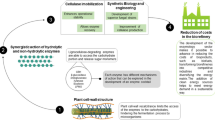
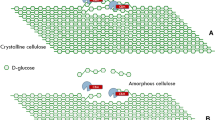
Abstract
Plant biomass, commonly referred to as lignocellulose, represents a renewable and thus sustainable substrate for the liquid biofuel and chemical industries, which is carbon dioxide neutral. There is much debate concerning the economic viability of lignocellulose-based liquid biofuels based, primarily, on the cost of the enzymes required to saccharify plant biomass into its component sugars. As a result there has been a substantial investment in enzyme technology targeted towards improving the efficiency of plant cell wall degradation. This Chapter provides an overview of our current knowledge of plant cell wall degrading enzymes at a structural and biochemical level. The article also describes strategies that can be deployed to discover novel, industrially significant, enzyme functions, and how protein engineering can be used to increase the catalytic efficiency of some enzymes, and broaden the substrate specificity of others. Finally the Chapter highlights the emerging importance of polysaccharide oxidases in lignocellulosic deconstruction focussing on the role these enzymes play in opening up the structure of crystalline cellulose, explaining how they are capable of potentiating the activity of glycoside hydrolases (cellulases) against these recalcitrant structures.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aachmann FL, Sorlie M, Skjak-Brak G, Eijsink VGH, Vaaje-Kolstad G (2012) NMR structure of a lytic polysaccharide monooxygenase provides insight into copper binding, protein dynamics, and substrate interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:18779–18784
Alhassid A, Ben-David A, Tabachnikov O, Libster D, Naveht E, Zolotnitsky G, Shoham Y, Shoham G (2009) Crystal structure of an inverting GH 43 1,5-alpha-L-arabinanase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus complexed with its substrate. Biochem J 422:73–82
Amano Y, Shiroishi M, Nisizawa K, Hoshino E, Kanda T (1996) Fine substrate specificities of four exo-type cellulases produced by Aspergillus niger, Trichoderma reesei, and Irpex lacteus on (1 → 3), (1 → 4)-β-D-glucans and xyloglucan. J Biochem 120:1123–1129
Armand S, Drouillard S, Schulein M, Henrissat B, Driguez H (1997) A bifunctionalized fluorogenic tetrasaccharide as a substrate to study cellulases. J Biol Chem 272:2709–2713
Bayer EA, Lamed R, Himmel ME (2007) The potential of cellulases and cellulosomes for cellulosic waste management. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:237–245
Beguin P, Aubert JP (1994) The biological degradation of cellulose. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13:25–58
Boraston AB, Bolam DN, Gilbert HJ, Davies GJ (2004) Carbohydrate-binding modules: fine-tuning polysaccharide recognition. Biochem J 382:769–781
Bras JL, Cartmell A, Carvalho AL, Verze G, Bayer EA, Vazana Y, Correia MA, Prates JA, Ratnaparkhe S, Boraston AB, Romao MJ, Fontes CM, Gilbert HJ (2011) Structural insights into a unique cellulase fold and mechanism of cellulose hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:5237–5242
Cantarel BL, Coutinho PM, Rancurel C, Bernard T, Lombard V, Henrissat B (2009) The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucl Acids Res 37:233–238
Cartmell A, Topakas E, Ducros VM, Suits MD, Davies GJ, Gilbert HJ (2008) The Cellvibrio japonicus mannanase CjMan26C displays a unique exo-mode of action that is conferred by subtle changes to the distal region of the active site. J Biol Chem 283:34403–34413
Correia MA, Mazumder K, Bras JL, Firbank SJ, Zhu Y, Lewis RJ, York WS, Fontes CM, Gilbert HJ (2011) Structure and function of an arabinoxylan-specific xylanase. J Biol Chem 286:22510–22520
Cuskin F, Flint JE, Gloster TM, Morland C, Basle A, Henrissat B, Coutinho PM, Strazzulli A, Solovyova AS, Davies GJ, Gilbert HJ (2012) How nature can exploit nonspecific catalytic and carbohydrate binding modules to create enzymatic specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:20889–20894
DeBoy RT, Mongodin EF, Fouts DE, Tailford LE, Khouri H, Emerson JB, Mohamoud Y, Watkins K, Henrissat B, Gilbert HJ, Nelson KE (2008) Insights into plant cell wall degradation from the genome sequence of the soil bacterium Cellvibrio japonicus. J Bacteriol 190:5455–5463
Ding SY, Liu YS, Zeng Y, Himmel ME, Baker JO, Bayer EA (2012) How does plant cell wall nanoscale architecture correlate with enzymatic digestibility? Science 338:1055–1060
Divne C, Stahlberg J, Reinikainen T, Ruohonen L, Pettersson G, Knowles JK, Teeri TT, Jones TA (1994) The three-dimensional crystal structure of the catalytic core of cellobiohydrolase I from Trichoderma reesei. Science 265:524–528
Ducros VM, Zechel DL, Murshudov GN, Gilbert HJ, Szabo L, Stoll D, Withers SG, Davies GJ (2002) Substrate distortion by a β-mannanase: snapshots of the Michaelis and covalent-intermediate complexes suggest a B(2,5) conformation for the transition state. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 41:2824–2827
Fontes CM, Gilbert HJ (2010) Cellulosomes: highly efficient nanomachines designed to deconstruct plant cell wall complex carbohydrates. Annu Rev Biochem 79:655–681
Forsberg Z, Vaaje-Kolstad G, Westereng B, Bunaes AC, Stenstrom Y, MacKenzie A, Sorlie M, Horn SJ, Eijsink VGH (2011) Cleavage of cellulose by a CBM33 protein. Protein Sci 20:1479–1483
Gilad R, Rabinovich L, Yaron S, Bayer EA, Lamed R, Gilbert HJ, Shoham Y (2003) CelI, a noncellulosomal family 9 enzyme from Clostridium thermocellum, is a processive endoglucanase that degrades crystalline cellulose. J Bacteriol 185:391–398
Gilbert HJ, Stalbrand H, Brumer H (2008) How the walls come crumbling down: recent structural biochemistry of plant polysaccharide degradation. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:338–348
Han YJ, Chen HZ (2007) Synergism between corn stover protein and cellulase. Enzyme Microb Technol 41:638–645
Han Y, Dodd D, Hespen CW, Ohene-Adjei S, Schroeder CM, Mackie RI, Cann IK (2010) Comparative analyses of two thermophilic enzymes exhibiting both β-1,4 mannosidic and β-1,4 glucosidic cleavage activities from Caldanaerobius polysaccharolyticus. J Bacteriol 192:4111–4121
Harris PJ, Stone BA (2008) Chemistry and molecular organization of plant cell walls. In: Himmel ME (ed) Biomass recalcitrance: deconstructing the plant cell wall for bioenergy. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 60–93
Harris PV, Welner D, McFarland KC, Re E, Poulsen J-CN, Brown K, Salbo R, Ding H, Vlasenko E, Merino S, Xu F, Cherry J, Larsen S, Lo Leggio L (2010) Stimulation of lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis by proteins of glycoside hydrolase family 61: structure and function of a large, enigmatic family. Biochemistry 49:3305–3316
Himmel ME, Bayer EA (2009) Lignocellulose conversion to biofuels: current challenges, global perspectives. Curr Opin Biotechnol 20:316–317
Hogg D, Woo EJ, Bolam DN, McKie VA, Gilbert HJ, Pickersgill RW (2001) Crystal structure of mannanase 26A from Pseudomonas cellulosa and analysis of residues involved in substrate binding. J Biol Chem 276:31186–31192
Irwin D, Shin DH, Zhang S, Barr BK, Sakon J, Karplus PA, Wilson DB (1998) Roles of the catalytic domain and two cellulose binding domains of Thermomonospora fusca E4 in cellulose hydrolysis. J Bacteriol 180:1709–1714
Kleywegt GJ, Zou JY, Divne C, Davies GJ, Sinning I, Stahlberg J, Reinikainen T, Srisodsuk M, Teeri TT, Jones TA (1997) The crystal structure of the catalytic core domain of endoglucanase I from Trichoderma reesei at 3.6 Å resolution, and a comparison with related enzymes. J Mol Biol 272:383–397
Koivula A, Kinnari T, Harjunpaa V, Ruohonen L, Teleman A, Drakenberg T, Rouvinen J, Jones TA, Teeri TT (1998) Tryptophan 272: an essential determinant of crystalline cellulose degradation by Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolase Cel6A. FEBS Lett 429:341–346
McKee LS, Pena MJ, Rogowski A, Jackson A, Lewis RJ, York WS, Krogh KB, Vikso-Nielsen A, Skjot M, Gilbert HJ, Marles-Wright J (2012) Introducing endo-xylanase activity into an exo-acting arabinofuranosidase that targets side chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:6537–6542
McKie VA, Black GW, Millward-Sadler SJ, Hazlewood GP, Laurie JI, Gilbert HJ (1997) Arabinanase A from Pseudomonas fluorescens subsp. cellulosa exhibits both an endo- and an exo- mode of action. Biochem J 323:547–555
McQueen-Mason S, Cosgrove DJ (1994) Disruption of hydrogen bonding between plant cell wall polymers by proteins that induce wall extension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:6574–6578
Mohnen D (2008) Pectin structure and biosynthesis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:266–277
Mohnen D, Bar-Peled M, Somerville C (2008) Biosynthesis of plant cell walls. In: Himmel ME (ed) Biomass recalcitrance: deconstructing the plant cell wall for bioenergy. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 94–187
Montanier C, van Bueren AL, Dumon C, Flint JE, Correia AM, Prates JA, Firbank SJ, Lewis RJ, Grondin GG, et al (2009) Evidence that family 35 carbohydrate binding modules display conserved specificity but divergent function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:3065–3070
Montanier CY, Correia MA, Flint JE, Zhu Y, Basle A, McKee LS, Prates JA, Polizzi SJ, Coutinho PM, Lewis RJ, Henrissat B, Fontes CM, Gilbert HJ (2011) A novel, noncatalytic carbohydrate-binding module displays specificity for galactose-containing polysaccharides through calcium-mediated oligomerization. J Biol Chem 286:22499–22509
Nurizzo D, Turkenburg JP, Charnock SJ, Roberts SM, Dodson EJ, McKie VA, Taylor EJ, Gilbert HJ, Davies GJ (2002) Cellvibrio japonicus α-L-arabinanase 43A has a novel five-blade β-propeller fold. Nat Struct Biol 9:665–668
Peña MJ, Zhong R, Zhou GK, Richardson EA, O’Neill MA, Darvill AG, York WS, Ye ZH (2007) Arabidopsis irregular xylem8 and irregular xylem9: implications for the complexity of glucuronoxylan biosynthesis. Plant Cell 19:549–563
Proctor MR, Taylor EJ, Nurizzo D, Turkenburg JP, Lloyd RM, Vardakou M, Davies GJ, Gilbert HJ (2005) Tailored catalysts for plant cell-wall degradation: redesigning the exo/endo preference of Cellvibrio japonicus arabinanase 43A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2697–2702
Quinlan RJ, Sweeney MD, Lo Leggio L, Otten H, Poulsen JC, Johansen KS, Krogh KBRM, Jorgensen CI, Tovborg M, Anthonsen A, Tryfona T, Walter CP, Dupree P, Xu F, Davies GJ, Walton PH (2011) Insights into the oxidative degradation of cellulose by a copper metalloenzyme that exploits biomass components. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:15079–15084
Ragauskas AJ, Williams CK, Davison BH, Britovsek G, Cairney J, Eckert CA, Frederick WJ Jr, Hallett JP, Leak DJ, Liotta CL, Mielenz JR, Murphy R, Templer R, Tschaplinski T (2006) The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials. Science 311:484–489
Reese ET, Siu RG, Levinson HS (1950) The biological degradation of soluble cellulose derivatives and its relationship to the mechanism of cellulose hydrolysis. J Bacteriol 59:485–497
Rouvinen J, Bergfors T, Teeri T, Knowles JK, Jones TA (1990) Three-dimensional structure of cellobiohydrolase II from Trichoderma reesei. Science 249:380–386
Sakon J, Irwin D, Wilson DB, Karplus PA (1997) Structure and mechanism of endo/exocellulase E4 from Thermomonospora fusca. Nat Struct Biol 4:810–818
Sorensen HR, Jorgensen CT, Hansen CH, Jorgensen CI, Pedersen S, Meyer AS (2006) A novel GH43 α-L-arabinofuranosidase from Humicola insolens: mode of action and synergy with GH51 α-L-arabinofuranosidases on wheat arabinoxylan. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:850–861
Sticklen MB (2008) Plant genetic engineering for biofuel production: towards affordable cellulosic ethanol. Nat Rev Genet 9:433–443
Tailford LE, Ducros VM, Flint JE, Roberts SM, Morland C, Zechel DL, Smith N, Bjornvad ME, Borchert TV, Wilson KS, Davies GJ, Gilbert HJ (2009) Understanding how diverse β-mannanases recognize heterogeneous substrates. Biochemistry 48:7009–7018
Tomme P, Warren RA, Gilkes NR (1995) Cellulose hydrolysis by bacteria and fungi. Adv Microb Physiol 37:1–81
Teeri TT (1997) Crystalline cellulose degradation: New insight into the function of cellobiohydrolases. Trends Biotechnol 15:160–167
Tolonen AC, Chilaka AC, Church GM (2009) Targeted gene inactivation in Clostridium phytofermentans shows that cellulose degradation requires the family 9 hydrolase Cphy3367. Mol Microbiol 74:1300–1313
Urbanowicz BR, Pena MJ, Ratnaparkhe S, Avci U, Backe J, Steet HF, Foston M, Li H, O’Neill MA, Ragauskas AJ, Darvill AG, Wyman C, Gilbert HJ, York WS (2012) 4-O-methylation of glucuronic acid in Arabidopsis glucuronoxylan is catalyzed by a domain of unknown function family 579 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:14253–14258
Vaaje-Kolstad G, Horn SJ, van Aalten DMF, Synstad B, Eijsink VGH (2005) The non-catalytic chitin-binding protein CBP21 from Serratia marcescens is essential for chitin degradation. J Biol Chem 280:28492–28497
Vaaje-Kolstad G, Westereng B, Horn SJ, Liu Z, Zhai H, Sorlie M, Eijsink VGH (2010) An oxidative enzyme boosting the enzymatic conversion of recalcitrant polysaccharides. Science 330:219–222
Vaaje-Kolstad G, Bohle LA, Gaseidnes S, Dalhus B, Bjoras M, Mathiesen G, Eijsink VGH (2012) Characterization of the chitinolytic machinery of Enterococcus faecalis V583 and high-resolution structure of its oxidative CBM33 enzyme. J Mol Biol 416:239–254
van den Broek LA, Lloyd RM, Beldman G, Verdoes JC, McCleary BV, Voragen AG (2005) Cloning and characterization of arabinoxylan arabinofuranohydrolase-D3 (AXHd3) from Bifidobacterium adolescentis DSM20083. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:641–647
Varrot A, Schulein M, Davies GJ (1999) Structural changes of the active site tunnel of Humicola insolens cellobiohydrolase, Cel6A, upon oligosaccharide binding. Biochemistry 38:8884–8891
Weiner RM, Taylor LE 2nd, Henrissat B, Hauser L, Land M, Coutinho PM, Rancurel C, Saunders EH, Longmire AG, Zhang H, Bayer EA, Gilbert HJ, Larimer F, Zhulin IB, Ekborg NA, Lamed R, Richardson PM, Borovok I, Hutcheson S (2008) Complete genome sequence of the complex carbohydrate-degrading marine bacterium, Saccharophagus degradans strain 2-40 T. PLoS Genet 4:e1000087
Xie G, Bruce DC, Challacombe JF, Chertkov O, Detter JC, Gilna P, Han CS, Lucas S, Misra M, Myers GL, Richardson P, Tapia R, Thayer N, Thompson LS, Brettin TS, Henrissat B, Wilson DB, McBride MJ (2007) Genome sequence of the cellulolytic gliding bacterium Cytophaga hutchinsonii. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3536–3546
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media New York
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Gilbert, H.J. (2014). Developing Novel Enzyme Repertoires for the Efficient Deconstruction of Plant Biomass Tailored for the Bioenergy Industry. In: McCann, M., Buckeridge, M., Carpita, N. (eds) Plants and BioEnergy. Advances in Plant Biology, vol 4. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-9329-7_12
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-9329-7_12
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-9328-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-9329-7
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)