Summary
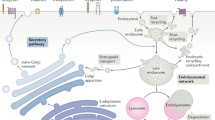
Receptor trafficking is essential to the delivery of nutrients and to the proper regulation of signaling pathways in mammalian cells. Numerous transmembrane receptors undergo clathrin-mediated endocytosis, followed by sorting in the early endosome. The low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor-related protein (LRP) is a multiligand endocytic receptor and a member of the LDL receptor family. At the cell surface, it binds to and continuously internalizes numerous ligands including lipoproteins, proteases, protease inhibitors, growth factors, and β-amyloid precursor protein via clathrin-mediated endocytosis. Its rapid endocytosis rate allows efficient clearance of extracellular and transmembrane ligands. Once internalized into the early or sorting endosome, LRP ligands are delivered to lysosomes to be degraded, whereas LRP is efficiently recycled to the plasma membrane. Herein, the authors describe quantitative methods to measure the endocytosis and recycling capacity of receptors, using LRP as a model receptor.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maxfield, F.R. and McGraw, T.E. (2004) Endocytic recycling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 121–132 .
Bonifacino, J.S. and Traub, L.M. (2003) Signals for sorting of transmembrane proteins to endosomes and lysosomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72, 395–447.
van Kerkhof, P., Lee, J., McCormick, L., et al. (2005) Sorting nexin 17 facilitates LRP recycling in the early endosome. Embo J. 24, 2851–2861.
Carlton, J., Bujny, M., Rutherford, A. and Cullen, P. (2005) Sorting nexins—unifying trends and new perspectives. Traffic 6, 75–82.
Herz, J. and Strickland, D.K. (2001) LRP: a multifunctional scavenger and signaling receptor. J. Clin. Invest. 108, 779–784.
Trommsdorff, M., Borg, J.P., Margolis, B. and Herz, J. (1998) Interaction of cytosolic adaptor proteins with neuronal apolipoprotein E receptors and the amyloid precursor protein. J. Bio.l Chem. 273, 33556–33560.
Trommsdorff, M., Gotthardt, M., Hiesberger, T., et al. (1999) Reeler/Disabled–like disruption of neuronal migration in knockout mice lacking the VLDL receptor and ApoE receptor 2. Cell 97, 689–701.
Lillis, A.P., Mikhailenko, I. and Strickland, D.K. (2005) Beyond endocytosis: LRP function in cell migration, proliferation and vascular permeability. J. Thromb. Haemost. 3, 1884–1893.
Li, Y., Marzolo, M.P., van Kerkhof, P., Strous, G.J. and Bu, G. (2000) The YXXL motif, but not the two NPXY motifs, serves as the dominant endocytosis signal for low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 17187–17194.
Obermoeller-McCormick, L.M., Li, Y., Osaka, H., FitzGerald, D.J., Schwartz, A.L., Bu, G., et al. (2001) Dissection of receptor folding and ligand-binding property with functional minireceptors of LDL receptor-related protein. J. Cel.l Sci. 114, 899–908.
Austin, C.D., De Maziere, A.M., Pisacane, P.I., Van Dijk, S.M., et al. (2004) Endocytosis and sorting of ErbB2 and the site of action of cancer therapeutics trastuzumab and geldanamycin. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 5268–5282.
Schapiro, F.B., Soe, T.T., Mallet, W.G. and Maxfield, F.R. (2004) Role of cytoplasmic domain serines in intracellular trafficking of furin. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 2884–2894.
Acknowledgments
Work in the authors’ laboratory is supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Alzheimer’s Association, and the American Health Assistance Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2008 Humana Press, a part of Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Knisely, J.M., Lee, J., Bu, G. (2008). Measurement of Receptor Endocytosis and Recycling. In: Vancura, A. (eds) Membrane Trafficking. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 457. Humana Press. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-261-8_24
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-261-8_24
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press
Print ISBN: 978-1-58829-925-3
Online ISBN: 978-1-59745-261-8
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols