Abstract
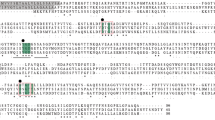
Only a few natural inhibitors of aspartic proteinases have been discovered to date. A small number of peptides from bacterial origins have been shown to inhibit members of this protease family.1-2 Larger proteinaceous inhibitors of aspartic proteases have been discovered in the potato3 (cathepsin D inhibitor), in yeast,4 and the intestinal nematode Ascaris.5–7 Similar genes have been discovered in other parasitic nematodes.8 The Ascaris aspartic proteinase inhibitor (PI-3) is a 16.7 kDa protein that specifically inhibits pepsin, gastricsin, and, less strongly, cathepsin E. This inhibitor possesses six cysteine residues which form three disulfide bridges, and it contains helical and strand structural motifs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Umezawa, T. Aoyagi, H. Morishima, M. Matsuzaki, M. Hamada and T. Takeuchi, Journal of Antibiotics, 23, p. 259,(1970).
M. Fukumura, S. Satoi, N. Kuwana and S. Murao, Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 35, p. 1310, (1971).
M. Mares, B. Meloun, M. Pavlik, V. Kostka and M. Baudys, FEBS Letters, 251, p. 94, (1989).
T. Dreyer, M. J. Valler, J. Kay, P. Charlton, and B. M. Dunn, Biochemical Journal, 231, p. 777, (1985).
G. M. Abu-Erreish and R. J. Peanasky, Journal of Biological Chemistry, 249, p. 1558, (1974a, b).
M. J. Valler, J. Kay, T. Aoyagi and B. M. Dunn, J. Enzyme Inhibition, 1, p. 77, (1985).
M. Martzen, B. McMullen, N. Smith, K. Fujikawa and R. J. Peanasky, Biochemistry, 29, p. 7366, (1990).
X. Q. Hong, J. S. Mejia, S. Kumar, F. B. Perlerand C. K. S. Carlow, Parasitology, 112, p. 331, (1996).
M. Barman, Senior thesis, University of Florida, 1995.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 1998 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Zalatoris, J., Rao-Naik, C., Fecho, G., Girdwood, K., Kay, J., Dunn, B.M. (1998). Expression, Purification, and Characterization of the Recombinant Pepsin Inhibitor from Ascaris suum . In: James, M.N.G. (eds) Aspartic Proteinases. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol 436. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-5373-1_54
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4615-5373-1_54
Publisher Name: Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN: 978-1-4613-7452-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-4615-5373-1
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive