Summary
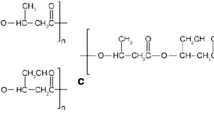
Aliphatic polyesters presently constitute the most attractive class of artificial polymers which can degrade in contact with living tissues or under outdoor conditions. Work has been in progress for the last two decades which has led to their applications in surgery and in pharmacology. Basically, these compounds are also of interest for outdoor applications such as packagings or mulch films and in plant therapy by controlled delivery of pesticides or insecticides in agriculture, although they are still too expensive. Factors which can affect their biodegradation have been investigated world-wide. However, the literature contains confusing statements and controversial data. This chapter is aimed at clarifying the state-of-the-art. After general considerations, including comments on terminology and on enzymatic, hydrolytic degradation mechanisms, discussion is focused on the effects of influencing factors, namely, main structural parameters, the presence of chemically active additives, and the composition of degradation media. Although poly(α-hydroxyacids) derived from lactic and glycolic acids are, by far, the most important members of the aliphatic polyester family, the poly(β-hydroxyacids) and other aliphatic polyesters such as poly(ε-caprolactone), polydioxanones, etc. are also considered.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hassig, A. and Stampfli, K. (1969) Plasma substitutes: past and present. Bibliotheca. Haemat., 33, 1–8.
Rosato, D. V. (1983) Polymers, processes and properties of medical plastics including markets and applications, in Biocompatible Polymers, Metals and Composites, (ed. M. Szycher), Technomic. Publ. Co. Inc., Lancaster, Chapter 45, pp. 1019–67.
Charles, E. L. and Buffalo, N. Y. (1954) Preparation of high molecular weight polyhydroxyacetic ester, US Patent 2,668162.
Schmitt E. E. and Polistina, R. A. (1967) Surgical sutures, US Patent 3,297,033.
Frazza, E. J. and Schmitt, E. E. (1971) A new absorbable suture, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Symposium, 1, 43–58.
Vert, M. (1992) Introductory remarks, in Biodegradable Polymers and Plastics, (eds M. Vert et al.), Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp. 1–3.
Heller, J. (1983) Use of polymers in controlled drug release, in Biocompatible Polymers, Metals and Composites, (ed. M. Szycher), Technomic Publ. Co. Inc., Lancaster, Chapter 24, pp. 551–84.
Langer, R. S. and Peppas, N. A. (1981) Present and future applications of biomaterials in controlled drug delivery systems, Biomaterials, 2, 201–14.
Langer, R. S. and Peppas, N. A. (1983) Chemical and physical structure of polymers as carriers for controlled release of bioactive agents: a review, J. Macromol Sci., REC. Macromol. Chem Phys., C23, 61–126.
Gilding, D. K. (1981) Biodegradable polymers, Biocompat. Clin. Implant. Mater., 2, 209–32.
Williams, D. F. (1982) Biodegradation of surgical polymers, J. Mater. Sci., 17, 1233–46.
Pitt, C. G., Marks, T. A. and Schindler, A. (1981) Biodegradable drug delivery systems based on aliphatic polyesters: application to contraceptives and narcotic antagonists, in National Institute on Drug Abuse Research Monograph, (eds R. E. Willette and G. Barnett), Naltrexone, Volume 28, pp. 232–53.
Gilbert, R. D., Stannett, V., Pitt, C.G. and Schindler, A. (1982) The design of biodegradable polymers: two approachs, in Development in Polymer Degradation (ed. N. Grassie), Volume 4, Applied Science Publishers, London, pp. 259–93.
Graham, N. B. and Wood, D. A. (1982) Hydrogels and biodegradable polymers for the controlled delivery of drugs, Polym. News, 8, 230–6.
Griffin, G. J. L. (1980) Synthetic polymers and the living environment, Pure Appl. Chem., 52, 399–407.
Holland, S. J., Tighe, B. J. and Gould, P. L. (1986) Polymers for biodegradable medical devices. 1. The potential of polyesters as controlled macromolecular release systems, J. Control. Rel., 4, 155–80.
Guillet, J. E., Huber, H. X. and Scott, J. (1992) Studies of the biodegradation of synthetic plastics, in Biodegradable Polymers and Plastics (eds M. Vert et al.), Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp. 73–92.
Albertsson, A. C. and Karlsson, S. (1990) Biodegradation and test methods for environmental and biomedical applications of polymers, in Degradable Materials: Perspectives, Issues and Opportunities (eds. S. A. Barenberg, J. L. Brash, R. Narayan and A. E. Redpath), CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 263–86.
Ottenbrite, R. M., Albertsson, A. C. and Scott, G. (1992) Discussion on degradation terminology, in Biodegradable Polymers and Plastics (eds M. Vert et al.), Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge 73–92.
Vert, M. (1981) Bioresorbable polyesters for bone surgery, Makromol. Chem., Suppl., 5, 30–41.
Huang, S. J., Bitritto, M. and Leong, K. W. et al. (1978) The effects of some structural variations on the biodegradability of step-growth polymers, Stabilization and Degradation of Polymers (Am. Chem. Soc.), 17, 209–214.
Vert, M., Li, S. M., Spenlehauer, G. and Guerin, P., (1992) Bioresorbability and biocompatibility of aliphatic polyesters, J. Mater Sci., Materials in Medicine, 3, 432–46.
Leray, J., Vert, M. and Blanquaert, D. (1976) Nouveau matériau de prothése osseuse et son application, French Patent Appl. 76,281,63.
Vert, M., Christel, P., Chabot, F. and Leray, J. (1984) Bioresorbable plastic materials for bone surgery, in Macromolecular Biomaterials, (eds G. W. Hastings and P. Ducheyne), CRC Press, Boca Raton, Chapter 6, pp. 119–42.
Chabot F., Vert, M., Chapelle, S. and Granger, P. (1983) Configurational structures of lactic acid stereocopolymers as determined by 13C—1H n.m.r., Polymer, 24, 53–60.
Williams, D. F. (1977) Enzyme-polymer interactions, J. Bioeng., 1, 279–94.
Baba, H., Tanahashi, N., Kumagai, Y. and Doi, Y. (1992) Effects of molecular structure on enzymatic degradation of polyesters, Nippon Kagaku Kaishi, 5, 527–33.
Ray, J. A., Doddi, N. and Regula, D. et al. (1981) Polydioxanone (PDS), a novel monofilament synthetic absorbable suture, Surg. Gynecol. Obstet., 153, 497–507.
Beck L. R. and Tice, T. R. (1983) Poly(lactic acid) and poly(lactic acid-co-glycolic acid) contraceptive delivery systems, in Advances in Human Fertility and Reproductive Endocrinology: Vol. 2, Long Acting Steroid Contraception, Raven Press, New York, pp. 175–199.
Williams, D. F. and Mort, E. (1977) Enzyme accelerated hydrolysis of poly(glycolic acid), J. Bioeng., 1, 231–38.
Reed, A. M. (1978) In vitro and in vivo studies of biodegradable polymers for use in medicine and surgery, PhD thesis, University of Liverpool, UK.
Salthouse, T. N. and Matlaga, B. F. (1975) Approach to the numerical quantitation of acute tissue response to biomaterials, Biomater. Med. Devices Artif. Organs, 3, 47–56.
Herrmann, J. B., Kelly, R. J. and Higgins, G. A. (1970) Polyglycolic acid sutures, laboratory and clinical evaluation of a new absorbable suture material, Arch. Surg., 100, 486–90.
Williams, D. F. (1981) Enzyme hydrolysis of polylactic acid, Eng. Med., 10, 5–7.
Ashley, S. L. and McGinity, J. W. (1989) Enzyme-mediated drug release from poly(DL-lactide) matrices, Congr. Int. Technol. Pharm., 5, 195–204.
Salthouse, T. N. and Matlaga, B. F. (1975) Polyglactin 910 suture absorption and the role of cellular enzymes, Surg. Gynecol. Obstet., 142, 544–50.
Schakenraad, J. M., Hardonk, M. J., Feijen, J., et al. (1990) Enzymatic activity toward poly(L-lactic acid) implants, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 24, 529–45.
Younes, H., Nataf, P. R., Cohn, D. et al. (1988) Biodegradable PELA block copolymers: in vitro degradation and tissue reaction, Biomat., Art. Cells, Art. Org., 16, 705–19.
Tsakala, T. M. (1987) Formulations à libération progressive à base de polymères biodégradables, application à la chimiothérapie expérimentale à la malaria, PhD thesis, Université Catholique de Louvain La Neuve, Belgium.
Zaikov, G. E. (1985) Quantitative aspects of polymer degradation in the living body, JMS-Rev. Macromol Chem. Phys., C25, 551–97.
Tabata, Y. and Ikada, Y. (1988) Macrophage phagocytosis of biodegradable microspheres composed of L-lactic acid/glycolic acid homo- and copolymers, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 22, 837–58.
Woodward, S. C., Brewer, P. S. and Moatmed, F. et al. (1985) The intracellular degradation of poly(ε-caprolactone), J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 19, 437–44.
Schindler, A. and Pitt, C. G. (1982) Biodegradable lastomeric polyesters, Polym. Prepr., Amer. Chem. Soc., Div. Polym. Chem., 23, 111–12.
Pitt, C. G. and Schindler, A. (1983) Biodegradable polymers of lactones, US Patent 4, 379, 138.
Pitt, C. G., Hendren, R. W., Schindler, A. and Woodward, S. C. (1984) The enzymatic surface erosion of aliphatic polyesters, J. Control. Rel., 1, 3–14.
Cox, M. K. (1992) The effect of material parameters on the properties and biodégradation of ‘BIOPOL’, in Biodegradable Polymers and Plastics, (eds M. Vert et al.), Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge pp. 95–100.
Doi, Y., Kumagai, Y., Tanahashi, N. and Mukai, K. (1992) Structural effects on biodegradation of microbial and synthetic poly(hydroxyalkanoates), in Biodegradable Polymers and Plastics (eds M. Vert et al.), Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp. 139–48.
Doi, Y., Kanesawa, Y., Kunioka, M. and Saito, T. (1990) Biodegradation of microbial copolyesters: poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxyvalerate), Macromolecules, 23, 26–31.
Kanesawa, Y. and Doi, Y. (1990) Hydrolytic degradation of microbial poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) fibres, Makromol. Chem., Rapid Commun., 11, 679–82.
Kumagai, Y. and Doi, Y. (1992) Enzymatic degradation of binary blends of microbial poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) with enzymatically active polymers, Polym. Degr. Stabl., 37, 253–6.
Gilmore, D. F., Lotti, N. and Lenz, R. W. et al (1992) Biodegradability of blends of poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) with ester-substituted celluloses, in Biodegradable Polymers and Plastics (eds M. Vert et al.), Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp. 251–4.
Pitt, C. G. (1992) Non-microbial degradation of polyesters: mechanisms and modifications, in Biodegradable Polymers and Plastics, (eds M. Vert et al.), Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp. 7–19.
