Abstract
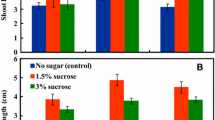
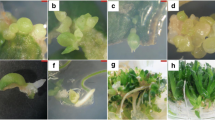
Immature soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr) embryos, or cotyledons isolated from them, were cultured on modified MS medium containing B5 vitamins and NAA (50 μM) to induce somatic embryogenesis. The effects of media variables, dissection treatments and light conditions were investigated in this system. The efficiency of embryogenesis increased as sugar concentration decreased from 12 to 1.5%; sucrose and glucose were similarly effective as carbon sources. In an examination of the effects of medium pH, values between pH 5.0 and 7.0 gave similar embryogenesis efficiencies, but the frequency of normal embryos was greater in media with low pH values. In buffered medium (10 mM MES), a pH of 5.0 was inhibitory to embryogenesis, and most normal embryos were produced at pH 5.5. Under various dissection treatments, embryogenesis efficiency and root and callus production were increased by tissue damage. Somatic embryogenesis was observed both in darkness and in light, although embryo development was impaired under high light (80 μE m-2 s-1) conditions. The ability of somatic embryos to germinate was closely correlated with embryo normality, and was influenced little by the hormone content of germination media. Of various media tested for their ability to support the growth of germinated embryos, a medium based on hydroponic nutrient salts, supplemented with yeast extract, and gelled with Difco-Bacto agar gave the best plantlet growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- μE m-2 s-1 :
-
microEinsteins per square meter per second
- NAA:
-
α-napthalene acetic acid
- N50:
-
MS salts with B5 vitamins and 50 μM NAA (Napthalene acetic acid)
- MES:
-
2(n-morpholino) ethanesulphuric acid
- BAP:
-
benzylamino purine
- IBA:
-
indole butyric acid
References
Ackerson RC (1985) Invertase activity and abscisic acid in relation to carbohydrate status in developing reproductive structures. Crop Sci 25: 615–618
Ammirato PV (1983) Embryogenesis. In: Evans DA, Sharp WR, Ammirato PV, Yamada Y (Eds) Handbook of Plant Cell Culture, Vol. I, 82–123. New York: Macmillan
Barwale UB, Kerns HR, Widholm JM (1986) Plant regeneration from callus cultures of several soybean genotypes via embryogenesis and organogenesis. Planta 167: 473–481
Beversdorf WD, Bingham ET (1977) Degrees of differentiation obtained in tissue cultures of Glycine species. Crop Sci 17: 307–311
Christianson ML, Warmick DA, Carlson PS (1983) A morphogenetically competent soybean suspension culture. Science 222: 632–634
Collins GB and Phillips GC (1982) Tissue culture and plant regeneration in Trifolium pratense. In: Earle ED, and Demarly Y (eds) Variability in Plants Regenerated from Tissue Culture. p. 26. New York; Praeger
Eskew DL, Welch RM, Cary EA (1983) Nickel: An essential micronutrient for legumes and possibly all higher plants. Science 22: 621–623
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50: 151–158
Helson VA (1965) Comparison of Grolux and cool white fluorescent lamps with and without incandescent as light sources used in plant growth rooms for growth and development of tomato plants. Can J Plant Sci 45: 461–466
Kao KN (1977) Chromosomal behaviour in somatic hybrids of soybean — Nicotiana glauca. Mol Gen Genet 150: 225–230
Lazzeri PA, Dunwell JM (1984) Establishment of isolated root cultures of Brassica species and regeneration from cultured-root segments of Brassica oleracea var. italica. Ann Bot 54: 351–361
Lazzeri PA, Hildebrand DF, Collins GB (1985) A procedure for plant regeneration from immature cotyledon tissue of soybean. Plant Mol Biol Rep 3: 160–167
Lazzeri PA, Hildebrand DF, Collins GB (1987) Soybean somatic embryogenesis: Effects of hormones and culture manipulations. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult (Submitted)
Li BJ, Langridge WHR, Szaley AA (1985) Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration in the soybean Glycine max. Plant Cell Rep 4: 344–347
Lippmann B, Lippmann G (1984) Induction of somatic embryos in cotyledonary tissue of soybean, Glycine max L. Merr. Plant Cell Rep 3: 215–218
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15: 473–494
Obenbdorf RL, Timpo EE, Byrne MC, Toaiu TV, Rytko GT, Hsu FC, Anderson GB (1984) Soya bean seed growth and maturation in vitro without pods. Ann Bot 53: 853–863
Ranch JP, Ogelsby L, Zielinski AC (1985) Plant regeneration from embryo-derived tissue cultures of soybeans. In vitro 21: 653–658
Schaefer J (1985) Regeneration in alfalfa tissue culture: Characterization of intracellular pH during somatic embryo production by solid-state P-31 NMR. Plant Physiol 79: 584–589
Schlegal G, Schneider-Maessen R (1981) Einfluss von Licht auf die Regeneration von Saint paulia ionantha H. Wendl in vitro. Gartenbauwissenschaft 46: 106–14
Strickland SG, McCall CM, Nichol JW, Stuart DA (1986) Enhanced somatic embryogenesis in Medicago sativa by addition of maltose and its higher homologs to the culture medium. In: Somers DA, Gegenbach BG, Biesboer DD, Hackett WP, Green CE (eds) Abstracts VI Internal Conf Plant Tiss Cell Cult, p. 188; Minneapolis; Univ. Minnesota
Stuart DA, Nelson J, Strickland SG, Nichol JW (1985) Factors affecting developmental processes in alfalfa cell cultures. In: Henke RR, Hughes KW, Constantin MP, Hollaender A (eds), Tissue Culture Forestry and Agriculture, 59–73. New York: Plenum
Thompson JF, Madison JT, Muenster A-ME (1977) In vitro culture of immature cotyledons of soyabean (Glycine max L. Merr). Ann Bot 41: 29–39
Williams EG, Maheswaran G (1986) Somatic embryogenesis: Factors influencing coordinate behaviour of cells as an embryogenic group. Ann Bot 57: 443–462
Yang Z, Chen Z, Lin Z, Zhang Z (1984) Soybean tissue culture: In vitro culture of leaves and the induction of regenerated plants. Bulletin of Sciences 16: 1012–1016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper (No. 86-3-97) is published with the approval of the director of the Kentucky Agricultural Experiment Station.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lazzeri, P.A., Hildebrand, D.F. & Collins, G.B. Soybean somatic embryogenesis: Effects of nutritional, physical and chemical factors. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 10, 209–220 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00037305
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00037305