Abstract
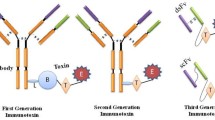
Cancer cells can be specifically killed by a class of therapeutic molecules called immunotoxins that combine the potent toxicity of natural plant and bacterial proteins with the tumor-specific binding capacity of monoclonal antibodies. Toxins such as ricin and diphtheria toxin have been linked to new cell surface binding moieties in order to target tumor cells for destruction. To the extent that tumor cells have cell surface receptors that distinguish them from normal and essential cells, immunotoxins can be considered as potential reagents for cancer therapy. Tumor cell specific ligands, such as growth factors or monoclonal antibodies, can be linked to protein toxins by random chemical modification of lysine or sulfhydral residues (Vitetta et al. 1987) or by fusion of the new protein domains at the COOH- or NH2-terminal of the protein by molecular biology techniques (Pastan et al. 1986).
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergstrom M, Collins P, Ehrin E (1983) Discrepancies in brain tumor extent as shown by computed tomography and positron emission tomography using [68Ga]EDTA, [1 C]glucose, and [1’C]methionine. J Comput Assist Tomogr 7: 1062–1066
Bobo RH, Laske DW, Akbasak A, Morrison PF, Dedrick RL, Oldfield EH (1994) Convection-enhanced delivery of macromolecules in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91: 2076–2080
Book A, Wiley R, Schweitzer J (1995) 192 IgG-saporin. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 89: 519–526
Boucher Y, Baxter L, Jain R (1990) Interstitial pressure gradients in tissue-isolated and subcutaneous tumors: implications for therapy. Cancer Res 50: 4478–4484
Brem H, Piantadosi S, Burger PC, Walker M, Selker R, Vick NA, Black K, Sisti M, Brem S, Mohr G, Muller P, Morawetz R, Schold SC (1995) OPlacebo-controlled trial of safety and efficacy of intraoperative controlled delivery by biodegradable polymers of chemotherapy for recurrent gliomas. Lancet 345: 1008–1012
Earnest F, Kelly PJ, Scheithauer BW, Kall BA, Cascino TL, Ehman RL, Forbes GS, Axley PL (1988) Cerebral astrocytomas: histopathologic correlation of MR and CT contrast enhancement with stereotactic biopsy. Radiology 166: 823–827
Fenstermacher J, Kaye T (1988) Drug “diffusion” within the brain. Ann NY Acad Sci 531: 29–39
Fishman RA, Chan PH (1990) Liposome entrapment of drugs and enzymes to enable passage across the blood-brain barrier. Pathophysiology of the blood-brain barrier. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Gatter K, Brown G, Trowbridge I, Woolston R-E, Mason D (1983) Transferrin receptors in human tissues: their distribution and possible clinical relevance. J Clin Pathol 36: 539–545
Greenfield L, Johnson VG, Youle RJ (1987) Mutations in diphtheria toxin separate binding from entry and amplify immunotoxin selectivity. Science 238: 536–539
Jeffries WA, Brandon MR, Hunt SV (1984) Transferrin receptor on endothelium of brain capillaries. Nature 312: 162–163
Johnson VG, Wilson D, Greenfield L, Youle RJ (1988) The role of the diphtheria toxin receptor in cytosol translocation. J Biol Chem 263: 1295–1300
Johnson VG, Wrobel C, Wilson D, Zovickian J, Greenfield L, Oldfield EH, Youle RJ (1989) Improved tumor-specific immunotoxins in the treatment of CNS and leptomeningeal neoplasia. J Neurosurg 70: 240–248
Kalaria R, Sromek S, Grahovac I, Harik S (1992) Transferrin receptors of rat and human brain and cerebral microvessels and their status in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 585: 87–93
Laird W, Groman N (1976) Isolation and characterization of tox mutants of corynebacteriophage beta. J Virol 19: 220–227
Laske DW, Ilercil O, Akbasak A, Youle RJ, Oldfield EH (1994) Efficacy of direct intratumoral therapy with targeted protein toxins for solid human gliomas in nude mice. J Neurosurg 80: 520–526
Laske D, Muraszko K, Oldfield E, DeVroom H, Sung C, Dedrick R, Simon T, Colendrea J, Copeland C, Katz D, Groves E, Greenfield L, Houston L, Youle R (1997a) Intrathecal immunotoxin therapy for leptomeningeal neoplasia. Neurosurgery (in press)
Laske D, Youle R, Oldfield E (1997b) Tumor regression with regional distribution of the targeted toxin Tf-CRM107 in patients with malignant brain tumors (in press)
Laske DW, Morrison PF, Lieberman D, Corthesy M, Reynolds J, Stewart-Henney P, Koong S, Cummins A, Paik C, Oldfield EH (1997e) Chronic interstitial infusion of protein to primate brain: determination of drug distribution and clearance with SPECT imaging. J Neurosurg (in press)
Lieberman DM, Laske DW, Morrison PF, Bankiewicz KS, Oldfield EH (1995) Convection-enhanced distribution of large molecules in gray matter during interstitial drug infusion. J Neurosurg 82: 1021–1029
Marmarou A, Nakamura T, Tanaka K (1984) The kinetics of fluid movement through brain tiss. Semin Neurol 4: 439–444
Martell L, Agrawal A, Ross D, Muraszko K (1993) Efficacy of transferrin receptor-targeted immunotoxins in brain tumor cell lines and pediatric brain tumors. Cancer Res 53: 1348–1353
Morrison PF, Laske DW, Bobo H, Oldfield EH, Dedrick RL (1994) High-flow microinfusion: tissue penetration and pharmakodynamics. Am J Physiol 266 (1,2): R292–305
Muraszko K, Sung C, Walbridge S, Greenfield L, Dedrick R, Oldfield E, Youle R (1993) Pharmacokinetics and toxicology of immunotoxins administered into the subarachnoid space in nonhuman primates and rodents. Cancer Res 53: 3752–3757
Nicholls PJ, Johnson VG, Andrew SM, Hoogenboom HR, Raus JC, Youle RJ (1993) Characterization of single-chain antibody (sFv)-toxin fusion proteins produced in vitro in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem 268: 5302–5308
Pardridge WM (1990) Chimeric peptides as a vehicle for neuropharmaceutical delivery through the blood-brain barrier. Pathophysiology of the blood-brain barrier. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Pastan I, Willingham M, FitzGerald D (1986) Immunotoxins. Cell 47: 641–644
Rapoport SI, Hori M, Klatzo I (1972) Testing of a hypothesis for osmotic opening of the blood-brain barrier. Am J Physiol 223: 223–231
Recht L, Torres CO, Smith TW, Raso V, Griffin TW (1990) Transferrin receptor in normal and neoplastic brain tissue implications for brain tumor immunotherapy. J Neurosurg 72: 941–945
Riedel CJ, Muraszko KM, Youle RJ (1990) Diphtheria toxin mutant selectively kills cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 5051–5055
Rosenberg FJ, Romano JJ, Shaw DD (1980) Metrizamide, iothalamate, and metrizoate: effects of internal carotid arterial injections on the blood-brain barrier of the rabbit. Invest Radiol 15 [6 Suppl]: S275–279
Sevick E, Jain R (1989) Viscous resistance to blood flow in solid tumors: effect of hematocrit on intra-tumor blood viscosity. Cancer Res 49: 3513–3519
Shin S-U, Friden P, Moran M et al. (1995) Transferrin-antibody fusion proteins are effective in brain targeting. PNAS 92: 2820–2824
Sung C, Wilson D, Youle R (1991) Comparison of protein synthesis inhibition kinetics and cell killing induced by immunotoxins. J Biol Chem 266: 14159–14162
Sung C, Dedrick R, Hall W, Johnson P, Youle R (1993) The spatial distribution of immunotoxins in solid tumors: assessment by quantitative autoradiography. Cancer Res 53: 2092–2099
Trowbridge I, Lesley J, Schulte R (1982) Murine cell surface transferrin receptor: studies with an anti-receptor monoclonal antibody. J Cell Physiol 112: 403–410
Vitetta E, Fulton R, May R, Uhr J (1987) Redesigning naturé s poisons to create anti-tumor reagents. Science 238: 1098–1102
Waite JJ, Chen AD, Wardlow ML, Wiley RG, Lappi DA, Thal LJ (1995) 192 immunoglobulin G-saporin produces graded behavioral and biochemical changes accompanying the loss of cholinergic neurons of the basal forebrain and cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuroscience 65: 463–476
Youle R (1991) Mutations in diphtheria toxin to improve immunotoxin selectivity and understand toxin entry into cells. Semin Cell Biol 2: 39–45
Zovickian J, Youle RJ (1988) Intrathecal immunotoxin therapy in an animal model of leptomeningeal neoplasia. J Neurosurg 68: 767–774
Zovickian J, Johnson VG, Youle RJ (1987) Potent and specific killing of human malignant brain tumor cells by an anti-transferrin receptor antibody-ricin immunotoxin. J Neurosurg 66: 850–861
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1998 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Oldfield, E.H., Youle, R.J. (1998). Immunotoxins for Brain Tumor Therapy. In: Frankel, A.E. (eds) Clinical Applications of Immunotoxins. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology, vol 234. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-72153-3_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-72153-3_7
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-72155-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-72153-3
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive