Abstract
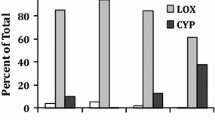
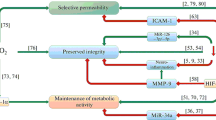
Increased concentrations of free fatty acids, especially arachidonic acid (AA), have been found in brain tissue under several conditions, such as ischemia (9), severe hypoxia (5) or hypoglycemia (1), cold injury (4), and seizures (8). In addition, release of AA into edema fluid sampled from perifocal brain areas surrounding a cold lesion has been detected (7). AA or its products obviously influence membrane function of parenchymal cells since they may induce cytotoxic edema (3). Electron microscopic investigations have shown lesions of endothelial cells of cerebral vessels exposed to AA (6). Therefore, AA and its metabolites may act as mediators of secondary brain damage, i.e., vasogenic edema. It was the aim of the present study to investigate the effects of AA on the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and the caliber of extraparenchymal cerebral arteries and veins when superfusing the cortical surface.
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agardh, C.D., Siesjö, B.K.: Hypoglycemic brain injury: phospholipids, free fatty acids and cyclic nucleotides in the cerebellum of the rat after 30 and 60 minutes of severe insulin-induced hypoglycemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metabol. 1, 267–275 (1981)
Busija, D.W., Heistad, D.: Effects of indomethacin on cerebral blood flow during hypercapnia in cats. Am. J. Physiol. 244, H519 - H524 (1983)
Chan,. P.H., Fishman, R.A.: Brain edema: induction in cortical slices by polyunsaturated fatty acids. Science 201, 358–360 (1978)
Chan, P.H., Fishman, R.A.: Phospholipid degradation and the early release of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the evolution of brain edema. In: Go, K.G., Baethmann, A. (eds.) Recent progress in the study and therapy of brain edema, pp. 193–202. Plenum Press, New York 1984
Gardiner, M., Nilsson, B., Rehncrona, S., Siesjö, B.K.: Free fatty acids in the rat brain in moderate and severe hypoxia. J. Neurochem. 36, 1500–1505 (1981)
Kontos, H.A., Wei, E.P., Povlishock, J.T., Dietrich, W.D., Magiera, C.J., Ellis, E.F.: Cerebral arteriolar damage by arachidonic acid and prostaglandin G2. Science 209, 1242–1245 (1980)
Maier-Hauff, K., Lange, M., Schürer, L., Guggenbichler, C., Vogt, W., Jacob, K., Baethmann, A.: Glutamate and free fatty acid concentrations in extracellular vasogenic edema fluid. In: Go, K.G., Baethmann, A. (eds.) Recent progress in the study and therapy of brain edema, pp. 183–192. Plenum Press, New York 1984
Siesjö, B.K., Ingvar, M., Westerberg, E.: The influence of bicuculline-induced seizures on free fatty acid concentrations in cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum. J. Neurochem. 39, 796–802 (1982)
Shiu, K.G., Nemmer, J.P., Nemoto, E.M.: Reassessment of brain free fatty acid liberation during global ischemia and its attenuation by barbiturate anesthesia. J. Neurochem. 40, 880–884 (1983)
Wei, E.P., Ellis, E.F., Kontos, H.A.: Role of prostaglandins in pial arteriolar response to CO2 and hypoxia. Am. J. Physiol. 238, H226 - H230 (1980)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1985 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wahl, M., Unterberg, A., Baethmann, A. (1985). Effects of Arachidonic Acid on Blood-Brain Barrier Function. In: Dietz, H., Brock, M., Klinger, M. (eds) Extra-Intracranial Vascular Anastomoses Microsurgery at the Edge of the Tentorium. Advances in Neurosurgery, vol 13. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-70603-5_50
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-70603-5_50
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-15615-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-70603-5
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive