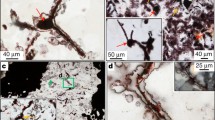
Abstract
Microbial life in hot and cold desert environments inhabits endolithic niches. The endolithic microorganisms include bacteria, fungi and lichens. To protect themselves from the inhospitable conditions, such as high UV radiation, dryness, and rapid temperature variations, microorganisms migrate into fractures or in pore spaces where the necessary nutrient, moisture, and light are sufficient for survival. Examples of endolithic communities are well documented from the Negev Desert, Antarctica and the Artic regions, and the Atacama Desert. The most common substrates are porous, crystalline sandstones with calcium carbonate cements and sulfate (gypsum) and other evaporite mineral crusts. The detection of sulfate on the Martian surface has sparked off considerable interest in the astrobiological potential of the evaporite deposits of continental environments, which may potentially host (or may have hosted) endolithic microorganisms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ascaso, C. and Wierzchos, J. (2002) New approaches to the study of Antarctic lithobiontic microorganisms and their inorganic traces, and their application in the detection of life in Martian rocks. Int. Microbiol. 5, 215–222.
Ascaso, C. and Wierzchos, J. (2003) The search for biomarkers and microbial fossils in Antarctic rocks microhabitats. Geomicrobiol. J. 20, 439–450.
Banerjee, M., Whitton, B.A. and Wynn Williams, D.D. (2000) Phosphatase activities of endolithic communities on rocks of the Antarctic Dry Valleys. Microb. Ecol. 39, 89–91.
Barbieri, R., Stivaletta, N., Marinangeli, L. and Ori, G.G. (2006) Microbial signatures in sabkha evaporite deposits of Chott el Gharsa (Tunisia) and their astrobiological implications. Planet. Space Sci. 54, 726–736.
Bell, R.A. (1993) Cryptoendolithic algae of hot semie lands and deserts. J. Phycol. 29, 133–139.
Bell, R.A., Athey, P.V. and Sommerfield, M.R. (1983) Preliminary observations on an endolithic alga of northwestern Arizona. J. Phycol. (Suppl.) 19, 7.
Bell, R.A., Athey P.V. and Sommerfield, M.R. (1986) Cryptoendolithic algal communities of the Colorado Plateau. J. Phycol. 22, 429–435.
Bridges, J.C. and Grady, M.M. (2000) Evaporite mineral assemblages in the nakhlite (Martian) meteorites. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 176, 267–279.
Campbell, S.E. (1982) Precambrian endoliths discovered. Nature 299, 429–431.
Cockell, C.S. (2000) The ultraviolet history of the terrestrial planet-implications for biological evolution. Planet. Space Sci. 48, 203–214.
Connon, S.A., Lester, E.D., Shafaat, H.S., Obenhuber, D.C. and Ponce, A. (2007) Bacterial diversity in hyperarid Atacama Desert soils. J. Geophys. Res. 112, G04S17.
Cowan, D.A. and Ah Tow, L. (2004) Endangerd Antarctic environments. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 58, 649–690.
Critchley, A.T., Wood, J., Horiguchi, T. and Bruton, A.G. (1987) An ultrastructural insight into a cryptoendolithic community. Proc. Electr. Microsc. Soc. S. Afr. 17, 101–102.
de la Torre, J.R., Goebel, B.M., Friedmann, I., Pace, N.R. (2003) Microbial diversity of cryptoendolithic communities from Mc Murdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 3858–3867.
Pade los Rios, A., Wierzchos, J., Sancho, L.G., Ascaso, C. (2003) Acid microenvironments in microbial biofilms of Antarctic endolithic microecosystems. Environ. Microb. 5, 231–237.
de los Rios, A., Wierzchos, J., Sancho, L.G., Ascaso, C. (2004) Exploring the physiological state of continental Antarctic endolithic microorganisms by microscopy. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 50, 143–152.
Dong, H., Rech, J.A., Jiang, H., Sun, H. and Buck, B.J. (2007) Endolithic cyanobacteria in soil gypsum: occurrences in Atacama (Chile), Mojave (United States), and Al-Jafr Basin (Jordan) Deserts. J. Geophys. Res. 112, G02030.
Dose, K., Bieger-Dose, A., Birgit, E., Feister, U., Gomez-Silva, B., Klein, A., Risi, S. and Stride, C. (2001) Survival of microorganisms under the extreme conditions of the Atacama Desert. Origins Life Evol. B., Springer Netherlands Publisher, 31, 287–303.
Douglas, S. and Yang, H. (2002) Microbial signatures in evaporites: presence of rosickyte in an endoevaporitic microbial community from Death Valley. California. Geology 30, 1075–1078.
Drees, K.P., Neilson, J.W, Betancourt, J.L., Quade, J., Henderson, D.A., Pryor, B.M., Maier, R.M. (2006) Bacterial Community Structure in the Hyperarid Core of the Atacama Desert, Chile. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72, 7902–7908.
Friedmann, E.I. (1971) Light and scanning electron microscopy of endolithic desert algal habitat. Phycologia 10, 411–428.
Friedmann, E.I. (1972) Ecology of lithophytic algal habitats in Middle Eastern and North America Desert. In: L.E. Rodin (ed.) Ecophysiological Foundation of Ecosystems Productivity in Arid Zone. U.S.S.R. Academy of Science, Nauka, Leningrad, pp 182–185.
Friedmann, E.I. (1980) Endolithic microbial life in hot and cold deserts. Origins Life 10, 223–235.
Friedmann, E.I. (1982) Endolithic microorganisms in the Antarctic cold desert. Science 215, 1045–1053.
Friedmann, E.I. and Galun, M. (1974) Desert algae, lichens, and fungi. In: G.W Brown (ed.) Desert Biology, Vol II. Academic, New York, pp 165–203.
Friedmann, E.I. and Koriem, A.M. (1989) Life on Mars: how it disappeared (if it was ever there). Adv. Space Res. 9, 167–172.
Friedmann, E.I. and Ocampo, R. (1976) Endolithic blue-green algae in the dry Valley: primary producers in the Antarctic desert ecosystem. Science 193, 1247–1249.
Friedmann, E.I. and Ocampo-Friedmann, R. (1984) Endolithic microorganisms in extreme dry environments: analysis of lithobiontic microbial habitat. In: M.J. Klug and LA. Reddy (eds.) Current Perspectivies in Microbial Ecology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 177–185.
Friedmann, I.E. and Ocampo-Friedmann, R. (1995) A primitive cyanobacterium as pioneer microorganism for Terraforming Mars. Adv. Space Res. 15, 243–246.
Friedmann, E.I. and Weed, R. (1987) Microbial trace-fossil formation, biogenous, and abiotic weat-hering in the Antarctic cold desert. Science 236, 703–705.
Friedmann, E.I., Lipkin, Y. and Ocampo-Paus, R. (1967) Desert algae of the Negev (Israel). Phycologia 6, 185–200.
Friedmann, E.I., Mckay, C.P. and Niewon, J.A. (1987) The cryptoendolithic microbial environment in the Ross Desert of Antarctica: continuous nanoclimate data, 1984–1986. Polar Biol. 7, 273–287.
Friedmann, E.I., Hua, M. and Ocampo-Friedmann, R. (1988) Cryptoendolithic lichen and cyanobacterial communities of the Ross Desert, Antarctica. Polarforschung 58, 251–259.
Gendrin, A., Mangold, N., Bibring, J.-R, Langevin, Y., Gondet, B., Poulet, F., Bonello, G., Quantin, C., Mustard, J., Arvidson, R. and LeMouelic, S. (2005) Sulfates in Martian layered terrains: the OMEGA/Mars Express view. Science 307, 1587–1591.
Gerdes, G., Krumbrein, W.E. and Noffke, N. (2000) Evaporite microbial sediment. In: R.E. Riding and S.M. Awramik (eds.) Microbial Sediments. Berlin/Heidelberg, Springer, pp 196–207.
Golubic, S., Friedmann, I. and Schneider, J. (1981) The lithobiontic ecological niche, with special reference to microorganisms. J. Sediment. Petrol. 51, 0475–0478.
Gooding, J.L. (1992) Soil mineralogy and chemistry on Mars: possible clues from salt and clays in SNC meteorites. Icarus 99, 28–41.
Grant, W.D., Gemmell, R.T. and Mcgenity, T.J. (1998) Halophiles. In: K. Horikoshi and W.D. Grant (eds.) Extremophiles: Microbial Life in Extreme Environments. Wiley Series in Ecological and Applied Microbiology, Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 93–132.
Hirsch, P., Hoffmann, B., Gallikowsky, C.C., Mevs, U., Siebert, J. and Sittig, M. (1988) Diversity and identification of heterotrophs from Antarctic rocks of the McMurdo Dry Valleys (Ross Desert). Polarforschung 58, 261–269.
Horowitz, N.H., Cameron, R.E. and Hubbard, J.S. (1972) Microbiology of the Dry Valleys of Antarctica. Antarctic. Sci. 176, 242–245.
Hughes, K.A. and Lawley, B. (2003) A novel Antarctic microbial endolithic community within gypsum crusts. Environ. Microbiol. 5, 555–565.
Ionescu, D., Lipski, A., Altendorf, K. and Oren, A. (2007) Characterization of the endoevaporitic microbial communities in a hypersaline gypsum crust by fatty acid analysis. Hydrobiologia 576, 15–26.
Kminek, G., Bada, J.L., Pogliano, K. and Ward, J.F. (2003) Radiation-dependent limit for the viability of bacterial spores in halite fluid inclusions and on Mars. Radiat. Res. 159, 722–729.
Knoll, A.H., Golubic, S., Grenn, J. and Sweet, K. (1986) Organically preserved microbial endoliths from the Late Proterozoic of East Greenland. Nature 321, 856–857.
Krumbein, W.E., Gorbushina, A.A. and Holtkamp-Tacken, E. (2004) Hypersaline microbial systems of sabkhas: examples of life’s survival in “extreme” conditions. Astrobiology 4, 450–459.
Lange, O.L., Kilian, E. and Ziegler, H. (1986) Water vapor uptake and photosynthesis of lichens: performance differences in species with green and blue-green algae as phycobionts. Oecologia 71, 104–110.
Langevin, Y., Poulet, F., Bibring, J.-P. and Gondet, B. (2005) Sulfates in the North Polar region of Mars detected by OMEGA/Mars Express. Science 307, 1584–1586.
Madigan, M.T., Martinko, J.M. and Parker, J. (2003) Brock Biology of Microorganisms. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ (tenth edition).
Maier, R.M., Drees, K.P., Neilson, J.W., Henderson, D.A., Quade, J. and Betancourt, J.L. (2004) Microbial life in Atacama Desert. Science 306, 1289–1290.
McKay, C.P., Friedmann, E.I., Warthon, R.A. and Davies, W.L. (1992) History of water on Mars: a biological perspective. Adv. Space Res. 12, 231–238.
McKay, C.P., Friedmann, E.I., Gomez-Silva, B., Caceres Villanueva, L., Andersen Dale, T. and Landheim, R. (2003) Temperature and moisture conditions for life in the extreme arid region of the Atacama Desert: four years of observations including the El Nino of 1997–1998. Astrobiology 3, 393–406.
McLennan, S.M., Bell, J.F. III, Calvin, W.M., et al. (2005) Provenance and diagenesis of the evaporite-bearing Burns formation, Meridiani planum, Mars. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett 240, 95–121.
Navarro-Gonzãles, R., Rainey, F.A., Molina, P., Bagaley, D.R., Hollen, B.J., de la Rosa, J., Small, A.M., Quinn, R.C., Grunthaner, F.J., Caceres, L., Gomez-Silva, B. and McKay, C.P. (2003) Mars-like soils in the Atacama Desert, Chile, and the dry limit of microbial life. Science 302, 1018–1021.
Nienow, J.A., McKay C.P. and Friedamnn, E.I. (1988a) The cryptoendolithic microbial environment in the Ross Desert of Antarctica: mathematical models of the thermal regime. Microb. Ecol. 16, 253–270.
Nienow, J.A., McKay, C.P. and Friedamnn, E.I. (1988b) The cryptoendolithic microbial environment in the Ross Desert of Antarctica: light in the photosynthetically active region. Microb. Ecol. 16, 271–289.
Omelon, C.R., Pollard, W.H. and Ferris, F.G. (2006a) Chemical and ultrastructural characterization of high Artic cryptoendolithic habitats. Geomicrobiol. J. 23, 189–200.
Omelon, C.R., Wayne, H.P. and Ferris, F.G. (2006b) Environmental controls on microbial colonization of high Arctic cryptoendolithic habitats. Polar Biol. 30, 19–29.
Onofri, S., Selbmann, L., Zucconi, L. and Pagano, S. (2004) Antarctic microfungi as models for exobiology. Planet. Space Sci. 52, 229–237.
Oren, A., Kuhl, M. and Karsten, U. (1995) An endevaporitic microbial mat within a gypsum crust: zonation of phototrophs, photopigments, and light penetration. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 128, 151–159.
Palmer, R.J. and Friedmann, E.I. (1990) Water relations and photosynthesis in the cryptoendolithic microbial habitat of hot and cold deserts. Micro. Ecol. 19, 111–118.
Pointing, S.B., Kimberley, A.W., Lacap, D.C., Rhodes, K.L. and McKay, C.P. (2007) Hypolithic community shifts occur as a result of liquid water availability along environmental gradients in China’s hot and cold hyperarid deserts. Env. Microbiol. 9, 414–424.
Potts, M. (1994) Dessication tolerance of prokaryotes. Microbiol. Rev. 58, 755–805.
Potts, M. and Friedmann, E.I. (1981) Effects of water stress on Cryptoendolihic cyanobacteria from hot desert rocks. Arch. Microbiol. 130, 267–271.
Rodriguez-Valera, F., Ruiz-Berraquero, F. and Ramos-Cormenzana, A. (1981) Characteristics of the heterotrophic bacterial populations in hypersaline environments of different salt concentrations. Microb. Ecol. 7, 235–243.
Satterfield, C.L., Lowenstein, T.K., Vreeland, R.H., Rosenzweig, W.D. and Powers, D.W. (2005) New evidence for 250 Ma age of halotolerant bacterium from a Permian salt crystal. Geology 33, 265–268.
Sawyer, D.J., McGehee, M.D., Canepa, J. and Moore, C.B. (2000) Water soluble ions in the Nakhla Martian meteorites. Meteoritics & Planet. Sci 35, 743–747.
Siebert, J. and Hirsch, P. (1988) Characterization of 15 selected coccal bacteria isolated from Antarctica rock and soil samples from the McMurdo-Dry Valleys (South Victoria Land). Polar Biol. 9, 37–44.
Siebert, J., Hirsch, P., Hoffmann, B., Gliesche, C.G., Peissl, K. and Jendrach, M. (1996) Biodivers. Conserv. 5, 1337–1363.
Squyres, S.W., Arvidson, R.E., Bell, J.F. III, et al. (2004) The Spirit Rover’s Athena Science Investigation at Gusev crater, Mars. Science 35, 794–799.
Sun, H.J. and Friedmann, E.I. (1999) Growth on geological time scales in the Antarctic cryptoendolithic microbial community. Geomicrobiol. J. 16, 193–202.
Treiman, A.H., Gleason, J.D. and Bogard, D.D. (2000) The SNC meteorites are from Mars. Planet. Space Sci. 48, 1213–1230.
Vaniman, D.T., Bish, D.L., Chipera, S.J., Fialips, C.I., Carey, J.W. and Feldman, W.C. (2004) Magnesium sulphate salts and the history of water on Mars. Nature 431, 663–665.
Vestal, J.R. (1988) Carbon metabolism in the cryptoendolithic microbiota in the Antarctic desert. Appl. Environm. Microbiol. 54, 960–965.
Villar, S.E.J., Edwards, H.G.M. and Cockell, C.S. (2005) Raman spectroscopy of endoliths from Antarctic cold desert environments. Analyst 130, 156–162.
Vreeland, R.H., Rosenzweig, W.D. and Powers, D.W. (2000) Isolation of a 250 million-year-old halotolerant bacterium from a primary salt crystal. Nature 407, 897–900.
Walker, J. and Pace, N.R. (2007) Endolithic microbial ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 61, 331–347.
Warren-Rhodes, K.A., Rhodes, K.L., Pointing, S.B., Ewing, S., Lacap, D.C., Gomez-Silva, B., Amundson, R., Friedmann, E.I. and McKay, C.P. (2006) Hypolithic cyanobacteria, dry limit of photosynthesis and microbial ecology in the hyperarid Atacama Desert. Microb. Ecol 52, 389–398.
Wierzchos, J. and Ascaso, C. (2001) Life, decay and fossilzation of endolithic microorganisms from the Ross Desert, Antartctica. Polar Biol. 24, 863–86
Wierzchos, J. and Ascaso, C. (2002) Microbial fossil record of rocks from the Ross Desert, Antarctica: implications in the search for past life on Mars. Int. J. Astrobiology 1, 51–59.
Wierzchos, J., Ascaso, C., Rancho, L.G. and Green, A. (2003) Iron-rich diagenetic minerals are biomarkers of microbial activity in Antarctic rocks. Geomicrobiol. J. 20, 15–24.
Wierzchos, J., De Los Rios, A., Sancho, L.G., Ascaso, C. (2004) Viability of endolithic microorganisms in rocks from McMurdo Dry Valley of Antarctica established by confocal and fluorescence microscopy. J. Microscopy 216, 57–61.
Wierzchos, J., Sancho, L.G. and Ascaso, C. (2005) Biomineralization of endolithic microbes in rocks from the Mcmurdo Dry Valleys of Antarctica: implications for microbial fossil formation and their detection. Environm. Microbiol. 7, 566–575.
Wierzchos, J., Ascaso, C. and McKay, C.P. (2006) Endolithic Cyanobacteria in Halite Rocks from the Hyperarid Core of the Atacama Desert. Astrobiology 6, 415–422.
Wynn-Williams, D.D. and Edwards, H.G.M. (2000) Antarctic ecosystems as model for extraterrestrial surface habitats. Planet. Space Sci. 48, 1065–1075.
Wynn-Williams, D.D., Edwards, H.G.M., Newton, E.M. and Holder J.M. (2002) Pigmentation as a survival strategy for ancient and modern photosynthetic microbes under high ultraviolet stress on planetary surface. Int. J. Astrobiology 1, 39–49.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer Science + Business Media B.V
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Stivaletta, N., Barbieri, R. (2009). Endoliths in Terrestrial Arid Environments: Implications for Astrobiology. In: Seckbach, J., Walsh, M. (eds) From Fossils to Astrobiology. Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology, vol 12. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8837-7_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8837-7_15
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-8836-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-8837-7
eBook Packages: Physics and AstronomyPhysics and Astronomy (R0)