1961 - Factors that limit the range of freshwater animals. Biol. Rev. 36: 151–198.
Macan, T. T. - 1963 - Freshwater Ecology. London, Longmans, Green. ppX + 338.
Macan, T. T. & Maudsley, R. - 1966 - The temperature of a moorland fishpond. Hydrobiologia 27: 1–22.
Martin, N. A. - 1972 - Temperature fluctuations within English lowland ponds. Hydrobiologia 40: 455–469.
Michael, R. G. - 1969 - Seasonal trends in physicochemical factors and plankton of a freshwater fishpond and their role in fish culture. Hydrobiologia 33: 144–160.
Pourriot, R. - 1972 - Étude hydrobiologique de deux petits étangs de prairie. Observations Sur la distribution de la température et du plancton et l'influence d'un couvert végétal à Lemna minor. Ann. Hydrobiol. 3: 33–46.
Rakusa-Suszczewski, S. - 1964 - Temperature variations in tropical shallow water pools (Brasil). Polskie Arch. Hydrobiol. 12: 421–142.
Rao, V. S. - 1971 - An ecological study of three freshwater ponds of Hyderabad - India. 1. The environment. Hydrobiologia 38: 213–223.
Reynoldson, T. B., Young, J. O. & Taylor, M. C. - 1965 - The effect of temperature on the life-cycle of four species of lake-dwelling triclads. J. Anim. Ecol. 34: 23–43.
Rzóska, J. - 1961 - Observations on tropical rainpools and general remarks on temporary waters. Hydrobiologia 17: 265–286.
Sitaramaiah, P. - 1966 - Studies on the ecology of a freshwater pond community. Hydrobiologia 27: 529–548.
Vaas, K. F. & Sachlan, M. - 1955 - Limnological studies on diurnal fluctuations in shallow ponds in Indonesia. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 12: 309–319.
Weir, J. S. - 1969 - Studies on Central African pans. III. Fauna and physicochemical environment of some ephemeral pools. Hydrobiologia 33: 93–116.
Young, J. O. - 1974, a - Life-cycles of some invertebrate taxa in a small pond together with changes in their numbers over a period of three years. Hydrobiologia, 45: 63–90.
Young, J. O. - 1974, b - Seasonal changes in the abundance of Microcrustacea in a small pond. Hydrobiologia, 45: 373–389.
Young, J. O. - 1974, c - The occurrence of diapause in the egg stage of the lifecycle of Phaenocora typhlops (Vejdovsky) (Turbellaria: Neorhabdocoela). J. Animal. Ecol. 43: 719–731.
Young, J. O. - 1975 - The population dynamics of Phaenocora typhlops (Vejdovsky) (Turbellaria: Neorhabdocoela) living in a pond. J. Anim. Ecol. 44: 251–262.
Young, J. O. & Gibson, R. - in press. - Some ecological studies on two populations of the freshwater hoplonemertean Prostoma eilhardi (Montgomery, 1894) from Kenya, Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 19.
Young, J. O. & Reynoldson, T. B. - 1966 - A quantitative study of the population biology of Dendrocoelum lacteum (Müller) (Turbellaria, Tricladida). Oikos 15: 237–264.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Young, J.O. Seasonal and diurnal changes in the water temperature of a temperate pond (England) and a tropical pond (Kenya). Hydrobiologia 47, 513–526 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00039595
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00039595