Abstract
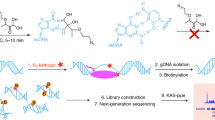
R-loops are three-stranded nucleic acid structures that consist of a DNA–RNA hybrid and a displaced single-stranded DNA. R-loops occur during transcription and participate in multiple physiological processes such as DNA repair, modulating DNA topology, and regulation of gene transcription. Dysfunctional R-loops associate with several human diseases such as neurological disorders and cancer. Therefore, accurately and comprehensively profiling native R-loops is crucial to understand their functions under both physiological and pathological conditions. Here, we describe a convenient native R-loop profiling method, R-loop CUT&Tag, which combines a DNA–RNA hybrid sensor (GST-His6–2 × HBD or S9.6 antibody) with a pA-Tn5-based cleavage under targets and tagmentation approach. R-loop CUT&Tag starts with 0.5 million cells and can sensitively detect native and specific R-loops at the promoter, gene body, and enhancer regions.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia-Muse T, Aguilera A (2019) R loops: from physiological to pathological roles. Cell 179(3):604–618
Aguilera A, Garcia-Muse T (2012) R loops: from transcription byproducts to threats to genome stability. Mol Cell 46(2):115–124
Marnef A, Legube G (2021) R-loops as Janus-faced modulators of DNA repair. Nat Cell Biol 23(4):305–313
Wang K, Wang H, Li C et al (2021) Genomic profiling of native R loops with a DNA-RNA hybrid recognition sensor. Sci Adv 7(8):eabe3516
Skourti-Stathaki K, Proudfoot NJ (2014) A double-edged sword: R loops as threats to genome integrity and powerful regulators of gene expression. Genes Dev 28(13):1384–1396
Crossley MP, Bocek M, Cimprich KA (2019) R-loops as cellular regulators and genomic threats. Mol Cell 73(3):398–411
Santos-Pereira JM, Aguilera A (2015) R loops: new modulators of genome dynamics and function. Nat Rev Genet 16(10):583–597
Sanz LA, Hartono SR, Lim YW et al (2016) Prevalent, dynamic, and conserved R-loop structures associate with specific Epigenomic signatures in mammals. Mol Cell 63(1):167–178
Yan Q, Shields EJ, Bonasio R et al (2019) Mapping native R-loops genome-wide using a targeted nuclease approach. Cell Rep 29(5):1369–80 e5
Chen L, Chen JY, Zhang X et al (2017) R-ChIP using inactive RNase H reveals dynamic coupling of R-loops with transcriptional pausing at gene promoters. Mol Cell 68(4):745–57 e5
Kaya-Okur HS, Wu SJ, Codomo CA et al (2019) CUT&Tag for efficient epigenomic profiling of small samples and single cells. Nat Commun 10(1):1930
Wang Q, Xiong H, Ai S et al (2019) CoBATCH for high-throughput single-cell epigenomic profiling. Mol Cell 76(1):206–16 e7
Lu B, Dong L, Yi D et al (2020) Transposase-assisted tagmentation of RNA/DNA hybrid duplexes. elife 9:e54919
Carter B, Ku WL, Kang JY et al (2019) Mapping histone modifications in low cell number and single cells using antibody-guided chromatin tagmentation (ACT-seq). Nat Commun 10(1):3747
Di L, Fu Y, Sun Y et al (2020) RNA sequencing by direct tagmentation of RNA/DNA hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117(6):2886–2893
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China Stem Cell and Translational Research (NO. 2019YFA0111100), NSFC Excellent Young Scientists Fund (82122006), and the China National Natural Science Foundation (82172641) awarded to K.L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Wang, H., Li, C., Liang, K. (2022). Genome-Wide Native R-Loop Profiling by R-Loop Cleavage Under Targets and Tagmentation (R-Loop CUT&Tag). In: Aguilera, A., Ruzov, A. (eds) R-Loops . Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2528. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2477-7_23
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-2477-7_23
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-2476-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-2477-7
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols