Abstract
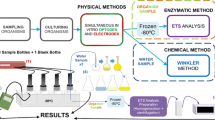
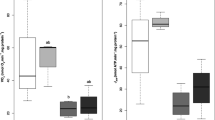
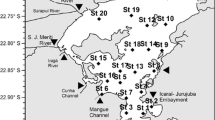
A method for measuring respiratory electron transport system activity (ETSA) in freshwater sediments is presented. It is a modification of the methods used for marine sediments by Christensen & Packard (1977) and Olànczuk-Neyman & Vosjan (1977). The assay is based on the reduction of the electron acceptor 2-(p iodophenyl) 3 (p nitrophenyl) 5 phenyl tetrazolium chloride (INT) by cell-free homogenates of sediment samples. This study shows that the method is sensitive, has good accuracy and can be used for freshwater sediments. The accuracy decreases at high turbidity and as yet has only been tested for sediments of the gyttja type. Untreated samples can be stored at low temperature for several weeks without any loss of activity. ETSA decreases with the depth of sediment and with increased amount of allochthonous material in the sediment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, S. I. & R. A. Kenner, 1977. A study of in vitro electron transport activity in marine phytoplankton as a function of temperature. J. Phycol. 13: 116–121.
Christensen, J. P. & T. T. Packard, 1977. Sediment metabolism from the North-west African upwelling system. Deep Sea Res. 24: 331–343.
Devol, A. H. & T. T. Packard, 1978. Seasonal changes in respiratory enzyme activity and productivity in Lake Washington microplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23: 104–111.
Jones, J. G. & B. M. Simon, 1979. The measurement of electron transport system activity in freshwater benthic and planktonic samples. J. appl. Bacteriol. 46: 305–315.
Kenner, R. A. & S. I. Ahmed, 1975. Measurements of electron transport activities in marine phytoplankton. Mar. Biol. 33: 119–127.
King, F. D. & T. T. Packard, 1975. Respiration and the activity of the respiratory electron transport system in marine zooplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 20: 849–854.
Olánczuk-Neyman, K. M. & J. H. Vosjan, 1977. Measuring respiratory electron-transport-system activity in marine sediment. Neth. J. Sea Res. 11(1): 1–13.
Owens, T. G. & F. D. King, 1975. The measurement of respiratory electron-transport-system activity in marine zooplankton. Mar. Biol. 33: 27–36.
Packard, T. T., 1971. The measurement of respiratory electron transport activity in marine phytoplankton. J. mar. Res. 29: 235–244.
Packard, T. T., M. L. Healy & F. A. Richards, 1971. Vertical distribution of the activity of respiratory electron transport system in marine plankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 16: 60–70.
Wieser, W. & M. Zech, 1976. Dehydrogenases as tools in the Study of Marine Sediments. Mar. Biol. 36: 113–122.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Broberg, A. A modified method for studies of electron transport system activity in freshwater sediments. Hydrobiologia 120, 181–187 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00032140
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00032140