Abstract
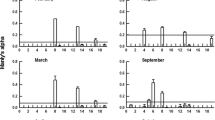
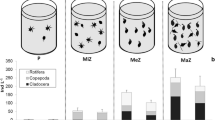
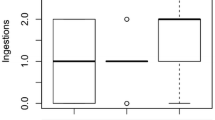
Selectivity coefficients (W’) and predation rates on Lake Michigan zooplankton were determined for Mysis relicta during spring through fall using an in situ method. W’ values indicated the following ranked order of prey preference: Cladocera > copepod copepodites and copepod nauplii > adult diaptomids and cyclopoids. With few exceptions, W’ values for different prey categories remained fairly constant despite greatly changing relative abundances of prey. Predation rates and prey selectivity were similar in most cases to those determined in laboratory studies. Ingestion rates (percent dry body weight · day−1) were correlated to total prey biomass (r = 0.38) and to effective prey biomass (r = 0.85), where the weighting factors were overall mean selectivity coefficients for the different prey categories. This result suggested that seasonally varying composition of prey caused much of the variation in ingestion rates among experiments. Feeding trials performed at the same depth with daytime and nighttime assemblages of zooplankton indicated that Cladocera may escape heavy Mysis predation at night by migrating from the metalimnetic-hypolimnetic interface into the epilimnion.
Contribution 333 from the Great Lakes Research Division, The University of Michigan and contribution 287 from the Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartrum, W. C., 1980. Experimental development of a model for the feeding of neritic copepods on phytoplankton. J. Plankton Res. 3: 25–51.
Beeton, A. M., 1960. The vertical migration of Mysis relicta in Lakes Huron and Michigan. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 17: 517–539.
Bowers, J. A. & Grossnickle, N. E., 1978. The herbivorous habits of Mysis relicta in Lake Michigan. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23: 767–776.
Cooper, S. D. & Goldman, C. R., 1980. Opossum shrimp (Mysis relicta) predation on zooplankton. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 37: 909–919.
Dodson, S. I., 1974. Adaptive change in plankton morphology in response to size selective predation: a new hypothesis of cyclomorphosis. Limnol. Oceanogr. 19: 721–729.
Frost, B. W., 1972. Effects of size and concentration of food particles on the feeding behavior of the marine plantonic copepod Calanus pacificus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17: 805–815.
Gauld, D. T., 1951. The grazing rate of plankton copepods. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K. 29: 695–706.
Goldman, C. R., Morgan, M. D., Threlkeld, S. T. & Angeli, N., 1979. A population dynamics analysis of the cladoceran disappearance from Lake Tahoe, California-Nevada. Limnol. Oceanogr. 24: 289–297.
Gosho, M. E., 1975. The introduction of Mysis relicta into freshwater lakes. Univ. Wash. Coll. Fish., Circ. 75–2. 66 pp.
Grossnickle, N. E., 1978. The herbivorous and predaceous habits of Mysis relicta in Lake Michigan. Ph. D. thesis, Univ. Wisconsin-Madison.
Hawkins, B. E. & Evans, M. S., 1979. Seasonal cycles of zooplankton biomass in southeastern Lake Michigan. J. Great Lakes Res. 5: 256–263.
Hutchinson, G. E., 1967. A Treatise on Limnology, Vol. 2. John Wiley, New York. 1115 pp.
Kerfoot, W. C., 1978. Combat between predatory copepods and their prey: Cyclops, Epischura, and Bosmina. Limnol. Oceanogr. 23: 1089–1102.
Larkin, P. A., 1948. Pontoporeiaand Mysis in Athabaska, Great Bear and Great Slave Lakes. Bull. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 78: 1–33.
Lasenby, D. C. & Langford, R. R., 1973. Feeding and assimilation of Mysis relicta. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18: 280–285.
Lewis, W. M., Jr., 1977. Feeding selectivity of a tropical Chaoborus population. Freshwat. Biol. 7: 311–325.
McQueen, D. J., 1969. Reduction of zooplankton standing stocks by predaceous Cyclops bicuspidatus thomasi in Marion Lake, British Columbia. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 26: 1605–1618.
Morgan, M. D. & Beeton, A. M., 1978. Life history and abundance of Mysis relicta in Lake Michigan. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 35: 1165–1170.
Murtaugh, P. A., 1981a. Selective predation by Neomysis mercedic in Lake Washington. Limnol. Oceanogr. 26: 445–453.
Murtaugh, P. A., 1981b. Size-selective predation on Daphnia by Neomysis mercedis. Ecology 62: 894–900.
Rawson, D. S., 1961. The lake trout of Lac la Ronge, Saskatchewan. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 18: 423–462.
Richards, R. C, Goldman, C. R., Frantz, T. C. & Wickwire, R., 1975. Where have all the Daphnia gone? The decline of a major cladoceran in Lake Tahoe, California-Neveda. Int. Ver. theor. Angew. Limnol. Verh. 19: 835–842.
Richerson, P. J., 1969. Community ecology of the Lake Tahoe plankton. Ph. D. thesis, Univ. of California, Davis, CA. 111 pp.
Rigler, F. H., 1971. Feeding rates. In: Edmondson, W. T. & Robertson, A. (Eds.) A Manual on Methods for the assessment of Secondary Production in Fresh Waters, pp. 228–254. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford.
Rybock, J. T., 1978. Mysis relicta Loven in Lake Tahoe: vertical distribution and nocturnal predation. Ph. D. thesis, Univ. of California, Davis.
Scavia, D., 1979. The use of ecological models of lakes in synthesizing available information and identifying research needs. In: Scavia, D. & Robertson, A., (Eds.) Scavia, D., pp. 109–168. Ann Arbor Science.
Sokal, R. R. & Rohlf, F. J., 1969. Biometry. W. H. Freeman, San Francisco, 776 pp.
Tattersall, W. M. & Tattersall, O. S., 1951. The British Mysidacea. Royal Soc., London.
Vanderploeg, H. A., 1981. Seasonal particle-size selection by Diaptomus sicilis in offshore Lake Michigan. Can. J. Fish, aquat. Sci. 38: 504–517.
Vanderploeg, H. A. & Scavia, D., 1979. Calculation and use of selectivity coefficients of feeding. Ecol. Modelling 7: 135–149.
Vanderploeg, H. A., Bowers, J. A., Chapelski, O. & Soo, H. K., 1982. Measuring in situ predation by Mysis relicta and observations on underdispersed microdistributions of Zooplankton. Hydrobiologia 93: 109–119.
Wells, L., 1960. Seasonal abundance and vertical movements of planktonic Crustacea in Lake Michigan. Fish. Bull. Fish Wildl. Sci. 60: 343–369.
Zyblut, E. R., 1970. Long-term changes in the limnology and macrozooplankton of a large British Columbia lake. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 27: 1239–1250.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1982 Dr W. Junk Publishers, The Hague
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Bowers, J.A., Vanderploeg, H.A. (1982). In situ predatory behavior of Mysis relicta in Lake Michigan. In: Morgan, M.D. (eds) Ecology of Mysidacea. Developments in Hydrobiology, vol 10. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-8012-9_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-8012-9_13
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-009-8014-3
Online ISBN: 978-94-009-8012-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive