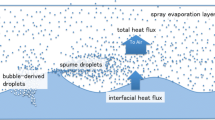
Abstract
Mariners have long been aware of the ability of strong winds at sea to generate large amounts of spray, and its occurrence even forms part of the definition of the Beaufort wind scale. More recently, scientific curiosity about the contribution of sea spray to sea-air fluxes of heat and water vapour has led to significant progress in their quantification. Yet the fact that this is a difficult field and that there remain large gaps in our understanding of it is perhaps best illustrated by the recent, and at times heated, exchanges in the literature (Hasse 1992; Andreas 1994a; Katsaros, De Leeuw 1994; Andreas 1994b; Andreas et al. 1995; Andreas, DeCosmo this volume).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreas, E.L. (1989) Thermal and size evolution of sea spray droplets. CRREL Rep. 89–11, U.S. Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, Hanover, N.H., 37pp.
Andreas E.L. (1990) Time constants for the evolution of sea spray droplets. Tellus, 42B, 481–497.
Andreas E.L. (1992) Sea spray and the turbulent air-sea heat fluxes. J. Geophys. Res., 97, 11429–11441.
Andreas E.L. (1994a) Comments on “On the contribution of spray droplets to evaporation” by L. Hasse, Bound.-Layer Meteorol., 68, 207–214.
Andreas E. L. (1994b) Reply to Katsaros and De Leeuw. J. Geophys. Res., 99, 14345–14350.
Andreas E.L. (1995) The temperature of evaporating sea spray droplets. J. Atmos. Sci., 52, 852–862.
Andreas, E.L., Edson, J.B., Monahan, E.C., Rouault, M.P., Smith, S.D. (1995) The spray contribution to net evaporation from the sea: A review of recent progress. Bound.-Layer Meteorol., 72, 3–52.
Andreas E.L. (1998) A new sea spray generation function for wind speeds up to 32 m/s. J. Phys. Oceanogr., in press.
Bender, M.A., Ginis, I., Kurihara, Y. (1993) Numerical simulations of tropical cyclone-ocean interaction with a high-resolution coupled model. J. Geophy. Res., 98D, 23245–23263.
Bengtsson, L., Botzet, M., Esch, M. (1996) Will greenhouse gas-induced warming over the next 50 years lead to higher frequency and greater intensity of hurricanes? Tellus 48A, 57–73.
Betts, A.K. (1973) Non-precipitating cumulus convection and its parameterisation. Quart.J. Royal Meteor. Soc.. 99, 178–196.
Betts, A.K., Simpson, J. (1987) Thermodynamic budget diagrams for the hurricane subcloud layer. J. Atmos. Sci.. 44. 842–849.
Black, P.G., Holland, G.J., Pudov, V. (1993) Observations of air-sea temperature difference in tropical cyclones as a function fo wind speed. In BMRC Research Report 46: Parameterisation of Physical Processes: Papers presented at the Fifth BMRC Modelling Workshop, Melbourne, Australia. Available from BMRC GPO Box 1289K, Melbourne Victoria 3001, Australia.
Blanc, T.V. (1985) Variation of bulk-derived surface flux, stability, and roughness results due to the use of different transfer coefficient schemes.. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 15, 650–669.
Black, P.G, Holland, G.J. (1995) The boundary layer of tropical cyclone Kerry (1979). Mon. Wea. Rev., 123,
Blumberg, A.F., Mellor, G. L. (1987) A description of a three-dimensional ocean circulation model. Three-Dimensional Coastal Ocean Circulation Models, vol. 4, edited by N.S. Heaps, American Geophysical Union, Washington, D.C., 280 pp.
Cione, JJ., Black, P.G. (1998) Surface thermodynamic observations within the tropical cyclone inner core. Papers presented at the 1998 Annual Meeting of the American Meteorological Society, Hurricane Intensity Symposium. Available online at http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/hrd/tcint98/AMS98_PI_29.pdf
Clarke, R.H., Dyer, A.J., Brook, R.R., Reid, D.G., Troup, A.J. (1971) The Wangara Experiment: Boundary Layer Data. Tech. Paper 19, Div. Meteor. Phys., CSIRO, Australia.
Clayson, C.A., Curry, J.A., Fairall, C.W. (1995) Evaluation of turbulent fluxes at the ocean surface using surface renewal theory. J. Geophys. Res., 101, 28503–28513.
Davidson, K.L., Schutz, L. (1983) Observational results on the influence of surface layer stability and inversion entrainment on surface layer marine aerosol number density. Opt. Eng., 22, 45–49.
Deardorff, J.W. (1976) Usefulness of liquid-water equivalent potential temperature in a shallow-cloud model. J. Appl. Meteor., 15, 98–102.
Deardorff, J.W. (1980) Stratocumulus-capped mixed layers derived from a three-dimensional model. Boundary-Layer Meteor., 18, 495–527.
DeCosmo, J., Katsaros, K.B., Smith, S.D, Anderson, R.J., Oost, W.A., Bumke, K., Chadwick, H. (1996) Airsea exchange of water vapor and sensible heat: The Humidity Exchange over the Sea (HEXOS) results. J. Geophvs. Res., 101, 12001–12016.
De Leeuw, G. (1986a) Vertical profiles of giant particles close above the sea surface. Tellus, 38B, 51–61.
De Leeuw, G. (1986b) Size distributions of giant aerosol particles close above sea level. J. Aerosol Sci., 17, 293–296.
De Leeuw, G. (1987) Near-surface particle size distribution profiles over the North Sea. J. Geophys. Res., 92C, 14631–14635.
De Leeuw, G. (1989) Investigations on turbulent fluctuations of particle concentrations and relative humidity in the marine atmospheric surface layer. J. Geophys. Res., 94C, 3261–3269.
De Leeuw, G. (1990a) Profiling of aerosol concentrations, particle size and relative humidity in the atmospheric surface layer over the North Sea. Tellus., 42B, 342–354.
De Leeuw, G. (1990b) Comment on “Vertical distribution of spray droplets near the sea surface of jet drop ejection and surface tearing”. J. Geophys. Res., 95, 9779–9782.
Earle, M.D. (1979) Practical determinations of design wave conditions, in Ocean Wave Climate, edited by M.D. Earle and A. Malahoff, pp 39–60, Plenum, New York.
Edson, J.B., Fairall, C.W., Larsen, SE., Mestayer, P.G. (1988) A random walk simulation of the turbulent transport of evaporating jet drops in the air-sea simulation tunnel during HEXIST. Proc. 7 th h Conf. On Ocean-Atmosphere Interaction, AMS, Anaheim, CA, 9–13.
Edson, J.B., Fairall, C.W. (1994) Spray droplet modeling. I: Lagrangian model simulation of the turbulent transport of evaporating droplets. J. Geophys. Res., 99, 25229–25311.
Edson, J.B., Anquetin, S., Mestayer, P.G., Sini, J.F. (1996) Spray droplet modelling. 2: An interactive eulerian-lagrangian model of evaporating spray droplets. J. Geophys. Res., 101, 1279–1293.
Emanuel, K.A. (1991) The theory of hurricanes. Ann. Rev. Fluid. Mech., 23, 179–196.
Emanuel, K.A. (1995) Sensitivity of tropical cyclones to surface exchange coefficients and a revised steadystate model incorporating eye dynamics. J. Atmos. Sci., 52, 3969–3976.
Fairall, C.W., Edson, J.B., Miller, M.A. (1990) Heat fluxes, whitecaps, and sea spray. In Surface Waves and Fluxes, Vol. 1, G. L. Geernaert and W.J. Plant (eds.), Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 173–208.
Fairall, C.W., Kepert, J.D., Holland, G.J. (1994) The effect of sea spray on surface energy transports over the ocean. The Global Atmospheric Ocean System, 2, 121–142.
Fairall, C.W., Bradley, E.F., Rogers, D.P., Edson, J.B., Young, G.S. (1996a) Bulk parameterization of air-sea fluxes in TOGA COARE. J. Geophys. Res., 101, 3747–3767.
Galperin, B., Kantha, L.H., Hassid, S., Rosati, A. (1988) A quasi-equilibrium turbulent energy model for geophysical flows. J. Atmos. Sci., 45, 55–62.
Garratt, J.R. (1992) The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 316 pp.
Geernaert, G.L. (1990) Bulk parameterization for wind stress and the heat fluxes. In Surface Waves and Fluxes, Vol. 1, G. L. Geernaert and W. J. Plant (eds.), Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 91–172.
Gerrity, J.P., Black, T.L., Treadon, R.E. (1994) The numerical solution of the Mellor-Yamada level 2.5 turbulent kinetic energy equation in the Eta model. Mon. Wea. Rev., 122, 1640–1646.
Gong, S.L., Barrie, L.A., Blanchet, J.-P. (1997) Modeling sea-salt aerosols in the atmosphere. I. Model development. J. Geophys. Res., 102, 3805–3818.
Girard, C., Delage, Y. (1990) Stable schemes for nonlinear vertical diffusion in atmospheric circulation models. Mon. Wea. Rev., 118, 737–745.
Grell, G.A., Dudhia, J., Stauffer, D. R. (1994) A description of the Fifth-Generation Penn State/NCAR Mesoscale Model (MM5). NCAR/TN-398+IA, National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO, 107 pp.
Gunther, H., Hasselmann, S., Janssen, P.A.E.M. (1992) The WAM Model Cycle 4. DKRZ Technical Report No. 4, Hamburg, October 1992.
Hasse, L. (1992) On the contribution of spray droplets to evaporation. Bound.-Layer Meteorol., 61, 309–313.
Helfand, H.M., LaBraga, J.C. (1988) Design of a nonsingular level 2.5 second order closure model for the prediction of atmospheric turbulence. J. Atmos. Sci., 45, 113–132.
Henderson-Sellers, A., Berz, G, Elsbeny, R., Emanuel, K., Gray, W.M., Landsea, C., Holland, G., Lighthill, J., Shieh, S.-L., Webster, P., Zhang, H. (1997) Tropical cyclones and global climate change: A post-IPCC assessment. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 79, 19–38.
Holland G.J. (1997) The maximum potential intensity of tropical cyclones. J. Atmos. Sci., 54, 2519–2541.
Jassen, P.A.E.M. (1991) The quasi-linear theory of wind wave generation applied to wave forecasting. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 21, 1631–1642.
Kaimal, J.C., Finnigan, J.J. (1994) Atmospheric Boundary Flows, Their Structure and Measurement. Oxford University Press, 289pp.
Katsaros, K.B., de Leeuw, G. (1994) Comment on “Sea spray and the turbulent air-sea heat fluxes” by E.L. Andreas. J. Geophys. Res., 99, 14339–14343.
Kepert, J.D. (1996) Comments on “The temperature of evaporating sea spray droplets”. J. Atmos. Sci., 53, 1634–1645.
Kepert, J.D., Fairall, C.W. (1998) Influence of evaporating sea spray on marine boundary layer fluxes and dynamics. Part I: Structure of a numerical model. J. Geophys. Res., in preparation.
Kinsman, B. (1965) Wind Waves, 676 pp., Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ., 1965.
Komen, G.J., Cavaleri, L., Donelan, M., Hasselmann, K., Hasselmann, S., Jassen, P.A.E.M. (1994) Dynamics and Modeling of Ocean Waves. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 532 pp.
Korolev, V.S., Petrichenko, S.A., Pudov, V.D. (1990) Heat and moisture exchange between the ocean and atmosphere in tropical storms Tess and Skip. Meteorologiya i Gidrologiya, 2, 108–111. (English translation in Soviet Meteorology and Hydrology, 2, 92–94).
Kraus, E.B., Businger, J.A. (1994) Atmosphere-Ocean Interaction. Oxford University Press, New York, 362 PP.
Lighthill, J., Holland, G., Gray, W.M., Landsea, C., Craig, G., Evans, J., Kurihara, Y., Guard, C. (1994) Global climate change and tropical cyclones. Bull. Am. Met. Soc., 75, 2147–2157.
Ling, S.C., Kao, T.W. (1976) Parameterisation of the moisture and heat transfer processes over the ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 11, 324–336.
Liu, Y., Zhang, D.-L., Yau, M.K. (1997) A multiscale numerical study of Hurricane Andrew (1992). Part I: Explicit simulation and verification. Mon. Wea. Rev., 125, 3073–3093.
Makin, V.K. (1998) Air-sea exchange of heat in the presence of wind waves and spray. J. Geophys. Res., 103, 1137–1152.
Mellor, G.L. (1977) The Gaussian cloud model relations. J. Atmos. Sci., 34, 356–358.
Mellor, G.L., Yamada, T. (1982) Developmetn of a turbulence closure model for geophysical fluid problems. Rev. Geophys. And Space Phys., 20, 851–875.
Mestayer, P.G., Van Eijk, A.M.J., De Leeuw, G., Tranchant, B. (1996) Numerical simulation of the dynamics of sea snrav over the waves. J. Geophys. Res., 101, 20771–20797.
Persson, P.O.G., Hare, J., Fairall, C.W., Ataturk, S., Katsaros, K. (1997) Air-sea interaction measurements during the Fronts and Atlantic Storms Tracks Experiment (FASTEX). Proc. 1e Symposium on Boundary Layers and Turbulence, AMS, Vancouver, BC, 28 July-1 August.
Pruppacher, H.R., Klett, J.D. (1978) Microphysics of Clouds and Precipitation. D. Reidel Publishing Company, 714 pp.
Rouault, M.P., Mestayer, P.G., Schiestel, R. (1991) A model of evaporating spray droplet dispersion. J. Geonhvs. Res., 96, 7181–7200.
Slinn, S.A., Slinn, W.G.N. (1980) Predictions for particle deposition in natural waters. Atmospheric Environment, 14, 1013–1016.
Smith, S.D., Katsaros, K.B., Oost, W.A., Mestayer, P.G. (1989) Two major experiments in the humidity exchange over sea (HEXOS) program. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 71, 161–172.
Smith, S.D.(1990) Influence of droplet evaporation on HEXOS humidity and temperature profiles. In Modelling the Fate and Influence of marine Spray (Eds. P. Mestayer, E. C. Monahan, and P. A. Beetham). Whitecap Ret. 7. University of Connecticut, marine Sciences Institute, Groton, pp 171–174.
Smith, S.D., Fairall, C.W., Geernaert, G.L., Hasse, L. (1996) Air-sea fluxes: 25 years of progress. Bound.Layer Meteorol., 78, 247–290.
Smolarkiewicz, P.K. (1983) A simple positive definite advection scheme with small implicit diffusion. Mon. Wea. Rev., 111, 479–486.
Sommeria, G., Deardorff, J.W. (1977) Subgrid-scale condensation in models of non-precipitating clouds. J. Atmos. Sci., 34, 344–355.
Toba, Y. (1965) On the giant sea-salt particles in the atmosphere. II — Theory of the vertical distribution in the 10-m layer over the ocean. Tellus, 17, 365–382. WAMDI (1988) The WAM Model — a third generation ocean wave prediction model. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 18, 1775–1810.
Wilson, B.W. (1965) Numerical prediciton of ocean waves in the North Atlantic for December, 1959. Dtsch. Hydrogr. Z., 18, 114–130.
Wu, J. (1990) Vertical distribution of spray droplets near the sea surface: Influence of jet drop ejection and surface tearing. J. Geophys. Res., 95, 9775–9778.
Yelland, M., Taylor, P.K. (1996) Wind stress measurements from the open ocean. J. Phys. Oceanogr., 26, 541–558.
Zhuang, Y., Lozowski, E.P., Wilson, J.D., Bird, G. (1993) Sea spray dispersion over the ocean surface: a numerical simulation. J. Geophys. Res., 98C, 16547–16553.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1999 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Kepert, J., Fairall, C., Bao, JW. (1999). Modelling the Interaction Between the Atmospheric Boundary Layer and Evaporating Sea Spray Droplets. In: Geernaert, G.L. (eds) Air-Sea Exchange: Physics, Chemistry and Dynamics. Atmospheric and Oceanographic Sciences Library, vol 20. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-9291-8_14
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-015-9291-8_14
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-90-481-5308-4
Online ISBN: 978-94-015-9291-8
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive