Abstract
Background
Breast cancer subtypes, distinguished by hormone receptor (HR) and HER2 status, have different clinicopathologic features. With recognition of the clinical relevance of HER2-low, there is debate as to whether this is a distinct subtype. Our study aimed to determine whether HER2-low breast cancers have specific clinicopathologic features that differ from those of HER2-negative and HER2-positive cancers.
Patients and Methods
A total of 11,072 patients undergoing upfront surgery from 1998 to 2010 were identified from a single-institution prospectively maintained database. HER2 status was classified by immunohistochemistry (IHC)/fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) as HER2 negative (41.2%), HER2 low (45%; IHC 1+ or 2+ with negative FISH), and HER2 positive (13.7%), and stratified by HR status. Univariate (UVA) and multivariable multinomial logistic regression analysis (MVA) were performed to determine associations among variables and subtypes.
Results
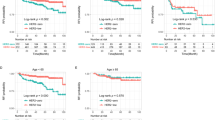
Compared with HER2-negative tumors, HER2 low was associated with lymphovascular invasion [odds ratio (OR) 1.2, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.06–1.36; p = 0.003], multifocality (OR 1.26, 95% CI 1.12–1.42; p < 0.001), nodal micrometastasis (OR 1.15, 95% CI 1.02–1.31; p = 0.024), and lower rates of ≥ 3 positive nodes (OR 0.77, 95% CI 0.66–0.90, p = 0.001). When stratified by HR expression, in both HR-positive and HR-negative tumors, age and multifocality were associated with HER2 low on UVA. On MVA, no variables were independently associated with both HR-negative and HR-positive/HER2-low tumors compared with HER2-negative tumors. In contrast, HER2-positive tumors, regardless of HR status, were associated with multifocality and an extensive intraductal component.
Conclusion
Clinicopathologic features of HER2-low tumors appear to be primarily related to HR status. Our findings do not support the characterization of HER2 low as a separate subtype.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ugras S, Stempel M, Patil S, Morrow M. Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2 status predict lymphovascular invasion and lymph node involvement. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21(12):3780–6.
He ZY, Wu SG, Yang Q, et al. Breast cancer subtype is associated with axillary lymph node metastasis: a retrospective cohort study. Med Baltimore. 2015;94(48):e2213.
Wiechmann L, Sampson M, Stempel M, et al. Presenting features of breast cancer differ by molecular subtype. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(10):2705–10.
Banerji U, van Herpen CML, Saura C, et al. Trastuzumab duocarmazine in locally advanced and metastatic solid tumours and HER2-expressing breast cancer: a phase 1 dose-escalation and dose-expansion study. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(8):1124–35.
Modi S, Jacot W, Yamashita T, et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated her2-low advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(1):9–20.
Modi S, Park H, Murthy RK, et al. Antitumor activity and safety of trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with HER2-low-expressing advanced breast cancer: results from a phase Ib study. J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(17):1887–96.
van der Lee MM, Groothuis PG, Ubink R, et al. The Preclinical profile of the duocarmycin-based HER2-targeting ADC SYD985 predicts for clinical benefit in low HER2-expressing breast cancers. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015;14(3):692–703.
Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, et al. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. Jama. 2006;295(21):2492–502.
Tarantino P, Jin Q, Tayob N, et al. Prognostic and biologic significance of ERBB2-low expression in early-stage breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2022;8(8):1177–83.
Ergun Y, Ucar G, Akagunduz B. Comparison of HER2-zero and HER2-low in terms of clinicopathological factors and survival in early-stage breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat Rev. 2023;115:102538.
Wei T, Wang D, Gao S, et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognostic significance of HER2-low expression in patients with early breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol. 2023;13:1100332.
Wolff AC, Hammond MEH, Allison KH, et al. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer: American society of clinical oncology/college of American pathologists clinical practice guideline focused update. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(20):2105–22.
Hortobagyi G, Connolly J. Breast In: Amin MB, Edge S, Greene F, eds. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th edition New York: Springer (2016).
Baez-Navarro X, van Bockstal MR, Andrinopoulou ER, van Deurzen CHM. HER2-Low breast cancer: incidence, clinicopathologic features, and survival outcomes from real-world data of a large nationwide cohort. Mod Pathol. 2023;36(4):100087.
Horisawa N, Adachi Y, Takatsuka D, et al. The frequency of low HER2 expression in breast cancer and a comparison of prognosis between patients with HER2-low and HER2-negative breast cancer by HR status. Breast Cancer. 2022;29(2):234–41.
Zhang H, Katerji H, Turner BM, Audeh W, Hicks DG. HER2-low breast cancers: incidence, HER2 staining patterns, clinicopathologic features, MammaPrint and BluePrint genomic profiles. Mod Pathol. 2022;35(8):1075–82.
Denkert C, Seither F, Schneeweiss A, et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of HER2-low-positive breast cancer: pooled analysis of individual patient data from four prospective, neoadjuvant clinical trials. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22(8):1151–61.
Peiffer DS, Zhao F, Chen N, et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis of erbb2-low breast cancer among patients in the national cancer database. JAMA Oncol. 2023;9(4):500–10.
Rosso C, Voutsadakis IA. Characteristics, clinical differences and outcomes of breast cancer patients with negative or low HER2 Expression. Clin Breast Cancer. 2022;22(4):391–7.
Schettini F, Chic N, Brasó-Maristany F, et al. Clinical, pathological, and PAM50 gene expression features of HER2-low breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2021;7(1):1.
Won HS, Ahn J, Kim Y, et al. Clinical significance of HER2-low expression in early breast cancer: a nationwide study from the Korean Breast Cancer Society. Breast Cancer Res. 2022;24(1):22.
Xu H, Han Y, Wu Y, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of HER2-low early-stage breast cancer: a single-institution experience. Front Oncol. 2022;12:906011.
Almstedt K, Heimes AS, Kappenberg F, et al. Long-term prognostic significance of HER2-low and HER2-zero in node-negative breast cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2022;173:10–9.
Tan R, Ong WS, Lee KH, et al. HER2 expression, copy number variation and survival outcomes in HER2-low non-metastatic breast cancer: an international multicentre cohort study and TCGA-METABRIC analysis. BMC Med. 2022;20(1):105.
Jacot W, Maran-Gonzalez A, Massol O, Sorbs C, Mollevi C, Guiu S, Boissière-Michot F, Ramos J. Prognostic value of HER2-low expression in non-metastatic triple-negative breast cancer and correlation with other biomarkers. Cancers. 2021;13(23):6059.
Mutai R, Barkan T, Moore A, et al. Prognostic impact of HER2-low expression in hormone receptor positive early breast cancer. Breast. 2021;60:62–9.
van den Ende NS, Smid M, Timmermans A, et al. HER2-low breast cancer shows a lower immune response compared to HER2-negative cases. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1):12974.
Chen M, Chen W, Liu D, et al. Prognostic values of clinical and molecular features in HER2 low-breast cancer with hormonal receptor overexpression: features of HER2-low breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2022;29(5):844–53.
Douganiotis G, Kontovinis L, Markopoulou E, et al. Prognostic Significance of Low HER2 Expression in Patients With Early Hormone Receptor Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Diagn Progn. 2022;2(3):316–23.
Bevilacqua JL, Kattan MW, Fey JV, Cody HS 3rd, Borgen PI, Van Zee KJ. Doctor, what are my chances of having a positive sentinel node? A validated nomogram for risk estimation. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(24):3670–9.
Silverstein MJ, Skinner KA, Lomis TJ. Predicting axillary nodal positivity in 2282 patients with breast carcinoma. World J Surg. 2001;25(6):767–72.
Fernandez AI, Liu M, Bellizzi A, et al. Examination of Low ERBB2 protein expression in breast cancer tissue. JAMA Oncol. 2022;8(4):1–4.
Lambein K, Van Bockstal M, Vandemaele L, et al. Distinguishing score 0 from score 1+ in HER2 immunohistochemistry-negative breast cancer: clinical and pathobiological relevance. Am J Clin Pathol. 2013;140(4):561–6.
Navarro XB, van Bockstal R, Nawawi D, et al. Interobserver variation in the assessment of her2 low expression in breast cancer: can we improve by adjusting criteria? An international interobserver study. Preprint preliminary report available online July 14 2022 at https://assets.researchsquare.com/files/rs-1807403/v1/df19e0d0-a4af-48a6-b190-764c4ebd0a9c.pdf?c=1663692040 (accessed August 19, 2023).
Chen R, Qi Y, Huang Y, et al. Diagnostic value of core needle biopsy for determining HER2 status in breast cancer, especially in the HER2-low population. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2023;197(1):189–200.
Lu Y, Zhu S, Tong Y, Fei X, Jiang W, Shen K, Chen X. HER2-low status is not accurate in breast cancer core needle biopsy samples: an analysis of 5610 consecutive patients. Cancers. 2022;14(24):6200.
Miglietta F, Griguolo G, Bottosso M, et al. HER2-low-positive breast cancer: evolution from primary tumor to residual disease after neoadjuvant treatment. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2022;8(1):66.
Agostinetto E, Rediti M, Fimereli D, Debien V, Piccart M, Aftimos P, Sotiriou C, de Azambuja E. HER2-low breast cancer: molecular characteristics and prognosis. Cancers. 2021;13(11):2824.
Acknowledgments
The preparation of this study was supported in part by NIH/NCI Cancer Center Support Grant No. P30 CA008748 to Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, and this study was presented in poster format at the 2023 American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting, 2–6 June 2023, Chicago, IL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
All authors have no conflict of interest disclosures to report.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Polidorio, N., Montagna, G., Sevilimedu, V. et al. Do HER2-Low Tumors Have a Distinct Clinicopathologic Phenotype?. Ann Surg Oncol 31, 2231–2243 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-023-14800-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-023-14800-w