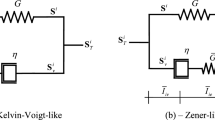
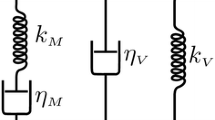
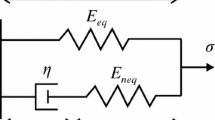
Abstract
Although inelastic response of solid materials at low stress levels has been observed and measured for over a century and a half (an account of the early work is given by Bell1), engineering thinking on material behavior has been dominated by the considerable success of the classical elastic and plastic theories. In contrast, the work on ‘dislocation dynamics’ in the 1950s and early 1960s by Johnston and Gilman2,3 and by Hahn4 and others was based on the concept of considering both elastic and plastic deformations to be generally non-zero at all stages of loading. Those formulations were one-dimensional and restricted to simple loading histories such as uniaxial extension and creep. One of the main interests in those studies was to obtain the form of the equations and the material constants from measurements of microstructural quantities.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. F. Bell, The Experimental Foundations of Solid Mechanics, Encyclopedia of Physics, Vol. VIa/1, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1973.
W. G. Johnston and J. J. Gilman, Dislocation velocities, dislocation densities, and plastic flow in lithium fluoride crystals, J. Appl. Phys., 30 (1959) 129–44.
J. J. Gilman, Dislocation mobility in crystals, J. Appl. Phys., 36 (1965) 3195.
G. T. Hahn, A model for yielding with special reference to the yield point phenomena of iron and related B.C.C. metals, Acta Metall., 10 (1962) 727–38.
S. R. Bodner, Constitutive equations for dynamic material behavior, in Mechanical Behavior of Materials Under Dynamic Loads, ed. U. S. Lindholm, Springer-Verlag, New York, 1968, pp. 176–90.
S. R. Bodner and Y. Partom, A large deformation elastic-viscoplastic analysis of a thick-walled spherical shell, ASME J. Appl. Mech., 39 (1972) 751–7.
D. C. Stouffer and S. R. Bodner, A constitutive model for the deformation induced anisotropic plastic flow of materials, Int. J. Eng. Sci., 17 (1979) 757–64.
S. R. Bodner and D. C. Stouffer, Comments on anisotropic plastic flow and incompressibility, Int. J. Eng. Sci., 21 (1983) 211–5.
S. R. Bodner and A. Merzer, Viscoplastic constitutive equations for copper with strain rate history and temperature effects, ASME J. Eng. Mat. Tech., 100 (1978) 388–94.
A. Merzer and S. R. Bodner, Analytical and computational repre-sentation of high rate of straining behavior, in Mechanical Properties of Materials at High Rates of Strain, ed. J. Harding, Inst. Physics Conf. Series, No. 47, London, 1979, pp. 142–51.
W. A. Spitzig, R. J. Sober and O. Redmond, The effect of hydrostatic pressure on the deformation behavior of maraging and HY-80 steels and its implication for plasticity theory, Metall. Trans., 7A (1976) 1703–10.
O. Richmond and W. A. Spitzig, Pressure dependence and dilatancy of plastic flow, in Proc. 15th Int. Congress of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, ed. F. P. J. Rimrott and B. Tabarrok, North Holland, New York, 1980.
R. W. Klopp, R. J. Clifton, and T. G. Shawki, Pressure-shear impact and the dynamic viscoplastic response of metals, Mech. Mater., 4 (1985) 375–85.
S. R. Bodner and Y. Partom, Dynamic inelastic properties of materials. Part II. Representation of time dependent properties of metals, Proc. Sth Congr. Int. Council Aeronautical Sciences (ICAS), Amsterdam, 1972.
S. R. Bodner and Y. Partom, Constitutive equations for elastic- viscoplastic strain-hardening materials, ASME J. Appl. Mech. 42 (1975) 385–9.
S. R. Bodner, A procedure for including damage in constitutive equations for elastic-viscoplastic work-hardening materials, Proc. IUTAM Symp. Physical Nonlinearities in Structural Analysis, ed. J. Hult and J. Lemaitre, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1981, pp. 21–8.
E. T. Onat and F. Fardshisheh, On the state variable representation of mechanical behavior of elastic-plastic solids, Proc. Symp. Foundations of Plasticity, P. Noordhoff, Groningen, The Netherlands, 1973, pp. 89–115.
E. T. Onat, Representation of inelastic behavior in the presence of anisotropy and of finite deformations, in Recent Advances in Creep and Fracture of Engineering Materials and Structures, ed. B. Wilshire and D. R. J. Owen, Pineridge Press, Swansea, 1982, pp. 231–64.
A. R. S. Ponter, Dynamic behavior of structures composed of strain and work-hardening visco-plastic materials, Int. J. Solids Struct., 16 (1980) 793–806.
H. Ghoneim, S. Matsouka and Y. Chen, Viscoplastic modelling with strain rate history dependence, ASME J. Appl. Mech., 50 (1983) 465–8.
A. Merzer and S. R. Bodner, Analytical formulation of a rate and temperature dependent stress-strain relation, ASME J. Eng. Mat. Tech., 101 (1979) 254–7.
J. L. Chaboche, Viscoplastic constitutive equations for the description of cyclic and anisotropic behaviour of metals, Bull. Acad. Polon. Sci., Ser. Sci. Techn., 25 (1) (1977) 33–42.
F. A. Leckie and D. R. Hayhurst, Constitutive equations for creep rupture, Acta Metall., 25 (1977) 1059–70.
S. R. Bodner, Evolution equations for anisotropic hardening and damage of elastic-viscoplastic materials, in Plasticity Today: Modelling, Methods and Applications, ed. A. Sawczuk and G. Bianchi, Elsevier Applied Science, Barking, 1984, pp. 471–82.
R. W. Rohde, Acta Metall., 17 (1969) 353.
J. M. Kelly and P. P. Gillis, The influence of a limiting dislocation flux on the mechanical response of polycrystalline metals, Int. J. Solids Struct. 10 (1974) 45 - 59.
A. M. Merzer, Steady and transient creep behavior based on unified constitutive equations, ASME J. Eng. Mat. Tech., 104 (1982) 18–25.
D. C. Stouffer and S. R. Bodner, A relationship between theory and experiment for a state variable constitutive equation, in Mechanical Testing for Deformation Model Development, ASTM STP 765, Philadelphia, 1982, pp. 239–50.
D. C. Stouffer, A constitutive representation for IN-100, AFWAL-TR- 81-4039, Wright-Patterson AFB, Ohio, 1981.
M. B. Bever, D. L. Holt and A. L. Titchener, The stored energy of cold work, in Progress in Materials Science, ed. B. Chalmers, J. W. Christian and T. B. Massalski, 17 (1973) 1–190.
J. D. Morrow, Dept. of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, Univ. Illinois, Champaign, private communication, 1979.
K. S. Chan, S. R. Bodner and U. S. Lindholm, Phenomenological modeling of hardening and thermal recovery in metals, Report on NASA Contract No. NAS 3-23925, Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio, Texas. ASME J. Eng. Mat. Tech. y (1986) submitted for publication.
U. F. Kocks, Laws for work-hardening and low temperature creep, ASME J. Eng. Mat. Tech., 98 (1976) 76–85.
U. S. Lindholm, High Velocity Deformation of Solids, ed. K. Kawata and J. Shioiri, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1979, pp. 26–35.
S. R. Bodner, I. Partom and Y. Partom, Uniaxial cyclic loading of elastic-viscoplastic materials, ASME J. Appl. Mech., 46 (1979) 805–10.
S. R. Bodner and K. S. Chan, Modelling of continuum damage for application in elastic-viscoplastic constitutive equations, J. Eng. Fract. Mech., 25 (1986) 705–12.
U. S. Lindholm et al., Constitutive modeling for isotropic materials, Second Annual Status Report on NASA Contract No. NAS3-23925, Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio, Texas, also NASA Report CR-174980, 1985.
A. M. Rajendran, S. J. Bless and D. S. Dawicke, Evaluation of Bodner-Partom model parameters at high strain rates, ASME J. Eng. Mat. Tech., 108 (1986) 75–80.
J. Aboudi, Elastoplasticity theory for porous materials, Mech. Mater., 3 (1984) 81–94.
M. Newman, Z. Zaphir and S. R. Bodner, Finite element analysis for time dependent inelastic material behavior, J. Comput. Struct., 6 (1976) 157–62.
Z. Zaphir and S. R. Bodner, Implementation of elastic-viscoplastic constitutive equations into ‘NONSAP’ with applications to fracture mechanics, in Proc. ADINA Conf, MIT Report 82448–9, ed. K. J. Bathe, August 1979.
Z. Zaphir, Analysis of an elastic-viscoplastic specimen with a crack, Ph.D. thesis, Tel Aviv Univ., 1983.
T. Hinnerichs, T. Nicholas and A. Palazotto, A hybrid experimental- numerical procedure for determining creep crack growth rates, Eng. Fract. Mech., 16 (1982) 265–77.
J. Smail and A. N. Palazotto, The viscoplastic crack growth behavior of a compact tension specimen using the Bodner-Partom flow law, Eng. Fract. Mech., 19 (1984) 137–58.
A. Sperling and Y. Partom, Numerical analysis of large elastic-plastic deformation of beams due to dynamic loading, Int. J. Solids Struct., 13 (1977) 865–76.
J. Aboudi and S. R. Bodner, Dynamic response of a slab of elastic- viscoplastic material that exhibits induced plastic anisotropy, Int. J. Eng. ScL, 18 (1980) 801–13.
S. R. Bodner and J. Aboudi, Stress wave propagation in rods of elastic-viscoplastic material, Int. J. Solids Struct., 19 (1983) 305–14.
J. Aboudi and J. D. Achenbach, Arrest of mode III fast fracture by a transition from elastic to viscoplastic material properties, J. Appl. Mech., 48 (1981) 509–14.
J. Aboudi and J. D. Achenbach, Numerical analysis of fast mode-I fracture of a strip of viscoplastic work-hardening material, Int. J. Fract., 21 (1983) 133–47.
A. M. Merzer, Modelling of adiabatic shear band development from small imperfections, J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 30 (1982) 323–38.
J. Aboudi, Effective constitutive equations for fiber-reinforced viscoplastic composites exhibiting anisotropic hardening, Int. J. Eng. Sei., 21 (1983) 1081–96.
J. Aboudi, Effective behavior of inelastic fiber-reinforced composites, Int. J. Eng. Sei., 22 (1984) 439–49.
J. Aboudi, Elastoplasticity theory for composite materials, Solid Mech. Arch., 11 (1986) 141–83.
T. M. Milly and D. H. Allen, A comparative study of nonlinear rate-dependent mechanical constitutive theories for crystalline solids at elevated temperatures, Report API-E-5-82, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, March 1982.
S. J. Kim and J. T. Oden, Generalized flow potentials in finite elastoplasticity. II. Examples, Int. J. Eng. Sei., 23 (1985) 515–30.
F. A. Leckie and E. T. Onat, Tensorial nature of damage measuring internal variables, in Proc. IUTAM Symp. Physical Non-linearities in Structural Analysis, ed. J. Hult and J. Lemaitre, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1981, pp. 140–55.
S. R. Bodner, Material modeling at high rates of strain. Proc. Int. Conf. on Impact Loading and Dynamic Behavior of Materials, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Metallkunde, Oberursel, FRG, 1987.
Y. Estrin and H. Mecking, An extension of the Bodner-Partom model of plastic deformation, Int. J. Plasticity, 2 (1986) 73–85.
K. S. Chan et al., Constitutive modeling for isotropic materials, Third Annual Status Report on NASA Contract NAS 3-23925, Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio, Texas, also NASA Report CR-179522, 1986.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1987 Elsevier Applied Science Publishers LTD
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Bodner, S.R. (1987). Review of a Unified Elastic—Viscoplastic Theory. In: Miller, A.K. (eds) Unified Constitutive Equations for Creep and Plasticity. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-3439-9_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-3439-9_6
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-94-010-8039-2
Online ISBN: 978-94-009-3439-9
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive