Summary
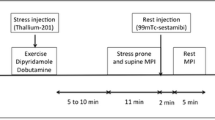
The development of technetium-99m (Tc-99m) labeled agents is a significant advance in myocardial perfusion imaging. Worldwide, thousands of patients have been studied with Tc-99m SestaMIBI. There is a general consensus that as far as detection of coronary artery disease is concerned, this new perfusion imaging agent compares well with Tl-201 (better than 80 % agreement), employing either physical exercise or pharmacological vasodilatation. There is some concern about the lower extraction fraction of Tc-99m SestaMIBI (60 %) compared to that of TI-201 (80 %). However at the present time it is unclear whether this difference is of clinical relevance. Because of the relatively high dose that can be administered, left ventricular function can be evaluated simultaneously by either first pass ejection fraction or ECG-gated regional wall motions studies. A unique application of Tc-99m SestaMIBI imaging is in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Because of the lack of significant redistribution, this imaging agent can be employed to assess the area at risk prior to initiation of thrombolytic therapy and later to assess the size of infarction as well as the extent of myocardial salvage. Myocardial imaging in this setting has been useful to predict patency of the infarct related artery. Recent experimental data indicate that Tc-99m SestaMIBI may not only be an indicator of myocardial blood flow, but also an indicator of myocardial viability. In conclusion, Tc-99m SestaMIBI provides: 1) better quality images; 2) is better suited for SPECT imaging; 3) allows first-pass assessment left ventricular ejection fraction, and 4) assessment of regional wall motion by ECG-gated images. Clinical applications include; detection of 5) coronary artery disease and 6) myocardial ischemia by either physical exercise or pharmacological vasodilatation. Furthermore, 7) assessment of risk area of coronary occlusion and 8) assessment of ultimate size of infarction are both possible.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wackers F. J., Berman D. S., Maddahi J., et al. Technetium-99m hexakis 2-methoxyisobutyl isonitrile: human biodistribution, dosimetry, safety, and preliminary comparison to thallium-201 for myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Med 1989;30:301–11.
Kiat H., Maddahi J., Roy L. T., et al. Comparison of technetium99m methoxy isobutyl isonitrile with thallium 201 for evaluation of coronary artery disease by planar and tomographic methods. Am Heart J 1989;117:1–11.
Kahn J. K., Henderson E. B., Akers A. S., et al. Prediction of reversibility of perfusion defects with a single post-exercise technetium-99m RP-30A gated tomographic image: the role of residual thickening. J Am Coll Cardiol 1988 (abstract);11 Suppl A:31A.
Iskandrian A. S., Heo J., Kong B., Lyons E., Marsch S., Use of technetium-99m isonitrile (RP-30A) in assessing left ventricular perfusion and function at rest and during exercise in coronary artery disease, and comparison with coronary arteriography and exercise thallium-201 SPECT imaging. Am J Cardiol 1989;64:270–5.
Maddahi J., Kiat H., Van Train K., et al. Myocardial perfusion imaging with technetium-99m sestamibi SPECT in the evaluation of cononary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 1990;66:SSE–62E.
Borges-Neto S., Coleman R. E., Jones R. H., Perfusion and function at rest and treadmill exercise using technetium-99m-SestaMIBI: comparison of one-and two-day protocols in normal volunteers. J Nucl Med 1990;131:1128–31.
Maniawski P. J., Allam A. H., Wackers F. J., Zaret B. L., A new non-geometric technique for simultaneous evaluation of regional function and myocardial perfusion from gated planar isonitrile images. Circulation 1989 (abstract);80(Suppl 2):IIS44.
Lee K. L., Pryor D. B., Pieper K. S., et al. Prognostic value of radionuclide angiography in medically treated patients with coronary artery disease. A comparison with clinical and catheterization variables. Circulation 1990;82: 1705–17.
Wackers F. J., Gibbons R. J., Verani M. S., et al. Serial quantitative planar technetium-99misonitrile imaging in acute myocardial infarction: efficacy for noninvasive assessment of thrombolytic therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol 1989;14:861–73.
Gibbons R. J., Verani M. S., Behrenbeck T., et al. Feasibility of tomographic 99mTc-hexakis-2-methoxy-2-methylpropyl-isonitrile imaging for the assessment of myocardial area at risk and the effect of treatment in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 1989;80:1277–86.
Allam A. H., Maniawski P. J., Verani M. S., Gibbons R. J., Zaret B. L., Wackers F. J., Simultaneous assessment of recovery of regional ventricular funtion and perfusion after thrombolysis using serial gated Tc-99m-isontrile imaging. Circulation 1989 (abstract);80 (4 SuppI2):II620.
Gregoire J., Theroux P., Detection and assessment of unstable angina using myocardial perfusion imaging: comparison between technetium-99m SestaMIBI SPECT and 12-lead electrocardiogram. Am J Cardiol 1990;66:42E–7E.
Kiat H., Berman D. S., Maddahi J., et al. Late reversibility of tomographic myocardial thallium-201 defects: an accurate marker of myocardial viability. J Am Coli Cardiol 1988;12:1456–63.
Bonow R. O., Dilsizian V., Cuocolo A., Bacharach S. L., Identification of viable myocardium in patients with chronic coronary artery disease and left ventricular dysfunction. Comparison of thallium scintigraphy with reinjection and PET imaging with 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose. Circulation 1991;83:26–37.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1992 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Wackers, F.J.T. (1992). Tc-99m SestaMIBI: Will it replace Tl-201 in clinical cardiology?. In: Reiber, J.H.C., Van Der Wall, E.E. (eds) Cardiovascular Nuclear Medicine and MRI. Developments in Cardiovascular Medicine, vol 128. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-2666-3_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-2666-3_16
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-5179-8
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-2666-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive