Abstract
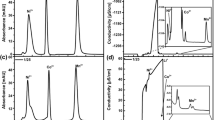
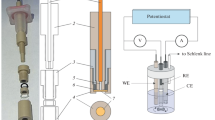
Flow systems for precise and accurate coulometric determinations of ions that were developed on the basis of electrolytic ion transfer at the aqueous|organic solution (W | O) interface are reviewed. The electrolysis cell in the system is composed of a porous poly(tetrafluoroethylene) tube (1.0 mm inner diameter), a metal wire (0.8 mm diameter) inserted into the tube, O into which the tube is immersed, a reference electrode in O and a platinum wire counter electrode in O. The electrolysis is carried out by forcing W containing a species of interest to flow through the narrow gap between the tube and the metal wire. The coulometric determination can be performed with an efficiency of more than 99% and a precision of better than 0.2% based on the ion transfer under an optimum condition, even if the ion is redox inert such as Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, ClO4–, picrate or alkylsulfonates. The system can be applied to selective electrolytic solvent extraction of ions.
Similar content being viewed by others
6 References
L. Szebelledy and Z. Somogyi, Z Anal. Chem., 1938, 112, 313.
J. J. Lingane, J. Am. Chem. Soc, 1945, 67, 1916.
P. Delahay, “New Instrumental Methods in Electrochemistry”, 1954, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 267.
A. J. Bard and K. S. V. Santhanam, “Electroanalytical Chemistry”, ed. A. J. Bard, 1970, Vol. 4, Marcel Dekker, New York, 215.
D. T. Sawyer and J. L. Roberts, Jr., “Experimental Electrochemistry for Chemists”, 1974, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 419.
S. Kihara, Z. Yoshida, H. Aoyagi, K. Maeda, O. Shirai, Y Kitatsuji, and Y Yoshida, Pure Appl. Chem., 1999, 71, 1771.
A. J. Bard and L. R. Faulkner, “Electrochemical Methods, Fundamentals and Applications”, 2nd ed., 2001, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 417.
Y Kitatsuji, Z. Yoshida, H. Kudo, and S. Kihara, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2002, 520, 133.
S. Sawada, M. Taguma, T. Kimoto, H. Hotta, and T. Osakai, Anal. Chem., 2002, 74, 1177.
A. Yoshizumi, A. Uehara, M. Kasuno, A. Kitatsuji, Z. Yoshida, and S. Kihara, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2005, 581, 275.
T. Okugaki, Y Kitatsuji, M. Kasuno, A. Yoshizumi, H. Kubota, Y Shibafuji, K. Maeda, Z. Yoshida, and S. Kihara, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2009, 629, 50.
M. Kasuno, Y Kakitani, Y Shibafuji, T. Okugaki, K. Maeda, T. Matsushita, and S. Kihara, Electroanalysis, 2009, 21, 2022.
E. Gohara and T. Osakai, Anal. Sci., 2010, 26, 375.
E. Grygolowicz-Pawlak and E. Bakker, Anal. Chem., 2010, 82, 4537.
M. Kasuno, K. Fujimoto, Y Kakitani, T. Matsushita, and S. Kihara, J. Electroanal. Chem., in press.
H. H. J. Girault and D. J. Schiffrin, “Electroanalytical Chemistry”, ed. A. J. Bard, 1989, Vol. 15, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1.
A. G. Volkov and D. W Deamer (ed.), “Liquid-Liquid Interfaces”, 1996, Theory and Methods, CRC Press, Boca Raton.
A. G. Volkov (ed.), “Liquid Interfaces in Chemical, Biological, and Pharmaceutical Applications”, 2001, Marcel Dekker, New York.
D. T. Sawyer and J. L. Roberts, Jr., “Experimental Electrochemistry for Chemists”, 1974, John Wiley and Sons, New York, 149.
S. Kihara and Z. Yoshida, Talanta, 1984, 31, 789.
M. Suzuki, M. Matsui, and S. Kihara, J. Electroanal. Chem., 1997, 420, 119.
Y Yoshida, Z. Yoshida, H. Aoyagi, Y Kitatsuji, A. Uehara, and S. Kihara, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2002, 452, 149.
A. J. Parker, Chem. Rev., 1969, 69, 1.
Y Yoshida, M. Matsui, O. Shirai, K. Maeda, and S. Kihara, Anal. Chim. Acta, 1998, 373, 213.
M. Kasuno, A. Uehara, N. Ichieda, T. Kitano, and S. Kihara, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2005, 579, 223.
Z. Samec and P. Papoff, Anal. Chem., 1990, 62, 1010.
T. Fujinaga and S. Kihara, CRC Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem., 1977, 6, 223.
W.-R. Külpmann, P. Lehmann, and H.-K. Strummvoll, “Electrolytes, Acid-Base Balance and Blood Gases: Clinical Aspects and Laboratory ”, 2007, 2nd enlarged and rev. ed., Springer, Wien.
Q. J. Wan, P. Kubáñ, J. Tanyanyiwa, A. Rainelli, and P. C. Hauser, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2004, 525, 11.
V Rumenjak, S. Milardovi, I. Kruhak, and B. S. Grabaric, Clin. Chim. Acta, 2003, 335, 75.
L. R. Morss, N. M. Edelstein, and J. Fuger (ed.), “The Chemistry of the Actinide and Transactinide Elements”, 3rd ed., 2006, Chaps. 6 and 7, Springer, Netherlands.
K. Motojima, T. Yamamoto, and Y Kato, Bunseki Kagaku, 1969, 18, 208.
T. Y Toribara, D. A. Morken, and C. Predmore, Talanta, 1963, 10, 205.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kihara, S., Kasuno, M. Rapid and Precise Coulometric Determination and Separation of Redox Inert Ions Based on Electrolysis for Ion Transfer at the Aqueous|Organic Solution Interface. ANAL. SCI. 27, 1–11 (2011). https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.27.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.27.1