Abstract
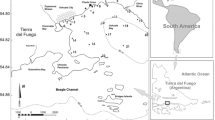
Mesozooplankton communities in coastal ecosystems have successfully adapted to a wide range of environments. However, the current rate of coastal modification is challenging the survival of resident species. In this chapter, we describe the structure and annual dynamics of the mesozooplankton community in recent years for three coastal systems in Argentina that are subject to human disturbance: (1) Bahía Blanca Estuary, (2) Pirámide Bay in Nuevo Gulf and (3) Ushuaia Bay in the Beagle Channel. The seasonal dynamics of mesozooplankton abundance in Bahía Blanca Estuary during 2009–2010 exhibited a unimodal pattern with an increase during the warm seasons, while organism abundance increased linearly with both salinity and turbidity. In Nuevo Gulf, research on the seasonal dynamics of mesozooplankton conducted during 2014–2015 exhibited a bimodal abundance pattern with peaks in late summer and spring. No significant relationships between mesozooplankton and the environmental variables included in Nuevo Gulf were found. The seasonal dynamics of mesozooplankton in Ushuaia Bay in the years 2006–2008 exhibited a bimodal abundance pattern with peaks in summer and early autumn; this pattern was mainly driven by the concentration of chlorophyll a. In Bahía Blanca Estuary, a gradual decrease in species richness was observed throughout the last four decades, while changes in species composition were also observed, suggesting that some species have the ability to acclimate to higher salinity and turbidity as well as to pollution. In Nuevo Gulf, the mesozooplankton community showed no significant modifications over time, which may be related to the low anthropogenic pressure. Although no profound shifts in mesozooplankton were observed in Ushuaia Bay, eutrophication may have an impact in the future through its effect on primary producers.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin OA, Ferrer L, Marcovecchio J (1996) Heavy metal concentrations in littorals sediments from the Beagle Channel, Tierra del Fuego, Argentina. Environ Monit Assess 41:219–231
Amin O, Comoglio L, Spetter C et al (2011) Assessment of land influence on a high-latitude marine coastal system: Tierra del Fuego, southernmost Argentina. Environ Monit Assess 175:63–73
Antacli JC, Sabatini ME, Silva RI et al (2014) Feeding and reproductive activity of the copepods Drepanopus forcipatus and Calanus australis during late summer on the southern Patagonian shelf (Argentina, 47°-55° S). Braz J Oceanogr 62:295–314
Arias AH, Vazquez-Botello A, Tombesi N et al (2010) Presence, distribution, and origins of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in sediments from Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina. Environ Monit Assess 160:301–314
Balestrini C, Manzella G, Lovrich GA (1998) Simulación de corrientes en el Canal Beagle y Bahía Ushuaia, mediante un modelo bidimensional. Servicio de Hidrografía Naval, Departamento de Oceanografía, Technical Report 98:1–58
Berasategui AA, Biancalana F, Fricke A et al (2017) The impact of sewage effluents on the fecundity and survival of Eurytemora americana in a eutrophic estuary of Argentina. Estuar Coast Shel Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2017.08.034
Biancalana F, Diodato SL, Hoffmeyer MS (2012a) Seasonal and spatial variation of mesozooplankton biomass in Ushuaia and Golondrina bays (Beagle Channel, Argentina). Braz J Oceanogr 60:99–106
Biancalana F, Menéndez MC, Berasategui AA et al (2012b) Sewage pollution effects on mesozooplankton structure in a shallow temperate estuary. Environ Monit Assess 184:3901–3913
Biancalana F, Dutto MS, Berasategui AA et al (2014) Mesozooplankton assemblages and their relationship with environmental variables: a study case in a disturbed bay (Beagle Channel, Argentina). Environ Monit Assess 186:8629–8647
Boltovskoy D (1981a) Atlas del zooplancton del Atlántico Sudoccidental y métodos de trabajo con el zooplancton marino. Publicación especial del INIDEP, Mar del Plata, Argentina
Boltovskoy D (1981b) Recuentos y análisis de los datos. Manipulación del material. In: Boltovskoy D (ed) Atlas del zooplancton del Atlántico Sudoccidental y métodos de trabajo con el zooplancton marino. Publicación especial del INIDEP, Mar del Plata, pp 7–107
Boltovskoy D (ed) (1999) South Atlantic zooplankton, vol 1–2. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden
Boltovskoy D, Almada P, Correa N (2011) Biological invasions: assessment of threat from ballast-water discharge in Patagonian (Argentina) ports. Environ Sci Pol 14:578–583
Bradford Grieve JM, Markoseva EL, Rocha CEF et al (1999) Copepoda. In: Boltovskoy D (ed) South Atlantic zooplankton. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden, pp 869–1098
Capitanio F, Pájaro M, Esnal GB (2005) Appendicularians: an important food supply for the Argentine anchovy Engraulis anchoita in coastal waters. J Appl Ichthyol 21:414–419
Cervellini P (2001) Variabilidad en la abundancia y retención de larvas de crustáceos decápodos en el estuario de Bahía Blanca, Provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina. Investig Mar 29(2):25–33
Chang KH, Doi H, Nishibe Y et al (2009) Spatial and temporal distribution of zooplankton communities of coastal marine waters receiving different human activities (fish and pearl oyster farmings). The Open Mar Biol J. https://doi.org/10.2174/187445080903010083
Chazarreta CJ (2015) Dinámica del transporte de zooplancton en el estuario de Bahía Blanca. PhD dissertation, Universidad Nacional del Sur. Bahía Blanca. Argentina
Chazarreta CJ, Hoffmeyer MS, Cuadrado DG (2015) Tidal effects on short-term mesozooplankton distribution in small channels of a temperate-turbid estuary, Southwestern Atlantic. Braz J Oceanogr 63(2):83–92
Commendatore MG, Nievas ML, Amin O et al (2012) Sources and distribution of aliphatic and polyaromatic hydrocarbons in coastal sediments from the Ushuaia Bay (Tierra del Fuego, Patagonia, Argentina). Mar Environ Res 74:20–31
Cuadrado DG, Ginsberg SS, Gomez EA (2007) Geomorfología. In: Piccolo MC, Hoffmeyer MS (eds) Ecosistema del Estuario de Bahía Blanca, 3rd edn. EdiUNS, Bahía Blanca, pp 29–38
D’Agostino VC (2016) Dinámica planctónica y transferencia de biotoxinas marinas a la Ballena Franca Austral (Eubalaena australis) a través de su alimentación en los golfos Nuevo y San José, Península Valdés, Chubut. PhD dissertation, Universidad Nacional del Sur, Bahía Blanca
D’Agostino VC, Hoffmeyer MS, Degrati M (2016) Faecal analysis of southern right whales (Eubalaena australis) in Península Valdés calving ground, Argentina: Calanus australis, a key prey species. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 96(4):859–868
David V, Sautour B, Chardy P et al (2005) Long-term changes of the zooplankton variability in a turbid environment: the Gironde estuary (France). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 64(2–3):171–184
Degrati M, Dans SL, Pedraza SN et al (2008) Diurnal behaviour of dusky dolphins, Lagenorhynchus obscurus, in Golfo Nuevo. J Mammal 89(5):1241–1247
Di Mauro R, Capitanio F, Viñas MD (2009) Capture efficiency for small dominant mesozooplankters (Copepoda, Appendicularia) off Buenos Aires Province (348S–418S), Argentine Sea, using two plankton mesh sizes. Braz J Oceanogr 57:205–214
Diodato S (2013) Respuesta de especies locales a procesos de eutrofización en la zona costera próxima a la ciudad de Ushuaia, Tierra del Fuego. PhD dissertation, Universidad Nacional del Sur, Bahía Blanca
Diodato S, Hoffmeyer MS (2008) Contribution of planktonic and detritic fractions to the natural diet of mesozooplankton in Bahía Blanca Estuary. Hydrobiologia 614:86–90
Dos Santos EP, Fiori SM (2010) Primer registro sobre la presencia de Crassostrea gigas en el estuario de Bahía Blanca (Argentina). Com Soc Malacol Urug 9:245–252
Drillet G, Goetze E, Jepsen PM et al (2008) Strain-specific vital rates in four Acartia tonsa cultures I: strain origin, genetic differentiation and egg survivorship. Aquaculture 280:109–116
Dutto M, López Abbate MC, Biancalana F et al (2012) The impact of sewage on environmental quality and the mesozooplankton community in a highly eutrophic estuary in Argentina. ICES J Mar Sci 69(3):399–409
Dutto MS, Kopprio GA, Hoffmeyer MS et al (2014) Planktonic trophic interactions in a human impacted estuary of Argentina: a fatty acid marker approach. J Plankton Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbu012
Esteves JL, Solís M, Gil M et al (1996) Dos Bahías Patagónicas: Bahía Nueva-Bahía Engaño. In: Abstracts of the international conference on pollution processes in coastal environments, Mar del Plata December 1996
Esteves JL, Commendatore MG, Nievas ML et al (2006) Hydrocarbon pollution in coastal sediments of Tierra del Fuego Islands, Patagonia Argentina. Mar Pollut Bull 52:582–590
Fernandez Severini MD, Hoffmeyer MS (2005) Mesozooplankton assemblages in two bays in the Beagle Channel (Argentina) during January 2001. Sci Mar 69:27–37
Fernández Severini MD, Botté SE, Hoffmeyer MS et al (2009) Spatial and temporal distribution of cadmium and copper in water and zooplankton in the Bahia Blanca estuary, Argentina. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 85:57–66
Fernández Severini MD, Botté ES, Hoffmeyer MS et al (2011) Lead concentrations in zooplankton, water, and particulate matter of a southwestern Atlantic temperate estuary (Argentina). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 61(2):243–260
Fernández Severini MF, Hoffmeyer MS, Marcovecchio J et al (2013) Heavy metals concentrations in zooplankton and suspended particulate matter in a southwestern Atlantic temperate estuary (Argentina). Environ Monit Assess 185(2):1495–1513
Ferrando A, Esteves JL, Elías R et al (2010) Intertidal macrozoobenthos in sandy beaches of Bahía Nueva (Patagonia, Argentina) and their use as bioindicators of environmental impact. Sci Mar 74(2):345–352
Fidalgo LG (2007) Mamíferos Marinos. In: Piccolo MC, Hoffmeyer MS (eds) Ecosistema del Estuario de Bahía Blanca, 3rd edn. EdiUNS, Bahía Blanca, pp 221–222
Fiori SM, Pratolongo P, Zalba SM et al (2016) Spatially explicit risk assessment for coastal invaders under different management scenarios. Mar Biol 163:245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-016-3017-5
Freije RH, Spetter CV, Marcovecchio JE et al (2008) Water chemistry and nutrients of the Bahía Blanca estuary. In: Neves R, Baretta J, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone Management in South America. IST Press, Lisboa, pp 241–254
Gadzała-Kopciuch R, Berecka B, Bartoszewicz J et al (2004) Some considerations about Bioindicators in environmental monitoring. Pol J Environ Stud 13(5):453–462
Garcia-Borboroglu P, Yorio P (2007) Breeding habitat requirements and selection by the threatened Olrog's Gull Larus atlanticus. Auk 124:1201–1212
Gatto AJ (2009) Ecología trófica de tres especies simpátricas de gaviotines en la costa norte de Patagonia. PhD dissertation, Universidad Nacional de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires
Gayoso AM (1999) Seasonal succession patterns of phytoplankton in the Bahía Blanca Estuary (Argentina). Bot Mar 42:367–375
Gil MN, Torres AI, Amin O et al (2011) Assessment of recent sediment influence in an urban polluted subantarctic coastal ecosystem. Beagle Channel (Southern Argentina). Mar Pollut Bull 62:201–207
Gil MN, Torres AI, Marinho CH et al (2014) Caracterización de Sedimentos Costeros y Flujos Bentónicos en una Bahía Patagónica de Argentina: Antes y Después de la Eliminación del Efluente Urbano. In: Marcovecchio J, Botté SE, Freije RH (eds) Procesos Geoquímicos de la Superficie en América Latina. SIFyQA, Bahía Blanca, pp 22–37
Grecco, L.E., Gómez, E.A., Botté et al (2011) Natural and anthropogenic heavy metals in estuarine cohesive sediments: geochemistry and bioavailability. Ocean Dyn 61, 285–293
Guinder VA, Popovich CA, Perillo GME (2009) Particulate suspended matter concentrations in the Bahía Blanca Estuary, Argentina: implication for the development of phytoplankton. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 85:157–165
Guinder VA, Popovich CA, Molinero JC et al (2013) Phytoplankton summer bloom dynamics in the Bahía Blanca Estuary in relation to changing environmental conditions. Cont Shelf Res 52:150–158
Hansen JE (1999) Estimación de parámetros poblacionales del efectivo de sardina fueguina (Sprattus fuegensis) de la costa continental Argentina. INIDEP Informe Técnico:27–28
Hoffmeyer MS (2004) Decadal change in zooplankton seasonal succession in the Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina, following introduction of two zooplankton species. J Plankton Res 26:181–189
Hoffmeyer MS, Cervellini PM (2007) Zooplancton temporario. In: Piccolo MC, Hoffmeyer MS (eds) Ecosistema del Estuario de Bahía Blanca, 3rd edn. EdiUNS, Bahía Blanca, pp 153–161
Hoffmeyer MS, Fernandez-Severini MD, Menendez MC et al (2008) Composition and dynamics of mesozooplankton assemblages in the Bahía Blanca estuary. In: Neves R, Baretta J, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone Management in South America. IST Press, Lisboa, pp 271–276
Hoffmeyer MS, Berasategui AA, Beigt D et al (2009) Environmental regulation of the estuarine copepods Acartia tonsa and Eurytemora americana during coexistence period. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 89:355–361
Hoffmeyer MS, Lindner MS, Carribero A et al (2010a) Planktonic food and foraging of Eubalaena australis, on Península Valdés (Argentina) nursery ground. Rev Biol Mar Oceanogr 45:131–139
Hoffmeyer MS, Barría MS, Pettigrosso RE et al (2010b) Informe año 2009. Programa de monitoreo de la calidad ambiental de la zona interior del estuario de Bahía Blanca. Anexo III Estudio del fitoplancton, micro- y mesozooplancton. Convenio MBB-UNS, 51 p
Hoffmeyer MS, Barría MS, Pettigrosso RE et al (2011). Informe año 2010. Programa de monitoreo de la calidad ambiental de la zona interior del estuario de Bahía Blanca. Anexo III Estudio del fitoplancton, micro- y mesozooplancton. Convenio MBB-UNS, 50 p
Irigoyen AJ, Eyras C, Parma A (2011) Alien algae Undaria pinnatifida causes habitat loss for rocky reef fishes in North Patagonia. Biol Invasions 13:17–24
Isla F, Bujalesky G, Coronato A (1999) Procesos estuarinos en el Canal Beagle, Tierra del Fuego. Rev Asoc Geol Argent 54:307–318
La Colla NS, Negrin VL, Marcovecchio JE et al (2015) Dissolved and particulate metals dynamics in a human impacted estuary from the SW Atlantic. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 166:45–55
Lawrence D, Valiela I, Tomasky G (2004) Estuarine calanoid copepod abundance in relation to season, salinity, and land-derived nitrogen loading, Waquoit Bay, MA. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 61:547–557
López Abbate MC, Molinero JC, Guinder VA et al (2012) Microplankton dynamics under heavily anthropogenic pressure. The case of the Bahía Blanca estuary, southwestern Atlantic Ocean. Mar Pollut Bull 95:305–314
Lopez-Cazorla AC (2007) Peces. In: Piccolo MC, Hoffmeyer MS (eds) Ecosistema del Estuario de Bahía Blanca, 3rd edn. EdiUNS, Bahía Blanca, pp 191–201
Lopez-Cazorla AC, Pettigrosso RE, Tejera L et al (2011) Diet and food selection by Ramnogaster arcuata (Osteichthyes, Clupeidae). J Fish Biol 78(7):2052–2066
Lorenzen CJ (1967) Vertical distribution of chlorophyll and phaeopigments: Baja California. Deep Sea Res 14:735–745
Lovrich G, Thatje S, Calcagno JA et al (2003) Changes in biomass and chemical composition during lecithotrophic larval development of the southern king crab Lithodes santolla (Molina). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 288:65–79
Marcovecchio JE, Botté SE, Delucchi F et al (2008) Pollution processes in Bahía Blanca estuarine environment. In: Neves R, Baretta J, Mateus M (eds) Perspectives on integrated coastal zone Management in South America. IST Press, Lisboa, pp 301–314
Mazio CA, Dragani WC, Caviglia FJ et al (2004) Tidal hydrodynamics in Golfo Nuevo, Argentina, and the adjacent continental shelf. J Coast Res 20(4):1000–1011
Mazzochi MG, Zagami G, Ianora A et al (1995) Copepods. In: Guglielmo L, Ianora A (eds) Atlas of Marine Zooplankton Straits of Magellan. Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp 219–222
Menéndez MC, Biancalana F, Berasategui AA et al (2011) Mesozooplankton composition and spatial distribution, Nuevo Gulf, Patagonia, Argentina. Check List 7:101–107
Mieszkowska N, Sugden H, Firth LB et al (2014) The role of sustained observations in tracking impacts of environmental change on marine biodiversity and ecosystems. Phil Trans R Soc A 372(2025):1–13
Mori AS, Furukawa T, Sasaki T (2013) Response diversity determines the resilience of ecosystems to environmental change. Biol Rev 88:349–364
Mouny P, Dauvin JC (2002) Environmental control of mesozooplankton community structure in the Seine estuary (English Channel). Influence des paramètres environnementaux sur la répartition spatio-temporelle du mésozooplancton de l’estuaire de la Seine. Oceanol Acta 25:13–22
Niehoff B, Schnack-Schiel S, Cornils A et al (2002) Reproductive activity of two dominant Antarctic copepod species, Metridia gerlachei and Ctenocalanus citer, in late autumn in the eastern Bellingshausen Sea. Polar Biol 25:583–590
Oliva AL, Quintas PY, La Colla NS et al (2015) Distribution, sources, and potential ecotoxicological risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from Bahía Blanca estuary, Argentina. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 69(2):163–172
Perillo GME, Piccolo MC, Palma ED et al (2007) Oceanografía física. In: Piccolo MC, Hoffmeyer MS (eds) Ecosistema del Estuario de Bahía Blanca, 3rd edn. EdiUNS, Bahía Blanca, pp 61–67
Petracci P, Sotelo MR, Díaz LI (2008) A new colony of Olrog’s Gull (Larus atlanticus) in the Bahía Blanca, Bahía Falsa and Bahía Verde Natural Reserve, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Hornero 23:37–40
Ramírez FC (1981) Zooplancton y producción secundaria. Parte I: distribución y variación estacional de los copépodos. Campañas de investigación pesquera realizadas en el Mar Argentino por los B/I “Shinkai Maru”y “Walter Herwig” y el B/P “Marburg”, años 1978 y 1979. Resultados de la parte argentina. Contrib. INIDEP 383:202–212
Raya Rey A, Schiavini ACM (2000) Distribution, abundance and associations of seabirds in the Beagle Channel, Tierra del Fuego, Argentina. Polar Biol 23(5):338–345
Richard S, Jamet JL (2001) An unusual distribution of Oithona nana Giesbrecht (1892) (Crustacea: Cyclopoida) in a Bay: The Case of Toulon Bay (France, Mediterranean Sea). J Coast Res 17(4):957–963
Rivarola M, Campagna C, Tagliorette A (2001) Demand-driven comercial whale-watching in Peninsula Valdés (Patagonia): conservation implications for right whales. J Cet Res Manage 2 (Special Issue): 145–151
Rivas AL, Beier EJ (1990) Temperature and salinity fields in the north Patagonian gulfs. Oceanol Acta 13(1):15–20
Rivas A, Ripa P (1989) Variación estacional de la estructura termohalina de Golfo Nuevo, Argentina. Geofis Int 28:3–24
Roman MR, Holliday DV, Sanford LP (2001) Temporal and spatial patterns of zooplankton in the Chesapeake Bay turbidity maximum. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 213:215–227
Sabatini ME (1989) Ciclo anual del copépodo Acartia tonsa Dana, 1849 en la zona interna de la Bahía Blanca (Pcia. de Buenos Aires, Argentina). Sci Mar 53:847–856
Sato NE, Hernández D, Viñas MD (2011) Feeding habits of Engraulis anchoita (Hubbs & Marini, 1935) larvae in coastal waters off Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Lat Am J Aquat Res 39:6–24
Scheffer M, Carpenter SR (2003) Catastrophic regime shifts in ecosystems: linking theory to observation. Trends Ecol Evol 18:648–656
Schwindt E, Gappa JL, Raffo MP et al (2014) Marine fouling invasions in ports of Patagonia (Argentina) with implications for legislation and monitoring programs. Mar Environ Res 99:60–68
Silva AP, Neumann-Leitão S, Schwamborn R et al (2004) Mesozooplankton of an impacted bay in North Eastern Brazil. Braz Arch Biol Techol 47(3):485–493
Simonetti P, Fiori SM, Botté SE et al (2013) Nidificación del ostrero común (Haematopus palliatus) en el estuario de Bahía Blanca, Buenos Aires, Argentina. Hornero 28(2):51–58
Solís M (1998) Monitoring in Nuevo Gulf (Argentina): Analysis of oceanographic data by Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Dissertation, International Institute for Infrastructural, Hydraulic and Environmental Engineering
Sommer U, Stibor H, Katechakis A et al (2002) Pelagic food web configurations at different levels of nutrient richness and their implications for the ratio fish production: primary production. Hydrobiologia 484:11–20
Spetter CV, Popovich CA, Arias A et al (2015) Role of nutrients in phytoplankton development during a winter diatom bloom in a eutrophic south American estuary (Bahía Blanca, Argentina). J Coast Res 31:76–87
Thatje S, Anger K, Calcagno JA et al (2005) Challenging the cold: crabs reconquer the Antarctic. Ecology 86:619–625
Torres AI, Gil MN, Amin OA et al (2009) Environmental characterization of a eutrophicated semi-enclosed system: nutrient budget (Encerrada Bay, Tierra del Fuego Island, Patagonia, Argentina). Water Air Soil Pollut 204:259–270
Turner JT (2004) The importance of small planktonic copepods and their roles in pelagic marine food webs. Zool Stud 43:255–266
Uriarte I, Villate F (2004) Effects of pollution on zooplankton abundance and distribution in two estuaries of the Basque coast (Bay of Biscay). Mar Pollut Bull 49:220–228
Williams JA, Muxagata E (2006) The seasonal abundance and production of Oithona nana (Copepoda:Cyclopoida) in Southampton Water. J Plankton Res 28(II):1055–1065
Wilson C, Sastre AV, Hoffmeyer MS et al (2015) Southern right whale (Eubalaena australis) calf mortality at Península Valdés, Argentina: are harmful algal blooms to blame? Mar Mamm Sci 32(2):423–451
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by a grant (PICT 2014-3091, ANPCYT Argentina) to M.S.H. and a grant (PIP0630, CONICET) to A.A.B. We thank CONICET (National Council of Scientific and Technical Research) and ANPCYT (National Agency for Scientific and Technical Promotion), the Ministry for Science, Technology and Productive Innovation (Argentina) fellowships for some co-authors of the chapter. We would also like to thank to staff of the Austral Centre of Scientific Research (CADIC)-CONICET in Ushuaia, the Centre of Marine Systems (CESIMAR)-CONICET in Puerto Madryn and the Argentine Institute of Oceanography (IADO)-CONICET in Bahía Blanca, for their help during sampling and nutrient determination. Special thanks are due to W. Melo from IADO for his help in drawing figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Berasategui, A.A. et al. (2018). Mesozooplankton Structure and Seasonal Dynamics in Three Coastal Systems of Argentina: Bahía Blanca Estuary, Pirámide Bay, and Ushuaia Bay. In: Hoffmeyer, M., Sabatini, M., Brandini, F., Calliari, D., Santinelli, N. (eds) Plankton Ecology of the Southwestern Atlantic. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-77869-3_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-77869-3_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-77868-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-77869-3
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)