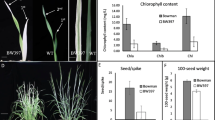
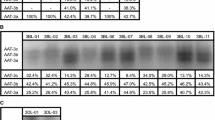
Abstract
A barley leaf cDNA library has been screened with two oligonucleotide probes designed to hybridize to conserved sequences in glutamine synthetase (GS) genes from higher plants. Two GS cDNA clones were identified as hybridizing strongly to one or both probes. The larger clone (pcHvGS6) contained a 1.6 kb insert which was shown by primer extension analysis to be an almost full-length cDNA. Both clones were more closely related to cDNAs for the chloroplast form of GS (GS2) from pea and Phaseolus vulgaris than to cDNAs for the cytosolic form (GS1). A sequence identicalto an N-terminal sequence determined from a purified preparation of the mature GS2 polypeptide (NH2-XLGPETTGVIQRMQQ) was found in the pcHvGS6-encoded polypeptide at residues 46–61, indicating a pre-sequence of at least 45 amino acids. The pre-sequence has only limited sequence homology to the pre-sequences of pea and P. vulgaris GS2 subunits, but is similarly rich in basic residues and possesses some of the structural features common to the targeting sequences of other chloroplast proteins. The molecular lesions responsible for the GS2-deficient phenotypes of eight photorespiratory mutants of barley were investigated using a gene-specific probe from pcHvGS6 to assay for GS2 mRNA, and an anti-GS antiserum to assay for GS2 protein. Three classes of mutants were identified: class I, in which absence of cross-reacting material was correlated with low or undetectable levels of GS2 mRNA; class II, which had normal or increased levels of GS2 mRNA but very little GS2 protein; and class III, which had significant amounts of GS2 protein but little or no GS2 activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander DC, McKnight TD, Williams BG: A simplified and efficient vector-primer cDNA cloning system. Gene 31: 79–89 (1984).
Avni A, Edelman M, Rachailovich I, Aviv D, Fluhr R: A point mutation in the gene for the large subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase affects holoenzyme assembly in Nicotiana tabacum. EMBO J 8: 1915–1918 (1989).
Baima S, Haegi A, Strøman P, Casadoro G: Characterization of a cDNA clone for barley leaf glutamine synthetase. Carlsberg Res Commun 54: 1–9 (1989).
Bennett MJ, Lightfoot DA, Cullimore JV: cDNA sequence and differential expression of the gene encoding the glutamine synthetase γ polypeptide of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Mol Biol 12: 553–565 (1989).
Blackwell RD, MurrayA JS, Lea PJ: Inhibition of photosynthesis in barley with decreased levels of chloroplastic glutamine synthetase activity. J Exp Bot 38: 1799–1809 (1987).
Brangeon J, Nato A, Forchioni A: Ultrastructural detection of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase protein and its subunit mRNAs in wild-type and holoenzyme-deficient Nicotania using immuno-gold and in situ-hybridization techniques. Planta 177: 151–159 (1989).
Broglie R, Coruzzi G, Lamppa G, Keith B, Chua N-H: Structural analysis of nuclear genes coding for the precursor to the small subunit of wheat ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Bio/technology 1: 55–61 (1983).
Calzone FJ, Britten RJ, Davidson EM: Mapping of gene transcripts by nuclease protection assays and cDNA primer extension. In: Berger SL, Kimmel AR (eds) Guide to Molecular Cloning Techniques. Methods in Enzymology, vol 152, pp. 611–632, Academic Press, San Diego (1987).
Cannell M, Mulcahy M, Karp A, Shewry PR: Chromosomal assignment of characterized cDNAs and genes using RFLP analysis of ditelosomic addition lines. Barley Genet Newsl, in press (1989).
Cullimore JV, Lara M, Lea PJ, Miflin BJ: Purification and properties of two forms of glutamine synthetase from the plant fraction of Phaseolus root nodules. Planta 157: 245–253 (1983).
Cullimore JV, Miflin BJ: Immunological studies on glutamine synthetase using antisera raised to the two plant forms of the enzyme from Phaseolus root nodules. J Exp Bot 35: 581–587 (1984).
Dean C, van den Elzen P, Tamaki S, Dunsmuir P, Bedbrook J: Differential expression of the eight genes of the petunia ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit multigene family. EMBO J 4: 3055–3061 (1985).
Devreux J, Haeberli P, Smithies O: A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucl Acids Res 12: 387–395 (1984).
Doering JL, Burket AE: Plasmid screening in bacterial colonies grown on Colony/Plaquescreen membranes. NEN Product News 4: 1–4 (1984).
Edwards JW, Coruzzi GM: Photorespiration and light act in concert to regulate the expression of the nuclear gene for chloroplast glutamine synthetase. Plant Cell 1: 241–248 (1989).
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B: A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 137: 266–267 (1984).
Forde BG, Cullimore JV: The molecular biology of glutamine synthetase in higher plants. Oxf Surv Plant Molec Cell Biol, in press (1989).
Gebhardt C, Oliver JE, Forde BG, Saarelainen R, Miflin BJ: Primary structure and differential expression of glutamine synthetase genes in nodules, roots and leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris. EMBO J 5: 1429–1435 (1986).
Hake S, Taylor WC, Freeling M: Molecular analyses of genetically stable mutants of the maize Adh1 gene. Mol Gen Genet 194: 42–48 (1984).
Hanahan D, Meselson M: High density plasmid screening. Gene 10: 63–67 (1980).
Hanks SK: Homology probing: identification of cDNA clones encoding members of the protein-serine kinase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 388–392 (1987).
Haymerle H, Herz J, Bressan GM, Frank R, Stanley KK: Efficient construction of cDNA libraries in plasmid expression vectors using an adaptor strategy. Nucl Acids Res 14: 8615–8624 (1986).
Hirel B, Gadal P: Glutamine synthetase in rice. A comparative study of the enzyme from roots and leaves. Plant Physiol 66: 619–623 (1980).
Jofuku KD, Schipper RD, Goldberg RB: A frameshift mutation prevents kunitz trypsin inhibitor mRNA accumulation in soybean embryos. Plant Cell 1: 427–435 (1989).
Joshi CP: Putative polyadenylation signals in nuclear genes of higher plants: a compilation and analysis. Nucl Acids Res 15: 9627–9640 (1987).
Karlin-Neumann GA, Tobin EM: Transit peptides of nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins share a common amino-acid framework. EMBO J 5: 9–13 (1986).
Kendall AC, Hall NP, Keys AJ, Lea PJ, Turner JC, Wallsgrove RM: Carbon and nitrogen metabolism in photorespiratory mutants of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). In: Marcelle R, Clijsters H, van Poucke M (eds) Biological Control of Photosynthesis, pp. 257–265, Martinus Nijhoff, Dordrecht (1986).
Kendall AC, Wallsgrove RM, Hall NP, Turner JC, Lea PJ: Carbon and nitrogen metabolism in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) mutants lacking ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase. Planta 168: 316–323 (1986).
Keys AJ, Bird IF, Cornelius MJ, Lea PJ, Wallsgrove RM, Miflin BJ: Photorespiratory nitrogen cycle. Nature 275: 741–743 (1978).
Lathe R: Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data: theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol 183: 1–12 (1985).
Laursen RA: Solid-phase Edman degradation. An automatic peptide sequencer. Eur J Biochem 20: 89–102 (1971).
Lightfoot DA, Green NK, Cullimore JV: The chloroplast-located glutamine synthetase of Phaseolus vulgaris L: nucleotide sequence, expression in different organs and uptake into isolated chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol 11: 191–202 (1988).
McNally SF, Hirel B, Gadal P, Mann AF, Stewart GR: Glutamine synthetases of higher plants: evidence for a specific isoform content related to their possible physiological role and their compartmentation within the leaf. Plant Physiol 72: 22–25 (1983).
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J: Molecular cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1982).
Mann AF, Fentem PA, Stewart GR: Identification of two forms of glutamine synthetase in barley (Hordeum vulgare). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 88: 515–521 (1979).
Mann AF, Fentem PA, Stewart GR: Tissue localization of barley (Hordeum vulgare) glutamine synthetase isoenzymes. FEBS Lett 110: 265–267 (1980).
Messing J, Crea R, Seeburg PH: A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucl Acids Res 9: 309–321 (1981).
Miflin J, Lea PJ: Ammonia assimilation. In: MiflinBJ (ed) The Biochemistry of Plants, vol 5, pp. 169–202, Academic Press, New York (1980).
Orkin SH, Kazazian HH Jr: The mutation and polymorphism of the human β-globin gene and its surrounding DNA. Ann Rev Genet 18: 131–171 (1984).
Reiss B, Wasmann CC, Schell J, Bohnert HJ: Effect of mutations on the binding and translocation functions of a chloroplast transit peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 886–890 (1989).
Scallon BJ, Dickenson DD, Nielsen NC: Characterization of the null allele for the Gy4, glycinin gene from soybean. Mol Gen Genet 208: 107–113 (1987).
Schmidt GW, Mishkind ML: Rapid degradation of unassembled ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunits in chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80: 2632–2636 (1983).
Snustad DP, Hunsperger JP, Chereskin BM, Messing J: Maize glutamine synthetase cDNAs: Isolation by direct genetic selection in Escherichia coli. Genetics 120: 1111–1124 (1988).
Spreitzer RJ, Goldschmidt-Clermont M, Rahire M, Rochaix J-D, Ogren WL: Nonsense mutation in the Chlamydomonas chloroplast gene that codes for the large subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in Chlamydomones reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 5460–5464.
Staden R: Automation of the computer handling of gel reading data produced by the shotgun method of DNA sequencing. Nucl Acids Res 10: 4731–4751 (1982).
Suggs SV, Hirose J, Miyake T, Kawashima EM, Johnson MJ, Itakura K, Wallace RB: Use of synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides for the isolation of specific cloned DNA sequences. ICN-UCLA Symp Mol Cell Biol 23: 682–693 (1981).
Tingey SV, Coruzzi GM: Glutamine synthetase of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia — cloning and in vivo expression. Plant Physiol 84: 366–373 (1987).
Tingey SV, Tsai F-Y, Edwards JW, Walker EL, Coruzzi GM: Chloroplast and cytosolic glutamine synthetase are encoded by homologous nuclear genes which are differentially expressed in vivo. J Biol Chem 263: 9651–9657 (1988).
Tingey SV, Walker EL, Coruzzi GM: Glutamine synthetase genes of pea encode distinct polypeptides which are differentially expressed in leaves, roots and nodules, EMBO J 63: 1–9 (1987).
Tischer E, DasSarma S, Goodman HM: Nucleotide sequence of an alfalfa glutamine synthetase gene. Mol Gen Genet 203: 221–229 (1986).
Tobin AK, Ridley SM, Stewart GR: Changes in the activities of chloroplast and cytosolic isoenzymes of glutamine synthetase during normal leaf growth and plastid development in wheat. Plant 163: 544–548 (1985).
Wachter E, Machleidt W, Hofner H, Otto J: Aminopropyl glass and its p-phenylene diisothiocyanate derivative, a new support in solid phase Edman degradation of peptides and proteins. FEBS Lett 35: 97–102 (1973).
Wallsgrove RM, Keys AJ, Lea PJ, Miflin BJ: Photosynthesis, photorespiration and nitrogen metabolism. Plant Cell Environ 6: 301–309 (1983).
Wallsgrove RM, Turner JP, Hall NP, Kendall AC, Bright SWJ: Barley mutants lacking chloroplast glutamine synthetase — biochemical and genetic analysis. Plant Physiol 83: 155–158 (1987).
Wasmann CC, Reiss B, Bohnert H: Complete processing of a small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from pea requires the amino acid sequence I1e-Thr-Ser. J Biol Chem 263: 617–619 (1988).
Woods D: Oligonucleotide screening of cDNA libraries. BRL Focus 6: 1–3 (1984).
Zimmerman CL, Apella E, Pisano JJ: Rapid analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem 77: 569–573 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freeman, J., Marquez, A.J., Wallsgrove, R.M. et al. Molecular analysis of barley mutants deficient in chloroplast glutamine synthetase. Plant Mol Biol 14, 297–311 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028767
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028767