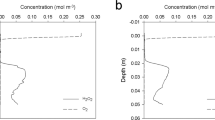
Abstract:
Hydrocarbon contamination of marine cyanobacterial mats influences the structure and the function of their microbial communities. In this chapter, we describe the microsensor setup and the practical procedures involved in the use of O2, sulfide and pH electrodes to measure various metabolic processes in cyanobacterial mats. Microsensors, which are needle-shaped glass electrodes with tip diameters of 1–30 μm, are appropriate tools for investigating the effect of pollution on photosynthesis, oxygen consumption and sulfate reduction with high spatial resolution and under in situ conditions. Microsensor measurements allow the detection of mat physico-chemical microenvironment and the estimation of zonation and rates of metabolic processes. Fast oxygen microsensors are employed to determine the depth distribution and rates of oxygenic gross photosynthesis using light-dark shift method. From the rates of gross photosynthesis and the steady-state oxygen concentration profiles, net photosynthesis and oxygen consumption in the photosynthetic and the non-photosynthetic zones can be calculated by direct flux calculations. Previous research applying microsensors demonstrated a stimulation of aerobic respiration and sulfate reduction but inhibition of photosynthesis in polluted cyanobacterial mats compared to unpolluted controls. These physiological changes, when monitored along with changes in bacterial communities and contaminants concentration, provide an overview of the whole ecosystem response to hydrocarbon pollution and hints as to which bacterial groups might be involved in the degradation of contaminants.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abed RMM, Kohls K, de Beer D (2007) Effect of salinity changes on the bacterial diversity, photosynthesis and oxygen consumption of cyanobacterial mats from an intertidal flat of the Arabian Gulf. Environ Microbiol 9: 1384–1392.
Abed RMM, Polerecky L, Al-Najjar M, de Beer D (2006) Effect of temperature on photosynthesis, oxygen consumption, and sulfide production in an extremely hypersaline cyanobacterial mat. Aquat Microb Ecol 44: 21–30.
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer K-H (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microb Reviews 59: 143–169.
Benthien M, Wieland A, de Oteyza TG, Grimalt JO, Kühl M (2004) Oil-contamination effects on a hypersaline microbial mat community (Camargue, France) as studied with microsensors and geochemical analysis. Ophelia 58: 135–150.
Berg P, Risgaard-Petersen N, Rysgaard S (1998) Interpretation of measured concentration profiles in sediment pore water. Limnol Oceanogr 43: 1500–1510.
Canfield D, Des Marais DJ (1993) Biochemical cycles of carbon, sulfur, and free oxygen in a microbial mat. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57: 3971–3984.
Cline JD (1969) Spectrophotometric determination of hydrogen sulfide in natural waters. Limnol Oceanogr 14: 454–458.
de Beer D, Kühl M, Stambler N, Vaki L (2000) A microsensor study of light enhanced Ca2+ uptake and photosynthesis in the reef-building hermatypic coral Favia sp. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 194: 75–85.
Gieseke A, de Beer D (2007) Use of microelectrodes to measure in situ microbial activities in biofilms, sediments, and microbial mats. In Molecular Microbial Ecology Manual. ADL Akkermans, DV Elsas (eds.). Dordrecht (NL): Kluwer.
Gieseke A, Purkhold U, Wagner M, Amann R, Schramm A (2001) Community structure and activity dynamics of nitrifying bacteria in a phosphate-removing biofilm. Appl Environ Microbiol 67: 1351–1362.
Grasshoff K, Kremling K, Ehrhardt M (1999) Methods of seawater analysis. Weinheim: Wiley.
Grötzschel S, Köster J, Abed RMM, de Beer D (2002) Degradation of petroleum model compounds immobilized on clay by a hypersaline microbial mat. Biodegradation 13: 273–283.
Grötzschel S, Köster J, de Beer D (2004) Degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) by a hypersaline mat and related functional changes in the mat community. Microb Ecol 48: 254–262.
Hinke J (1969) Glass microelectrodes for the study of binding and compartmentalisation of intracellular ions. In Glass microelectrodes. M Lavallee, OF Schanne, NC Herbert (eds.). NewYork: Wiley, pp 349–375.
Jeroschewski P, Steuckart C, Kühl M (1996) An amperometric microsensor for the determination of H2S in aquatic environments. Anal Chem 68: 4351–4357.
Jørgensen BB, Revsbech NP (1985) Diffusive boundary layers and the oxygen uptake of sediments and detritus. Limnol Oceanogr 30: 111–122.
Köhler-Rink S, Kühl M (2000) Microsensor studies of photosynthesis and respiration in larger symbiotic foraminifera. I. The physico-chemical microenvironment of Marginopora vertebralis, Amphistegina lobifera and Amphisorus hemprichii. Mar Biol 137: 473–486.
Kühl M (1993) Photosynthesis, O2 respiration and sulfur cycling in a cyanobacterial biofilm. In: R Guerrero and C Pedros-Alio (eds.). Trends in Microbial Ecology. Spanish Society for Microbiology, pp. 163–167.
Kühl M, Jørgensen BB (1992) Microsensor measurements of sulfate reduction and sulfide oxidation in compact microbial communities of aerobic biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 58: 1164–1174.
Kühl M, Revsbech NP (2000) Biogeochemical microsensors for boundary layer studies. In The benthic boundary layer. B Boudreau, BB Jorgensen (eds.). Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp 180–210.
Kühl M, Steuchart C, Eickert G, Jeroschewski P (1998) A H2S microsensor for profiling biofilms and sediments: Application in an acidic lake sediment. Aquat Microb Ecol 15: 201–209.
Lee N, Nielsen PH, Andreasen KH, Juretschko S, Nielsen JL, Schleifer K-H, Wagner M (1999) Combination of fluorescently in situ hybridization and microautoradiography- a new tool for structure-function analyses in microbial ecology. Appl Environ Mcirobiol 65: 1289–1297.
Manefield M, Whiteley AS, Griffiths RI, Bailey MJ (2002) RNA stable isotope probing, a novel means of linking microbial community to phylogeny. Appl Environ Mcirobiol 68: 5367–5373.
Millero FJ, Plese T, Fernandez M (1988) The dissociation of hydrogen-sulfide in seawater. Limnol Oceanogr 33: 269–274.
Revsbech NP (1989) An oxygen microelectrode with a guard cathode. Limnol Oceanogr 55: 1907–1910.
Revsbech NP, Jørgensen BB (1983) Photosynthesis of benthic microflora measured with high spatial resolution by the oxygen microprofile method: capabilities and limitations of the method. Limnol Oceanogr 28: 749–756.
Revsbech NP, Jørgensen BB (1986) Microelectrodes: their use in microbial ecology. Adv Microb Ecol 9: 293–352.
Revsbech NP, Jørgensen BB, Blackburn TH, Cohen Y (1983) Microelectrode studies of the photosynthesis and O2, H2S and pH profiles of a microbial mat. Limnol Oceanogr 28: 1062–1074.
Revsbech NP, Ward DM (1983) Oxygen microelectrode that is insensitive to medium chemical composition: use in an acid microbial mat dominated by Cyanidium caldarium. Appl Environ Microbiol 45: 755–759.
Schramm A, Amann R (1999) Nucleic acid-based techniques for analizing the diversity, structure, and dynamics of microbial communities in wastewater treatment. In Biotechnology, J Winter (ed). 2nd edn. Weinheim: John Wiley-VCH, pp. 86–108.
Widdel F, Rabus R (2001) Anaerobic biodegradation of saturated and aromatic hydrocarbons. Curr Opin Biotechnol 12: 259–276.
Wieland A, de Beer D, van Dusschoten D, Damgaard LR, Kühl M, van As H (2001) Fine-scale measurement of diffusivity in a microbial mat with NMR imaging. Limnol Oceanogr 44: 248–259.
Wieland A, Kühl M (2000) Short-term temperature effects on oxygen and sulfide cycling in a hypersaline cyanobacterial mat (Solar Lake, Egypt). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 196: 87–102.
Wieland A, Zopfi J, Benthien M, Kühl M (2005) Biogeochemistry of an iron-rich hypersaline microbial mat (Camargue, France). Microb. Ecol 49: 34–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2010 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this entry
Cite this entry
Abed, R.M.M., Beer, D.d. (2010). Microsensor Techniques to Study in situ Bacterial Metabolic Processes in Hydrocarbon-Polluted Marine Cyanobacterial Mats. In: Timmis, K.N. (eds) Handbook of Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-77587-4_288
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-77587-4_288
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-77584-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-77587-4
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesReference Module Biomedical and Life Sciences