Abstract
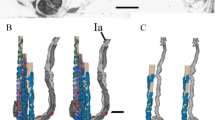
The experiments described below were carried out on muscle spindles isolated from the tenuissimus muscle of the cat hind leg and illustrate the physiological behaviour of three types of intrafusal muscle fibre called the ‘dynamic bag1 fibre’ (Db1) the ‘static bag2 fibre’ (Sb2) and the ‘nuclear chain fibres’ (Ch).The same three types of intrafusal fibre are found in primate spindles, including those in man, which differ only in minor respects from those in the cat. Details of spindle morphology in rat, cat, baboon and man are available elsewhere (Barker 1974; Boyd & Smith, 1984; Boyd & Gladden, 1985).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbuthnott, E.R., Ballard, K.J., Boyd, I.A., Gladden, M.H. & Sutherland, F. (1982). The ultrastructure of cat fusimotor endings and their relationship to foci of sarcomere convergence in intrafusal fibres. J. physiol., 331, 285–309.
Banks, R.W., Barker, D., Bessou, P., Pagès, B. & Stacey, M.J. (1978). Histological analysis of cat muscle spindles following direct observation of the effects of stimulating dynamic and static motor axons. J. Physiol., 283, 605–619.
Banks, R.W., Barker, D. & Stacey, M.J. (1982). Form and distribution of sensory terminals in cat hindlimb muscle spindles. Phil. Trans. R. Soc B, 99, 329–364.
Barker, D. (1974). The morphology of muscle receptors. In Handbook of Sensory Physiology, Vol. 3, Pt.2, Muscle Receptors. Ed. Hunt, C.C.. Springer. Verlag, New York, pp. 1–190.
Barker, D., Emonet. Dénand, F., Laporte, Y., Proske, U. & Stacey, M.J. (1973). Morphological identification and intrafusal distribution of the endings of static fusimotor axons in the cat. J. Physiol., 230, 405–427.
Boyd, I.A. (1971). Specific fusimotor control of nuclear bag and nuclear chain fibres in cat muscle spindles. J. Physiol., 214, 30–31 P.
Boyd, I.A. (1976a). The response of fast and slow nuclear bag fibres in isolated cat muscle spindles to fusimotor stimulation, and the effect of intrafusal contraction on the sensory endings. Q Jl exp Physiol., 61, 203–254.
Boyd, I.A. (1976b). The mechanical properties of dynamic nuclear bag fibres, static nuclear bag fibres and nuclear chain fibres in isolated cat muscle spindles. Prog. Brain Res., 44, 33–50.
Boyd, I.A. (1981). The action of the three types of intrafusal fibre in isolated cat muscle spindles on the dynamic and length sensitivities of primary and secondary sensory endings. In Muscle Receptors and Movement Eds. Taylor, A. & Prochazka, A. Macmillan, London, pp. 17–32.
Boyd, I.A. (1985a). Muscle spindles and stretch reflexes. In Scientific Basis of Clinical Neurology. Eds. Swash, M. & Kennard, C. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp. 74–97.
Boyd, I.A. (1985b). Static intrafusal systems in cat muscle spindles. Q.Jl exp. Physiol. (In press).
Boyd, I.A. & Gladden, M.H. (1965). The Muscle Spindle. Macmillan, London.
Boyd, I.A., Gladden, M.H., McWilliam, P.N. & Ward, J. (1977). Control of dynamic and static nuclear bag fibres and nuclear chain fibres by gamma and beta axons in isolated cat muscle spindles. J. Physiol., 265, 133–162.
Boyd, I.A., Gladden, M.H. & Ward, J. (1981). The contribution of mechanical events in the dynamic bag intrafusal fibre in isolated cat muscle spindles to the form of the la afferent axon discharge. J. Physiol., 317, 80–81P.
Boyd, I.A., Murphy, P.R. & Mann, C. (1985). The effect of chain fibre ‘driving’ on the length sensitiviby of primary sensory endings in the tenuissimus, peroneus tertius and soleus muscles. In The Muscle Spindle. Eds. Boyd, I.A. & Gladden, M.H. Macmillan, London. (In press).
Boyd, I.A., Murphy, P.R. & Moss, V.A. (1985). Analysis of primary and secondary afferent responses to stretch during activation of the dynamic bag. fibre or the static bag2 fibre separately in cat muscle spindles. In The Muscle Spindle. Eds. Boyd, I.A. & Gladden, M.H.. Macmillan, London. (In press).
Boyd, I.A. & Smith, R.S. (1984). The muscle spindle. In Peripheral Neuropathy. Eds. Dyck, P.J., Thomas, P.K., Lambert. E.H. & Bunge, R., Dyck, P.J., Thomas, P.K., Lambert. E.H. & Bunge, R.. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp. 171–202.
Boyd, I.A., Sutherland, F. & Ward, J. (1985). The origin of the increase in the length sensitiviby of secondary sensory endings produced by some fusimotor axons. In The Muscle Spindle. Eds. Boyd, I.A. & Gladden, M.H.. Macmillan, London, (In press).
Boyd, I.A. & Ward, J. (1975). Motor control of nuclear bag and nuclear chain intrafusal fibres in isolated living muscle spindles from the cat. J. Physiol., 244, 85–112.
Crowe, A. & Matthews, P.B.C. (1964). Further studies of static and dynamic fusimotor fibres. J. Physiol., 174, 152–151.
Dutia, M.B. (1980). Activation of cat muscle spindle primary, secondary and intermediate sensory endings by suxamethonium. J. Physiol., 304, 315–330.
Fukami, Y. (1985). Active force and sensory response of single isolated cat muscle spindles in vitro. In The Muscle Spindle. Eds. Boyd, I.A. & Gladden. M.H. Macmillan, London. (In press).
Gladden, M.H. (1976). Structural features relative to the function of intrafusal muscle fibres in the cat. Prog. Brain Res., 44, 51–59.
Jami, L., Lan Couton, D. & Petit, J. (1980). A study with the glycogen-depletion method of intrafusal distribution of axons that increase sensitiviby of spindle secondary endings. J. Neurophysiol., 45, 16–26.
Jami, L., Petit, J. & Scott, J.J.A. (1985). “Driving” of spindle primary endings by static ß axons. In The Muscle Spindle. Eds. Boyd, I.A. & Gladden, M.H.. Macmillan, London, (In press).
Kucera, J. (1964). Nonselective motor innervation of nuclear bag1 intrafusal muscle fibers in the cat. Cell Tissue Res., 256, 385–391.
Kucera, J. (1985). Selective and non. selective motor innervation of intrafusal muscle fibers in the cat. In The Muscle Spindle, Eds. Boyd, I.A. & Gladden, M.H. Macmillan, London. (In press).
Laporte, Y., Emonet-Denand, F. & Hunt, C.C (1965). Does stretch excite the bag1 fibre? In The Muscle Spindle. Eds. Boyd, I.A. Gladden, M.H. Macmillan, London. (In press).
Rack, P.M.H. & Westbury, D.R. (1966). The effects of suxamethonium and acetylcholine on the behaviour of cat muscle spindles during dynamic stretching, and during fusimotor stimulation. J. Physiol., 186, 696–713.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1985 W.J.P. Barnes and M.H. Gladden
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Boyd, I.A. (1985). Intrafusal Muscle Fibres in the Cat and their Motor Control. In: Barnes, W.J.P., Gladden, M.H. (eds) Feedback and Motor Control in Invertebrates and Vertebrates. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-7084-0_8
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-7084-0_8
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-011-7086-4
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-7084-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive