Abstract
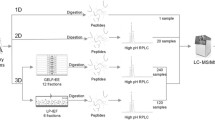
The study on dynamic analysis of human urinary proteome is the foundation that we discriminate certain various urinary proteins as potential bio-marker derived from the disease itself or normal physiological change. In our results, based on RPLC-MS/MS and spectral count to study pooled and individual urine samples and other researchers’ studies, it can be known that the content of many urinary proteins maintain relatively stable. We have reason to believe that the relatively stable urinary protein is a very valuable resource as biomarkers. Many similar proteins such as prostaglandin-H2 D-isomerase and apolipoprotein D proteins have been proved our hypothesis. The following field, the number, preservation and treatment methods of urine sample, the standardization of analysis method and data processing, and suitable quantitative method, is ought to the focus of future study.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi J, Kumar C, Zhang Y, Olsen JV, Mann M (2006) The human urinary proteome contains more than 1500 proteins, including a large proportion of membrane proteins. Genome Biol 7:R80
Fliser D, Novak J, Thongboonkerd V, Argiles A, Jankowski V, Girolami MA, Jankowski J, Mischak H (2007) Advances in urinary proteome analysis and biomarker discovery. J Am Soc Nephrol (JASN) 18:1057–1071
Hirawa N, Uehara Y, Ikeda T, Gomi T, Hamano K, Totsuka Y, Yamakado M, Takagi M, Eguchi N, Oda H, Seiki K, Nakajima H, Urade Y (2001) Urinary prostaglandin D synthase (beta-trace) excretion increases in the early stage of diabetes mellitus. Nephron 87:321–327
Hirawa N, Uehara Y, Yamakado M, Toya Y, Gomi T, Ikeda T, Eguchi Y, Takagi M, Oda H, Seiki K, Urade Y, Umemura S (2002) Lipocalin-type prostaglandin d synthase in essential hypertension. Hypertension 39:449–454
Jain S, Rajput A, Kumar Y, Uppuluri N, Arvind AS, Tatu U (2005) Proteomic analysis of urinary protein markers for accurate prediction of diabetic kidney disorder. J Assoc Phys India 53:513–520
Kentsis A, Monigatti F, Dorff K, Campagne F, Bachur R, Steen H (2009) Urine proteomics for profiling of human disease using high accuracy mass spectrometry. Proteomics Clin Appl 3:1052–1061
Molina L, Salvetat N, Ameur RB, Peres S, Sommerer N, Jarraya F, Ayadi H, Molina F, Granier C (2011) Analysis of the variability of human normal urine by 2D-GE reveals a “public” and a “private” proteome. J Proteomics 75:70–80
Nagaraj N, Mann M (2011) Quantitative analysis of the intra- and inter-individual variability of the normal urinary proteome. J Proteome Res 10:637–645
Nedelkov D (2005) Population proteomics: addressing protein diversity in humans. Expert Rev Proteomics 2:315–324
Nedelkov D, Kiernan UA, Niederkofler EE, Tubbs KA, Nelson RW (2006) Population proteomics: the concept, attributes, and potential for cancer biomarker research. Mol Cell Proteomics (MCP) 5:1811–1818
Rodriguez JC, Diaz M, Gonzalez LO, Sanchez J, Sanchez MT, Merino AM, Vizoso F (2000) Apolipoprotein D expression in benign and malignant prostate tissues. Int J Surg Invest 2:319–326
Sun W, Chen Y, Li F, Zhang L, Yang R, Zhang Z, Zheng D, Gao Y (2009) Dynamic urinary proteomic analysis reveals stable proteins to be potential biomarkers. Proteomics—Clin Appl 3:370–382
Utsunomiya T, Ogawa K, Yoshinaga K, Ohta M, Yamashita K, Mimori K, Inoue H, Ezaki T, Yoshikawa Y, Mori M (2005) Clinicopathologic and prognostic values of apolipoprotein D alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 116:105–109
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Chen, Y. (2015). Variations of Human Urinary Proteome. In: Gao, Y. (eds) Urine Proteomics in Kidney Disease Biomarker Discovery. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 845. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9523-4_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-9523-4_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-017-9522-7
Online ISBN: 978-94-017-9523-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)