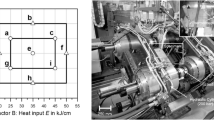
Abstract
Hot crack prevention during welding processing of metallic materials is an essential prerequisite of component safety. The causes of solidification cracking can be attributed to the occurrence of metallurgical and thermomechanical effects. Even though numerous hot cracking test procedures have been developed until now, unexpected solidification cracking during component welding cannot be avoided, since specifically in the hot cracking test the thermomechanical conditions and the local crack-critical strain rates around the weld pool may be very different from those in the component.
In the presented numerical analyses, contrary to the well-known energy distribution models (according to Goldak, for example), the experimentally determined weld pool geometry has directly been implemented as a 3D-function into the numerical simulations and thus conduced to high computational accuracy.
The investigations were carried out using nickel-base Alloy 602 CA, since its solidification resistance exhibits a significant dependence on the shielding gas, which enabled studies of hot crack-critical as well as hot crack-uncritical material behaviour. Validation was carried out with the help of the MVT-test which allowed additional variation of the specimen loading rate. Numerical calculation of the solidification crack-critical limiting temperature versus various welding parameters and the investigated shielding gases could be performed. In order to provide a transferability of hot cracking tests to components, critical specimen loading rates were determined and the local crack-critical strain rates in close vicinity of a weld pool were calculated. It is demonstrated that the local critical strains and strain rates represent a crack criterion for a transferability.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hemsworth B, Boniszewski T, Eaton NF (1969) Classification and definition of high temperature welding cracks in alloys. Metal Construction and British Welding Journal 1, pp 5–15
Wolf M, Kannengieβer T (2005) Moderne Prüfverfahren zur Bestimmung der Heiβrisssicherheit beim Schweiβen von hochlegierten Stählen und Nickelbasislegierungen. DVM Report 641, In: Werkstoffprüfung 2005, ISSN 1861-8154, pp 419–426
Kannengiesser T, McInerney T, Florian W, Böllinghaus T, Cross CE (2002) The Influence of local weld deformation on hot cracking susceptibility. In: Mathematical Modelling of Weld Phenomena 6, Book 0784 Maney Publishing, ISBN: 1-902653-56-4, pp 803–818
Kannengiesser T, Cross CE (2006) Effect of tack placement on local weld displacement and solidification cracking during arc welding of aluminium alloy 6083. In: Proceedings to IIW conference, 21.-22.11.2006, Bangkok, Thailand, pp 480–491
Matsuda F, Nakagawa H, Nakata K, Kohomoto H, Honda Y (1983) Quantitative evaluation of solidification brittleness of weld metal during solidification by means of in-situ observation and measurement. Transactions of JWRI 12 (1), pp 65–72
Corporate Publication (2001) ThyssenKrupp VDM, Werkstoffblatt 4137 Nicrofer 6025H/HT – Alloy 602/602 CA, Edition March
Zinke M, Hübner A, Herold H, Hoffmann T (2003) Erhöhung der Heiβrisssicherheit von hochwarmfesten Ni-Basislegierungen durch die Anwendung stickstoffhaltiger Schutzgase beim Schweiβen. ISBN: 3-87155-683-1, DVS-Report 225, pp 249–256
Herold H, Pshennikov A, Hübner A, Slyvinski A, Krafka H (2001) Was sagen die Heiβrissprüfungen mit dem PVR- und MVT-Verfahren über die Schweiβbarkeit aus. DVS-Report 216, pp 255–260
Goldak J, Chakravarti A, Bibby M (1984) A new finite element model for welding heat sources. Metallurgical Transaction B (15B), June, pp 299–305
Wei Y, Dong Z (2005) Simulation and predicting weld solidification cracks. In: Hot Cracking Phenomena in Welds, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN: 3-540-22332-0, pp 185–222
Prokhorov NN, Prokhorov NN (1969) A general equation for the surface of the solidification front during welding. Svar. Proiz. 8, pp 1–4
Wolf M (2006) Zur Phänomenologie der Heiβrissbildung beim Schweiβen und Entwicklung aussagekräftiger Prüfverfahren. Dissertation, Verlag für neue Wissenschaft GmbH, ISBN-10: 3-86509-599-2
Wolf M, Schobbert H, Böllinghaus T (2005) Influence of the weld pool geometry on solidification crack formation. In: Hot Cracking Phenomena in Welds, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, ISBN: 3-540-22332-0, pp 243–268
Katayama S (2000) Solidification phenomena of weld metals (1st report). Characteristic solidification morphologies, microstructures and solidification theory. Welding International 14 (12), S. 939–951, 2000
Hunziker O, Dye D, Reed RC (2000) On the formation of a centreline grain boundary during fusion welding. Acta Materialia 48, pp 4191–4202
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Wolf, M., Kannengieβer, T., Böllinghaus, T. (2008). Determination of Critical Strain Rate for Solidification Cracking by Numerical Simulation. In: Böllinghaus, T., Herold, H., Cross, C.E., Lippold, J.C. (eds) Hot Cracking Phenomena in Welds II. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-78628-3_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-78628-3_5
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-78627-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-78628-3
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)