Ginde, R. M. and Gupta, R. K. (1987) In vitro chemical degradation of poly(glycolic acid) pellets and fibres, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 33, 2411–29.
Singh, M., Singh, A. and Talwar, G. P. (1991) Controlled delivery of diphtheria toxoid using biodegradable poly(D,L-lactide) microcapsules, Pharm. Res., 8, 958–61.
Kimura, Y., Matsuzaki, Y., Yamane, H. and Kitao, T. (1989) Preparation of block copoly(ester-ether) comprising poly(lactide) and poly(oxypropylene) and degradation of its fibre in vitro and in vivo, Polymer, 30, 1342–9.
Casey, D. J. and Epstein, M. (1977) Normally solid, bioabsorbable hydrolyzable, polymeric reaction product, US Patent 4, 048. 25.
Pitt, C. G., Gratzel, M. M., Kimmel, G. L. et al. (1981) Aliphatic polyesters. 2. The degradation of poly(DL-lactide), poly(ε-caprolactone) and their copolymers in vivo, Biomaterials, 2, 215–20.
Hutchinson, F. G. (1982) Continuous release pharmaceutical compositions, E. U. Patent 0,058,481.
Hutchinson, F. G. and Furr, B. J. A. (1985) Biodegradable polymers for the sustained release of polypeptides, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 13, 520–3.
Sanders, L. M., McRae, G. I., Vitale, K. M. and Kell, B. A. (1985) Controlled delivery of an LHRH analogue from biodegradable injectable microspheres, J. Control. Rel., 2, 187–95.
St Pierre, T. and Chiellini, E. (1987) Biodegradability of synthetic polymers for medical and pharmaceutical applications: Part 2-Backbone hydrolysis, J. Bioact. Comp. Polym., 2, 4–30.
Lewis, D. H. (1990) Controlled release of bioactive agents from lactide/glycolide polymers, Drug Pharm. Sci., 45 (Biodegrad. Polym. Drug Delivery Syst.), 1–41.
Kenley, R. A., Lee, M. O., Mahoney, II, T. R. and Sanders, L. M. (1987) Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) decomposition kinetics in vivo and in vitro, Macromolecules, 20, 2398–403.
Schakenraad, J. M., Neuwenhuis, P., Molenaar, I. et al. (1989) In vivo and in vitro degradation of glycine/DL-lactic acid copolymers, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 23, 1271–88.
Helder, J., Dijkstra, P. J. and Feijen, J. (1990) In vitro degradation of glycine/dl-lactic acid copolymers, J. Biomed. Mater Res., 24, 1005–20.
Cohen, S., Yoshioka, T., Lucarelli, M. et al. (1991) Controlled delivery systems for proteins based on poly(lactic/glycolic acid) microspheres, Pharm. Res., 8, 713–20.
Holland, S. J., Jolly, A. M., Yasin, M. and Tighe, B. J. (1987) Polymers for biodegradable medical devices. II. Hydroxybutyrate-hydroxyvalerate copolymers: hydrolytic degradation studies, Biomaterials, 8, 289–95.
Knowles, J. C. and Hastings, G. W. (1991) In vitro degradation of a PHB/PHV copolymer and a new technique for monitoring early surface changes, Biomaterials, 12, 210–4.
Li, S. M., Garreau, H. and Vert M. (1988) Bioresorbable polyesters of the glycolic/lactic type: in vitro investigations of the mechanism of degradation, in Preprints of Kunming International Symposium on Polymeric Biomaterials, Kunming, China, 3–7 May.
Li, S. M. (1989) Etude de la dégradation des poly(α-hydroxy acides) aliphatiques dérivés des acides lactique et glycolique en milieux aqueux modèles, PhD thesis. University of Rouen, France.
Li, S. M., Garreau, H. and Vert, M. (1990) Structure-property relationships in the case of the degradation of massive aliphatic poly(α-hydroxy acids) in aqueous media. Part 1: Poly(DL-lactic acid), J. Mater. Sci.: Materials in Medicine, 1, 123–30.
Li, S. M., Garreau, H. and Vert, M. (1990) Structure-property relationships in the case of the degradation of massive poly(α-hydroxy acids) in aqueous media. Part 2: Degradation of lactide/glycolide copolymers: PLA37 5GA25 and PLA75GA25, J. Mater. Sci.: Materials in Medicine, 1, 131–9, 1990.
Li, S. M., Garreau, H. and Vert, M. (1990) Structure-property relationships in the case of the degradation of massive poly(α-hydroxy acids) in aqueous media. Part 3: Influence of the morphology of poly(L-lactic acid), J. Mater. Sci.: Materials in Medicine, 1, 198–206.
Vert, M., Li, S. M. and Garreau, H. (1991) More about the degradation of LA/GA-derived matrices in aqueous media, J. Control. Rel., 16, 15–26.
Therin, M., Christel, P. Li, S. M. et al. (1992) In vivo degradation of massive poly (α-hydroxy acids): validation of in vitro findings, Biomaterials, 13, 594–600.
Vert, M., Li, S. M. and Garreau, H. (1992) New insights on the degradation of bioresorbable polymeric devices based on lactic and glycolic acids, Clinical Materials, 10, 3–8.
Benicewicz, B. C., Shalaby, S. W., Clemow, A. J. T. and Oser, Z. (1990) In vitro and in vivo degradation of poly(L-lactide) braided multifilament yarns, ACS Symp. Ser., 433 (Agric. Synth. Polym.; Biodegrad. Util.), 161–6.
Huffman, K. R. and Casey, D. J. (1985) Effects of carboxylic end groups on hydrolysis of polyglycolic acid, J. Polym. Sci.: Polym. Chem. Ed., 23, 1939–54.
Makino, K., Arakawa, M. and Kondo, T. (1985) Preparation and in vitro degradation properties of polylactide microcapsules, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 33, 1195–201.
Shih, C., Higuchi, T. and Himmelstein, K. J. (1984) Drug delivery from catalysed erodible polymeric matrices of poly(ortho-esters), Biomaterials, 5, 237–40.
Thombre, A. G. and Himmelstein, K. J. (1985) A simultaneous transport-reaction model for controlled drug delivery from catalysed bioerodible polymer matrices, AiChE J., 31, 759–66.
Nguyen, T. H., Himmelstein, K. J. and Higuchi, T. (1986) Erosion of poly(ortho-ester) matrices in buffered aqueous solutions, J. Control. Rel., 4, 9–16.
Nguyen, T. H., Higuchi, T. and Himmelstein, K. J. (1987) Erosion characteristics of catalyzed poly(ortho-ester) matrices, J. Control. Rel., 5, 1–12.
Visscher, G. E., Robison, R. L. and Maulding, H. V. et al. (1985) Biodegradation and tissue reaction to 50:50 poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microcapsules, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 19, 349–65.
Visscher, G. E., Robison, R. L. and Maulding, H. V. et al. (1986) Note: Biodegradation of and tissue reaction to poly(DL-lactide) microcapsules, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 20, 667–76.
Reed, A. M. and Gilding, D. K. (1979) Biodegradable polymers for use in surgery — poly(glycolic)/poly(lactic acid) homo- and copolymers. l, Polymer, 20, 1459–64.
Fukuzaki, H., Yoshida, M., Asano, M. and Kumakura, M. (1989) Synthesis of copoly(DL-lactic acid) with relatively low molecular weight and in vitro degradation, Eur. Polym. J., 25, 1019–26.
Vert, M. (1992) Poly(α-hydroxy acids) derived from lactic and glycolic acids, characteristics and degradation in aqueous media, in Fourth World Biomaterials Congress, Berlin, Germany, 24–28, April.
Mauduit, J. (1991) Nouveaux systèmes antibiotiques à libération controlée à base de gentamycine et de polymères biorésorbables, PhD thesis, University of Rouen, France.
Grizzi, I., Garreau, H., Li, S. M. and Vert, M. (1995) Hydrolytic degradation of devices based on poly(DL-lactic acid); size dependence, Biomaterials, 16, 305–311.
Mauduit, J., Bukh, N. and Vert, M. (1993) Gentamycin/poly(lactic acid) blends aimed at sustained release local antibiotic therapy administered per-operatively: I. The case of gentamycin base and gentamycin sulfate in poly (DL-lactic acid) oligomers, J Control. Rel., 23, 209–20.
Mauduit, J., Bukh, N. and Vert, M. (1993) Gentamycin/poly(lactic acid)blends aimed at sustained release local antibiotic therapy administered per-operatively: II. The case of gentamycin sulfate in high molecular weight poly(DL-lactic acid) and poly(L-lactic acid), J. Control. Rel., 23, 221–30.
Mauduit, J., Bukh, N. and Vert, M. (1993) Gentamycin/poly(lactic acid) blends aimed at sustained release local antibiotic therapy administered per-operatively: III. The case of gentamycin sulfate in films of high and low molecular weight poly(DL-lactic acid), J. Control. Rel., 25, 43–49.
Li, S. M. and Vert, M. In vitro degradation of coral/PLA50 bioresorbable material, to be published.
Vert, M. (1986) Biomedical polymers from chiral lactides and functional lactone — properties and applications, Macromol. Chem., Macromol. Symp., 6, 109–22.
Fischer, E. W., Sterzel, H. J. and Wegner, G. (1973) Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical reactions, Kolloid-Z. u. Z. Polymere, 251, 980–90.
Carter, B. K. and Wilkes, G. L. (1984) Some morphological investigations on an absorbable copolyester biomaterial based on glycolic and lactic acid, in Polymers as Biomaterials, (eds S. W. Shalaby, A. S. Hoffman, B. D. Ratner and T. A. Horbett), Plenum Press, New York, pp. 67–92.
Fredericks, R. J., Melveger, A. J. and Dolegiewtz, L. J. (1984) Morphological and structural changes in a copolymer of glycolide and lactide occurring as a result of hydrolysis, J. Polym. Sci.: Polym. Phys. Ed., 22, 57–66.
Leeslag, J. W., Pennings, A. J. and Bos, R. R. M. et al. (1987) Bioresorbable materials of poly(L-lactide). VII. In vivo and in vitro degradation, Biomaterials, 8, 311–4.
Chu, C. C. (1981) Hydrolytic degradation of poly(glycolic acid): tensile strength and crystallinity study, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 26, 1727–34.
Chu, C. C. and Campbell, N. D. (1982) Scanning electron microscopic study of the hydrolytic degradation of poly (glycolic acid) suture, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 16, 417–30.
Browning, A. and Chu, C. C. (1986) The effect of annealing treatments on the tensile properties and hydrolytic degradative properties of poly(glycolic acid) sutures, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 20, 613–32.
Browning, A. and Chu, C. C. (1985) The effect of annealing treatments on the mechanical and degradative properties of poly(glycolic acid) sutures, in Proc. ACS Division of Polymeric Materials: Science and Engineering, Vol. 53, Fall Meeting 1985, Am Chem. Soc., Washington, DC, pp. 510–4.
Nakamura, T., Hitomi, S. and Watanabe, S. et al. (1989) Bioabsorption of polylactides with different molecular properties, J. Biomed Mater. Res., 23, 1115–30.
Miller, R. A., Brady, J. M. and Cutright, D. E. (1977) Degradation rates of oral resorbable implants (polylactates and polyglycolates): rate modification with changes in PLA/PGA copolymer ratios, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 11, 711–9.
Leeslag, J. W., Gogolewski, S. and Pennings, A. J. (1984) Bioresorbable materials of poly(L-lactide). V. Influence of secondary structure on the mechanical properties and hydrolability of poly(L-lactide) fibres produced by a dry-spinning method, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 29, 2829–42.
Siemann, U. (1985) The influence of water on the glass transition of poly(DL-lactic acid), Thermochemica Acta., 85, 513–16.
Grijpma, D. W., Nijenhuis, A. J. and Pennings, A. J. (1990) Synthesis and hydrolytic degradation behaviour of high-molecular-weight L-lactide and glycolide copolymers, Polymer, 31, 2201–6.
Li, S. M. and Vert, M. (1994) Crystalline oligomeric stereocomplex as intermediate compound in racemic poly(DL-lactic acid) degradation, Polym. Inter., 33, 37–41.
Cutright, D. E., Perez, B. and Beasley, J. D. et al. (1994) Degradation rates of polymers and copolymers of polylactic and polyglycolic acids, Oral Surg., 37, 142–52.
Reed, A. M. and Gilding, D. K. (1981) Biodegradable polymers for use in surgery —poly(glycolic)/poly(lactic acid) homo- and copolymers: 2. in vitro degradation, Polymer, 22, 494–8.
Zaikov, G. E. and Livshitz, V. S. (1987) The mechanism of chemical degradation of polymers. Part III. The anomaly in the hydrolysis of glycolide copolymers, Polym. Deg. Stabl., 17, 65–9.
Zhu, K. J., Lin, X. Z. and Yang, S. L. (1990) Preparation, characterization and properties of polylactide (PLA) — poly(ethylene glycol) copolymers: a potential drug carrier, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 39, 1–9.
Kaetsu, I., Yoshida, M. and Asano, M. et al. (1987) Biodegradable implant composites for local therapy, J. Control. Rel., 6, 249–63.
Zhu, J. M., Shao, Y. M., Zhang, S. Z. and Sui, W. M. (1991) Homopolymers and copolymers of glycolide and lactide, Journal of China Textile University (Eng. Ed.), 8, 57–61.
Ogawa, Y., Okada, H., Yamamoto, M. and Shimamoto, T. (1988) In vivo release profiles of leuprolide acetate from microcapsules prepared with polylactic acids or copoly(lactic/glycolic) acids and in vivo degradation of these polymers, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 36, 2576–81.
Amarpreet, S. S. and Hubbell, J. A. (1990) Rapidly degraded terpolymers of DL-lactide, glycolide and ε-caprolactone with increased hydrophilicity by copolymerization with polyethers, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 24, 1397–1411.
Beck, L. R., Pope, V. Z. and Flowers, C. E. et al. (1983) Poly(DL-lactide/glycolide)/Norethisterone microcapsules: An injectable biodegradable contraceptive, Biology of Reproduction, 28, 186–95.
Hyon, S. H., Jamshidi, K. and Ikada, Y. (1984) Melt spinning of poly(L-lactide) and hydrolysis of the fibre in vitro, in Polymers as Biomaterials, (eds S. W. Shalaby, A. S. Hoffman, B. D. Ratner and T. A. Horbett), Plenum Press, New York, pp. 51–65.
Tunc, D. C. (1984) Absorbable bone fixation device containing poly(L-lactide), Eur. Pat. Appl. EP 108, 635.
Tunc, D. C., Rohovsky, M. W. and Jadhav, B. et al. (1985) Evaluation of body absorbable bone fixation devices, Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng., 53, 502–4.
Tunc, D. C. and Jadhav, B. (1988) Development of absorbable ultra-high-strength polylactide, Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng., 59, 383–7.
Gerlach K. L. and Eitenmüller, J. (1988) Undersuchungen zum biologischen abbau vershiedener polymère der α-hydroxysäuren, Dtsch Zahnarztl, 43, 41–4.
Eitenmüller, J., Muhr, G., Gerlach, K. L. and Schmickal, T. (1989) New semirigid and bioabsorbable osteosynthesis devices with a high molecular weight polylactide (an experimental investigation), J. Bioact. Compat. Polym., 4, 215–41.
Vert, M., Chabot, F., Leray, J. and Christel, P. (1978) Nouvelles pièces d’ostéosynthèse, leur préparation et leur application, French Patent 78 29978.
Chawla, A. S. and Chang, T. M. S. (1985–6) In vivo degradation of poly(lactic acid) of different molecular weights, Biomed. Med. Dev. Art. Org., 13, 153–62.
Kwong, A. K., Chou, S., Sun, A. M. et al. (1986) In vitro and in vivo release of insulin from poly(lactic acid) microbeads and pellets, J. Control. Rel., 4, 47–62.
Visscher, G. E., Pearson, J. E. and Fong, J. W. et al. (1988) Effect of particle size on the in vitro and in vivo degradation rates of poly(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) microcapsules, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 22, 733–46.
Törmälä, P., Mikkola, H. M. and Vasenius, J., et al. (1991) Strength retention of self-reinforced, absorbable polyglycolide rods in hydrolytic environment, Angew. Makromol. Chem., 185–186, 293–302.
Zhu, J. H., Shen, Z. R., Wu, L. T. and Yang, S. L. (1991) In vitro degradation of polylactide and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres, J. Appl Polym. Sci., 43, 2099–106.
Maulding, H. V., Tice, T. R. and Cowsar, D. R. et al. (1986) Biodegradable microcapsules: acceleration of polymeric excipient hydrolytic rate by incorporation of a basic medicament, J. Control Rel., 3, 103–17.
Cha, Y. and Pitt, C. C. (1988) A one-week subdermal delivery system for L-methadone based on biodegradable microcapsules, J Control. Rel., 1, 69–78.
Cha, Y. and Pitt, C. C. (1989) The acceleration of degradation-controlled drug delivery from polyester microspheres, J Control. Rel., 8, 259–65.
Kishida, A., Yohioka, S., Takeda, Y. and Uchiyama, M. (1989) Formulation-assisted biodegradable polymer matrices, Chem. Pharm. Bull., 37, 1954–6.
Bodmeier, R. and Chen, H. G. (1989) Evaluation of biodegradable poly(lactide) pellets prepared by direct compression, J. Pharm. Sci., 78, 819–22.
Gupta, M. C. and Deshmukh, V. G. (1983) Radiation effects on poly(lactic acid), Polymer, 24, 827–30.
Chu, C. C. (1985) Degradation phenomena of two linear aliphatic polyester fibres used in medicine and surgery, Polymer, 26, 591–4.
Spenlehauer, G., Vert, M., Benoit, J. P. and Boddaert, A. (1989) In vitro and in vivo degradation of poly(DL-lactide/glycolide) type microspheres made by solvent evaporation method, Biomaterials, 10, 557–63.
Birkinshaw, C., Buggy, M., Henn, G. G. and Jones, E. (1992) Irradiation of poly(DL-lactide), Polym. Degr. Stabl, 38, 249–53.
Chu, C. C. (1981) An in vitro study of the effect of buffer on the degradation of poly(glycolic acid) sutures, J. Biomed. Mater Res., 15, 19–27.
Chu, C. C. (1981) The in vitro degradation of poly(glycolic acid) sutures — effect of pH, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 15, 795–804.
Chu, C. C. (1982) A comparison of the effect of pH on the biodegradation of two synthetic bioabsorbable sutures, Ann. Surg., 195, 55–9.
Chu, C. C. (1982) The effect of pH on the in vitro degradation of poly(glycolide/lac-tide) copolymer absorbable sutures, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 16, 117–24.
Chu, C. C. and Moncrief, G. (1983) An in vitro evaluation of the stability of mechanical properties of surgical suture materials in various pH conditions, Ann. Surg., 198, 223–8.
Makino, K., Ohshima, H. and Kondo, T. (1986) Mechanism of hydrolytic degradation of poly(L-lactide) microcapsules: effects of pH, ionic strength and buffer concentration, J. Microencapsulation, 3, 203–12.
Makino, K., Ohshima, H. and Kondo, T. (1987) Effects of plasma proteins on degradation properties of poly(L-lactide) microcapsules, Pharm. Res., 4, 62–5.
Miller, N. D. and Williams, D. F. (1984) The in vivo and in vitro degradation of poly(glycolic acid) suture material as a function of applied strain, Biomaterials, 5, 365–8.
Ikada, Y., Hyon, S.-H. and Jamshidi, K. et al. (1985) Release of antibiotic from composites of hydroxyapatite and poly(lacticacid), J. Control. Rel., 2, 179–86, 1985.
Suuronen, R., Pohjonen, T. and Taurio, R. et al. (1992) Strength retention of self-reinforced poly-L-lactide screws and plates: an in vivo and in vitro study, J. Mater. Sci.: Materials in Medicine, 3, 426–31.
Chegini, N., Hay, D. L., von Fraunhofer J. A. and Masterson, B. J. (1988) A comparative scanning electron microscopic study on degradation of absorbable ligating clips in vivo and in vitro, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 22, 71–9.
Pitt, C. G., Chasalow, F. I. and Hibionada, Y. M. et al. (1981) Aliphatic polyesters. I. The degradation of poly (ε-caprolactone) in vivo, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 26, 3779–87.
Gabelnick, H. L. (1983) Biodegradable implants: alternative approaches, in Advances in Human Fertility and Reproductive Endocrinology: Vol. 2, Long Acting Steroid Contraception, Raven Press, New York, pp. 149–73.
Pitt, C.G. and Gu, Z. W. (1987) Modification of the rates of chain cleavage of poly (ε-caprolactone) and related polyesters in the solid state, J. Control Rel., 4, 283–92.
Jarrett, P., Benedict, C. and Bell, J. P. et al. (1983) Mechanism of the biodegradation of polycaprolactone, Polym. Prepr., Amer. Chem. Soc, Div. Polym. Chem., 24, 32–3.
Jarrett, P., Benedict, C. and Bell, J. P. et al. (1985) Mechanism of the biodegradation of polycaprolactone, in Polymers as Biomaterials (eds S. W. Shalaby, A. S. Hoffman, B. D. Ratner and T. A. Horbett), Plenum pp. 181–92.
Fields, R. D., Rodriguez, F. and Finn, R. K. (1974) Microbial degradation of polyesters: polycaprolactone degraded by P. pullulans, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 18, 3571–59.
Grijmpa, D. W., Zondervan, G. J. and Pennings, A. J. (1991) High molecular weight copolymers of L-lactide and ε-caprolactone as biodegradable elastomeric implants materials, Polym. Bull., 25, 327–33.
Song, C. X., Sun, H. F. and Feng, X. D. (1987) Microspheres of biodegradable block copolymer for long acting controlled delivery of contraceptives, Polym. J., 19, 485–91.
Li, Y. X. (1988) Synthesis and studies of the controlled drug release system of biodegradable polymers as carriers, PhD Thesis, Peking University, China.
Fukuzaki, H., Yoshida, M., Asano, M. (1990) Synthesis of low molecular weight copoly (L-lactic acid/ε-caprolactone) by direct copolycondensation in the absence of catalysts, and enzymatic degradation of the polymers, Polymer, 31, 2006–14.
Cha, Y. and Pitt, C. G. (1990) The biodegradability of polyester blends, Biomaterials, 11, 108–12.
Von Korsatko, W., Wabnegg, B., Braunegg, G. (1983) Poly-D-(−)-3–hydroxy-byttersäure (PHB) — ein biologisch abbaubarer Arzneistoffträger zur Liberations-verzögerung. 1. Mitt: Eintwicklung von parenteral applizierbaren Matrixtabletten zur Langzeitabgabe von Arzneistoffen, Pharm. Ind., 42, 525–7.
Grassie, N., Murray, E. J. and Holmes, P. A. (1984) The thermal degradation of poly (-(D)-β-hydroxy butyric acid). Part 1. Identification and quantitative analysis of products, Polym. Degr. Stab., 6, 47–61.
Tanahashi, N. and Doi, Y. (1991) Thermal properties and stereoregularity of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) prepared from optically active β-butyrolactone with a zinc-based catalyst, Macromolecules, 24, 5732–3.
Bleoembergen, S., Holden, D. A., Bluhm, T. L. (1987) Synthesis of crystalline β-hydroxybutyrate/ β-hydroxyvalerate copolyesters by coordination polymerization of β-lactones, Macromolecules, 20, 3086–9.
Mergaert, J., Wouters, A., Swings, J. and Kersters, K. (1992) Microbial flora involved in the biodegradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates, in Biodegradable Polymers and Plastics, (eds M. Vert et al.), Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp. 95–100.
Yoshioka, S., Kishida, A. and Izumikawa, S. (1991) Base-induced polymer hydrolysis in poly (β-hydroxybutyrate/ ß-hydroxyvalerate) matrices, J. Control Rel., 16, 341–8.
Welland, E. L., Stejny, J., Halter, A. and Keller, A. (1989) Selective degradation of chain folded single crystals of poly(β hydroxybutyrate), Polym. Commun., 30, 302–4.
Holmes, P. A. (1985) Applications of PHB — a microbially produced biodegradable thermoplastic, Phys. Technol., 16, 32–6.
Stinson, M. W. and Merrick, J. M. (1974) Extracellular enzyme secretion by Pseudomonas lemoignei, J. Bacteriol., 119, 152–61.
Kemnitzer, J. E., McCarthy, S. P. and Gross, R. A. (1992) Poly (β-hydroxybutyrate) stereoisomers—a model study of the effects of stereochemical and morphological variables on polymer biological degradability, Macromolecules, 25, 5927–34.
Kronenthal, R. L. (1974) Biodegradable polymers in medicine and surgery, in Polymers in Medicine and Surgery, (eds R. L. Kronenthal, Z. User and E. Martin), Plenum press, New York, pp. 119–37.
Von Korsatko, W., Wabnegg, B. and Tillian, H. M. et al. (1984) Poly-d-(−)-3–hydroxybyttersäuer (PHB) — ein biologisch abbaubarer Arzneistoffträger zur Liberations-Verzögerung. 3. Mitt: Gewebsverträglishkeitsstudien parenteral applizierbarer poly-d-(−)-3–hydroxybyttersäure-tabletten in Gewebekultur und in vivo, Pharm. Ind., 46, 952–4.
Bissery, M. C., Varelote, F. and Thies, C. (1984) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of CCNU-loaded microspheres prepared from poly ((±) lactide) and poly (β-hydroxybutyrate), in Microspheres and Drug Therapy. Pharmaceutical and Medical Aspects (eds S. S. Davis, L. Illum, J. G. McVie and E. Tomlinson), Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, pp. 217–27.
Millar, N. D. and Williams, D. F. (1987) On the biodegradation of poly (ß-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) homopolymer and poly (ß-hydroxybutyrate/hydroxy-valerate) copolymers, Biomaterials, 8, 129–37.
Saito, T., Tomita, K., Juni, K. and Ooba, K. (1991) In vivo and in vitro degradation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) in rat, Biomaterials, 12, 309–12.
Augurt, T. A., Rosensaft, M. N. and Perciaccante, V. A. (1976) Surgical sutures of unsymmetrically substituted 1,4-dioxane-2, 5-diones, US Patent 3, 960, 152.
Augurt, T. A., Rosensaft, M. N. and Perciaccante, V. A. (1977) Polymers of unsymmetrically substituted 1, 4-dioxane-2, 5-diones, US Patent 4,033,938.
Rosensaft, M.N. and Webb, R. L. (1981) Synthetic polyester surgical articles, US Patent 4,243,775.
Rosensaft, M. N. and Webb, R. L. (1981) Synthetic polyester surgical articles, US Patent 4,300,565.
Katz, A. R., Mukherjee, D. P., Kaganov, A. L. and Gordon, S. (1985) A new synthetic monofilament absorbable suture made from polytrimethylene carbonate, Surg. Gynecol. Obstet., 161, 213–22.
Sanz, L. E., Patterson, J. A. and Kamath, R. et al. (1988) Comparison of MAXON suture with VICRYL, chromic CATGUT and PDS sutures in facial closure in rats, Obstet. Gynecol., 71, 418–22.
Doddi, N., Versfelt, C. C. and Wasserman, D. (1976) Synthetic absorbable surgical devices of polydioxanone, US Patent 4,052,988.
Greisler, H. P., Ellinger, J. and Schwarcz, T. H. et al. (1987) Arterial regeneration over polydioxanone prostheses in the rabbit, Arch. Surg., 122, 715–21.
Cornah, J. and Wallace, J. (1988) Polydioxanone (PDS): a new material for internal suspension and fixation, B. J. Oral and Maxillofacial Surg., 26, 250–54.
Biardzka, B. and Kaluzny, J. (1988) Experimental and clinical investigations on the suitability of polydioxanone threads for cerclage of the eyeball, Ophthalmologica (Basel), 197, 47–50.
Schoetz, D. J. J. R., Coller, J. A. and Veidenheimer, M. C. (1988) Closure of abdominal wounds with polydioxanone: a prospective study, Arch. Path. Lab. Med., 123, 72–4.
Lizuka, T., Mikkonen, P., Paukku, P. and Lindqvist, C. (1991) Reconstruction of orbital floor with polydioxanone plate, Inter. J. Oral Maxillofacial Surg., 20, 83–7.
Myers, J. L., Campbell, D. B. and Waldhausen, J. A. (1986) The use of absorbable monofilament polydioxanone suture in pediatric cardiovascular operations, Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, 92, 771–5.
Miles, J. S. (1986) Use of polydioxanone absorbable monofilament sutures in orthopeadic surgery, Orthopeadics (Thorofare), 9, 1533–6.
Ethicon Inc., (1980) Absorbable polymer—drug compositions, UK Patent 1, 573, 459.
Schaefer, C. J., Colombani, P. M. and Geelhoel, G. W. (1982) Absorbable ligating clips, Surg. Gynecol. Obstet., 154, 513–6.
Heller, J., Helwing, R. F., Baker, R. W. and Tuttle, M. W. (1983) Controlled release of water soluble macromolecules from bioerodible hydrogels, Biomaterials, 4, 262–6.
Heller, J. (1985) Water soluble polyesters, US Patent 4, 502, 976.
Baker, R. W., Tuttle, M. W. and Helwing, R. F. (1984) Novel erodible polymers for the delivery of macromolecules, Pharm. Technol., 26–30 Feb.
Han, Y. K., Edelman, P. G. and Huang, S. J. (1988) Synthesis and characterization of crosslinked polymers for biomedical composites, J. Macromol. Sci.-Chem., A25, 847–69.
Sawhney, A. S., Pathak, C. P. and Hubbell, J. A. (1993) Bioerodible hydrogels based on photopolymerized poly(ethylene glycol)-co-poly(α-hydroxyacid) diacrylate macromers, Macromolecules, 26, 581–7.
Pramanick, D. and Ray, T. T. (1988) Synthesis and biodegradation of copolyesters, from citric acid and glycerol, Polym. Bull., 19, 365–70.
Pramanick, D. and Ray, T. T. (1987) Synthesis and biodegradation of polymers derived from aspartic acid, Biomaterials, 8, 407–10.
Braud, C., Vert, M. and Lenz, R. W. (1981) Polyelectrolytical properties of poly-ß-malic acid and its partially benzylated derivatives, Proc. of IUPAC 27th International Symposium on Macromolecules, Strasbourg, France, 1981, Proceedings B5, Vol. II, pp. 1086–89.
Braud, C., Bund, C., Garreau, H. and Vert, M. (1983) Evidence of the amphiphilic structure of partially hydrogenolyzed poly(β-malic acid benzylester), Polym. Bull., 9, 198–203.
Braud, C. and Vert, M. (1984) Poly(β-malic acid) as a source of polyvalent drug carriers: possible effects of hydrophobic substituents in aqueous media, in Polymers as Biomaterials (eds S. W. Shalaby, A. S. Hoffman, B. D. Ratner and T. A. Horben), Plenum, pp. 1–15.
Caron, A., Braud, C., Bunel, C. and Vert, M. (1990) Blocky structure of copolymers obtained by Pd/C-catalyzed hydrogenolysis of benzyl protecting groups as shown by sequence-selective hydrolytic degradation in poly(β-malic acid) derivatives, Polymer, 31, 1797–802.
Guerin, P., Vert, M., Braud, C. and Lenz, R. W. (1985) Optically active poly(ß-malic acid), Polym. Bull., 14, 187–93.
Braud, C., Bunel, C. and Vert, M. (1985) Poly(β-malic acid): anew polymeric drug carrier, evidence for degradation in vitro, Polym. Bull., 13, 293–9.
Braud, C., Caron, A., Francillette, J., Guerin, P. and Vert, M. (1988). Poly (ß-malic acid) stereocopolymers: structural characteristics and degradation in aqueous media, Polym. Prepr. (Am. Chem. Soc., Div. Polym. Chem.), 29, 600–1.
Braud, C. and Vert, M. (1992) Degradation of poly(β-malic acid) — monitoring of oligomers formation by aqueous SEC and HPCE, Polym. Bull., 29, 177–83.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1995 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Li, S., Vert, M. (1995). Biodegradation of aliphatic polyesters. In: Scott, G., Gilead, D. (eds) Degradable Polymers. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-0571-2_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-0571-2_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-4253-6
Online ISBN: 978-94-011-0571-2
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive