Abstract
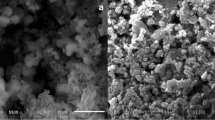
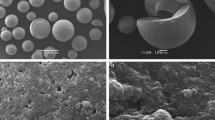
Crystalline and agglomerated spherical alpha zirconium phosphate nanoparticles hereafter α-ZrP were synthesized by a facile and rapid microwave-hydrothermal (MW-HT) approach within 30 min at 120 °C in the absence of any complexing or structure directing agent (SDA). The material was characterized by Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR), powdered X-ray diffraction (PXRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectroscopic analysis (EDS) and surface area analysis (BET). It crystallizes in the monoclinic P121/n1 space group with the following cell parameters: a = 5.288, b = 9.174, c = 15.384 Å and β = 102.384. Crystallite sizes in the range 3–4 nm evaluated using Scherer equation were obtained for α-ZrP. Ion exchange performance of α-ZrP towards removal of Cs+ and Sr2+ ions was examined under noncompetitive batch conditions. Distribution studies indicate higher selectivity of α-ZrP towards Sr2+ uptake (Kd ca. 4.3 × 104) in comparison with Cs+ (Kd ca. 2.4 × 103). This study suggested to agglomerated α-ZrP as potential adsorbent for the removal of radioactive Sr2+ from acidic wastewater.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AAS:
-
Atomic absorption spectroscopy
- BET:
-
Surface area analysis
- CP:
-
Co-precipitation
- DFT:
-
Density functional theory
- EDS:
-
Energy dispersive spectroscopic analysis
- FT-IR:
-
Fourier transform infrared
- IEC:
-
Ion exchange capacity
- K d :
-
Distribution coefficient
- MW-HT:
-
Microwave hydrothermal
- PXRD:
-
Powdered X-ray diffraction
- PZC:
-
Point of zero charge
- SDA:
-
Structure directing agents
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- ZrP:
-
Zirconium Phosphate
References
Rahman ROA, Ibrahium HA, Hung YT (2011) Liquid radioactive wastes treatment: a review. Water 3:551–565
Paulus WJ, Komarneni S, Roy R (1992) Bulk synthesis and selective exchange of strontium ions in Na4Mg6 Al4 Si4O20F4 mica. Nature 357:571–573
Sun JM, Shang C, Huang JC (2003) Co-removal of hexavalent chromium through copper precipitation in synthetic wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 37:4281–4287
Abdelfattah I, Ismail AA, Sayed FA et al (2016) Biosorption of heavy metals ions in real industrial wastewater using peanut husk as efficient and cost effective adsorbent. Environ Nanotech Monit Manag 6:176–183
Boccelli DL, Small MJ, Dzombak D (2005) Enhanced coagulation for satisfying the arsenic maximum contaminant level under variable and uncertain conditions. Environ Sci Technol 39:6501–6507
Vergili I, Kaya Y, Sen U et al (2012) Techno-economic analysis of textile dye bath wastewater treatment by integrated membrane processes under the zero liquid discharge approach. Resour Conserv Recycl 58:25–35
Jawor A, Hoek EMV (2010) Removing cadmium ions from water via nanoparticle-enhanced ultrafiltration. Environ Sci Technol 44:2570–2576
Abdolali A, Ngo HH, Guo W et al (2016) A breakthrough biosorbent in removing heavy metals: equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic and mechanism analyses in a lab-scale study. Sci Total Environ 542:603–611
Cheng Y, Wang XD, Jaenicke S et al (2018) Mechanochemistry-based synthesis of highly crystalline γ-zirconium phosphate for selective ion exchange. Inorg Chem 57:4370–4378
Wen T, Zhao Z, Shen C et al (2016) Multifunctional flexible free-standing titanate nanobelt membranes as efficient sorbents for the removal of radioactive 90Sr2+and 137Cs+ions and oils. Sci. Rep. 6, 20920. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep20920
Xiao X, Hayashi F, Shiiba H et al (2016) Platy KTiNbO5 as a selective Sr ion adsorbent: crystal growth, adsorption experiments, and DFT calculations. J Phys Chem C 120:11984–11992
Mertz JL, Fard ZH Kanatzidi MG et al (2013) Selective removal of Cs+,Sr2+ and Ni2+ by K2xMgxSn3−x S6(x = 0.5 − 1) (KMS-2) relevant to nuclear waste remediation. J Chem Mater 25:2116–2127
Manos MJ, Kanatzidis MG (2016) Metal sulfide ion exchangers: superior sorbents for the capture of toxic and nuclear waste-related metal ions. Chem Sci 7:4804–4824
Zhu Y, Shimizu T, Kitajima T (2014) Synthesis of robust hierarchically porous zirconium phosphate monolith for efficient ion adsorption. New J Chem. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nj01749h
He W, Ai K, Ren X et al (2017) Inorganic layered ion-exchangers for decontamination of toxic metal ions in aquatic systems. J Mater Chem A 5:19593–19606
Mrad O, Abdul-Hadi A, Arsan H (2011) Preparation and characterization of three different phases of zirconium phosphate: study of the sorption of 234Th,238U, and134 Cs. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 287:177–183
Bashir A, Ahad S, Pandith AH (2016) Soft template assisted synthesis of zirconium resorcinol phosphate nanocomposite material for the uptake of heavy-metal ions. Ind Eng Chem Res 55:4820–4848
Varshney KG, Pandith AH, Gupta U (1998) Synthesis and characterization of zirconium alumino phosphate: a new cation exchanger. Langmuir 14:7353–7358
Mu W, Yu Q, Zhang R et al (2017) Controlled fabrication of flower-like α-zirconium phosphate for the efficient removal of radioactive strontium from acidic nuclear wastewater. J Mater Chem A 5:24388–24395
Mosby BM, Goloby Clearfield A et al (2014) Designable architectures on nanoparticle surfaces: zirconium phosphate nanoplatelets as a platform for tetravalent metal and phosphonic acid assemblies. Langmuir 30:2513–2521
Hajipour AR, Karimi H (2014) Synthesis and characterization of hexagonal zirconium phosphate nanoparticles. Mater Lett 116:356–358
Bellezza F, Cipiciani A, Costantino U et al (2006) Zirconium phosphate nanoparticles from water-in-oil microemulsion. Colloid Polym Sci 285:19–25
Shuai M, Mejia AF, Chang YW et al (2013) Hydrothermal synthesis of layered α-zirconium phosphate disks: control of aspect ratio and polydispersity for nano-architecture. Cryst Eng Comm 15:1970–1977
Smeets S, Liu L, Dong (2015) Ionothermal synthesis and structure of a new layered zirconium phosphate. J Inorg Chem 54:7953–7958
Cheng Y, Wang X, Jaenicke S et al (2017) Minimalistic liquid-assisted route to highly crystalline α-zirconium phosphate. Chem Sus Chem. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201700885
Muraliganth T, Murugan A V and Manthiram A (2009) Facile synthesis of carbon-decorated single-crystalline Fe3O4 nanowires and their application as high performance anode in lithium ion batteries. Chem Commun:7360–7362
Pica M, Nocchetti M, Ridolfi B et al (2010) Nanosized zirconium phosphate/AgCl composite materials: a new synergy for efficient photocatalytic degradation of organic dye pollutants. J Mater Chem A 3:5525–5534
Culity BD (1976) Elements of X-ray diffraction. Addison-Wesly Publishing Co. Inc. (Chapter 14)
Zhang Q, Du Q, Jiao T et al (2013) Selective removal of phosphate in waters using a novel cation adsorbent: zirconium phosphate(ZrP) behavior and mechanism. J Chem Eng 221:315–321
Horsley SE, Nowell DV, Stewart DT (1974) The infrared and raman spectra of α -zirconium phosphate. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Spectrosc 30:535–541
Troup JM, Clearfield A (1977) On the mechanism of ion exchange in zirconium phosphates. 20. Refinement of the crystal structure of a-zirconium phosphate. Inorg Chem 16:12, 197
Kalita H, Rajput S, Kumar BNP et al (2016) Fe3O4@zirconium phosphate core–shell nanoparticles for pH-sensitive and magnetically guided drug delivery applications. RSC Adv 6:21285–21292
Gatabia MP, Moghaddam HM, Ghorbani M (2016) Point of zero charge of maghemite decorated multiwalled carbon nanotubes fabricated by chemical precipitation method. J Mol Liq 216:117–125
Ahad S, Islam N Pandith AH et al (2015) Adsorption studies of Malachite green on 5-sulphosalicylic acid doped tetraethoxysilane (SATEOS) composite material. RSC Adv 5:92788–92798
Inamuddin, Khan SA, Siddiqui WA et al (2007) Synthesis, characterization and ion-exchange properties of a new and novel ‘organic–inorganic’ hybrid cation exchanger: Nylon-6,6, Zr(IV) phosphate. Talanta 71:841–847
Ahad S, Bashir A, Pandith AH et al (2016) Exploring the ion exchange and separation capabilities of thermally stable acrylamide zirconium(IV) sulphosalicylate (AaZrSs) composite material. RSC Adv 6:35914–35927
Zhao J, Islam SM, Kanatzidis MG et al (2017) Homologous series of 2D chalcogenides Cs − Ag − Bi − Q (Q = S, Se) with ion-exchange properties. J Am Chem Soc 139:12601–12609
Wang L, Xu WH, Yang R et al (2013) Electrochemical and density functional theory investigation on high selectivity and sensitivity of exfoliated nano-zirconium phosphate toward lead(II). J Anal Chem 85:3984–3990
Acknowledgements
We thank the Head Department of Chemistry, the University of Kashmir for providing all the necessary facilities to carry out this work. We would also like to thank Mainak Roy and S. N. Achary, Chemistry Division, BARC, Mumbai for their help with PXRD and FT-IR studies. A. B. would like to thank the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), GOI, for financial assistance in the form of a Junior Research Fellowship (JRF). G. N. thanks the DST, GOI, for a research grant for carrying out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Bashir, A., Malik, L.A., Dar, G.N., Pandith, A.H. (2019). Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Agglomerated Spherical Zirconium Phosphate for Removal of Cs+ and Sr2+ Ions from Aqueous System. In: Inamuddin, Ahamed, M., Asiri, A. (eds) Applications of Ion Exchange Materials in the Environment. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-10430-6_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-10430-6_5
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-10429-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-10430-6
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)