Abstract
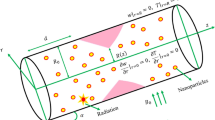
The current examination hypothetically explores physical characteristics of electro-magneto-hydrodynamics of circulation system under the sight of electroosmotic forces on concentrically catheterized diseased arterial segment having both stenosis and aneurysm along its boundaries. A hybrid fractional second-grade nanofluid model is under consideration. The governing laws are tackled precisely, and closed-form arrangements are gotten for the instances of mild stenosis and aneurysm. Exact articulations for heat transfer, electroosmotic potential, hemodynamic velocity, arterial wall shear stress, and catheter wall shear stress are acquired. Graphical portrayals for the impact of significant parameters on flow characteristics have been devised and talked about. It has been concluded that heat flow and hemodynamic velocity increase for spherical-shaped nanoparticles as compared to the other shapes of nanoparticles. Hemodynamic velocity in the stenotic segment is much lower than that of the aneurysmal segment. Our results show that the flow rate among both abnormal segments of the artery increases in the presence of a catheter and there is more magnitude of the wall shear stress on the catheter wall. Instantaneous streamlines patterns are used to investigate the global conduct of blood. The current study intends to be used in medical regimes for drug delivery and biomedicine.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Chaturani, R.P. Samy, A study of non-Newtonian aspects of Blood Flow through stenosed arteries and its application in arterial diseases. Biorheology 22, 521–531 (1985)
O.U. Mehmood, N. Mustapha, S. Shafie, Unsteady two dimensional blood flow in porous artery with multi-irregular stenosis. Transp. Porous Media 92, 259–275 (2012)
D. Gallo, G.D. Santis, F. Negri, D. Tresoldi, R. Ponzini, D. Massai, M.A. Deriu, P. Segers, B. Verhegghe, G. Rizzo, U. Morbiducci, On the use of in vivo measured flow rates as boundary conditions for image-based hemodynamic models of the human aorta: implications for indicators of abnormal flow. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 40, 729–741 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0431-1
B. Pincombe, J. Mazumdar, The effects of post-stenotic dilatations on the flow of a blood analogue through stenosed coronary arteries. Math. Comput. Modelling 25, 57–70 (1997)
U. Morbiducci, R. Ponzini, D. Gallo, C. Bignardi, G. Rizzo, Inflow boundary conditions for image-based computational hemodynamics: Impact of idealized versus measured velocity profiles in the human aorta. J. Biomech. 46, 102–109 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2012.10.012
S. Nadeem, S. Ijaz, Influence of metallic nanoparticles on blood flow through arteries having both stenosis and aneurysm. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 14, 668–679 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2015.2452932
A. Boccadifuoco, A. Mariotti, S. Celi, N. Martini, M.V. Salvetti, Uncertainty quantification in numerical simulations of the flow in thoracic aortic aneurysms, ECCOMAS congress 2016 - proceedings of the 7th European congress on computational methods in applied sciences and engineering 3 (2016) 6226–49.
R. Ellahi, S. Rahman, S. Nadeem, Blood flow of Jeffrey fluid in a catharized tapered artery with the suspension of nanoparticles. Phys. Lett. A 378, 2973–2980 (2014)
S.I. Abdelsalam, Kh.S. Mekheimer, A.Z. Zaher, Alterations in blood stream by electroosmotic forces of hybrid nanofluid through diseased artery: aneurysmal/stenosed segment. Chin. J. Phys. 67, 314–329 (2020)
A. Mariotti, A. Boccadifuoco, S. Celi, M.V. Salvetti, Hemodynamics and stresses in numerical simulations of the thoracic aorta: stochastic sensitivity analysis to inlet flow-rate waveform. Comput. Fluids 230, 105–123 (2021)
S.N. Akbar, S. Nadeem, Blood flow analysis in tapered stenosed arteries with pseudoplastic characteristics. Int. J. Biomath. 7, 1450065 (2014)
A.R. Mantha, G. Benndorf, A. Hernandez, R.W. Metcalfe, Stability of pulsatile blood flow at the ostium of cerebral aneurysms. J. Biomech. 42, 1081–1087 (2009)
S.I. Abdelsalam, K. Vafai, Particulate suspension effect on peristaltically induced unsteady pulsatile flow in a narrow artery: blood flow model. Math. Biosci. 283, 91–105 (2017)
R.K. Dash, G. Jayaraman, K.N. Mehta, Flow in a catheterized curved artery with stenosis. J. Biomech. 49, 61 (1999)
V.P. Srivastava, R. Rastogi, Blood flow through a stenosed catheterized artery: effects of hematocrit and stenosis shape. Comput. Math. Appl. 59(4), 1377–1385 (2010)
K.S. Mekheimer, M.A. El Kot, Mathematical modeling of axial flow between two eccentric cylinders: application on the injection of eccentric catheter through stenotic arteries. Int. J. Non-Lin. Mech. 47(8), 927–937 (2012)
J.V. Ramana Reddy, D. Srikanth, S.V.S.S.N.V.G. Krishna Murthy, Mathematical modelling of pulsatile flow of blood through catheterized unsymmetric stenosed artery effects of tapering angle and slip velocity. Eur. J. Mech-B/Fluids 48, 236–244 (2014)
A. Zaman, A. Nasir, B. Anwar, Numerical simulation of unsteady micropolar hemodynamics in a tapered catheterized artery with a combination of stenosis and aneurysm. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 54, 1423–1436 (2016)
T. Elnaqeeb, K.S. Mekheimer, F. Alghamdi, Cu-blood flow model through a catheterized mild stenotic artery with a thrombosis. Math. Biosci. 282, 135–146 (2016)
K.S. Mekheimer, M.A.E. Kot, Suspension model for blood flow through catheterized curved artery with time-variant overlapping stenosis. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 18(3), 452–462 (2015)
D. Srikanth, J.V. Ramana Reddy, S. Jain, A. Kale, Unsteady polar fluid model of blood flow through tapered -shape stenosed artery effects of catheter and velocity slip. Ain. Shams Eng. J. 6(3), 1093–1104 (2015)
J. Doffin, F. Chagneau, Oscillating flow between a clot model and a stenosis. J. Biomech. 14(3), 143–148 (1981)
M.M. Maskeen, A. Zeeshan, O.U. Mehmood, M. Hassan, Heat transfer enhancement in hydromagnetic alumina-copper/water hybrid nanofluid flow over a stretching cylinder. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 138, 1127–1136 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08304-7
S.I. Abdelsalam, M.M. Bhatti, New insight into AuNP applications in tumor treatment and cosmetics through wavy annuli at the nanoscale. Sci. Rep. 9, 1–14 (2019)
S. Das, R.N. Jan, O.D. Makinde, MHD Flow of Cu −; Al2O3 /water hybrid nanofluid in porous channel: analysis of entropy generation, Defect Diffus. Forum 377, 42–61 (2017)
S.P.A. Devi, S.S.U. Devi, Numerical investigation of hydromagnetic hybrid Cu −; Al2O3 /water nanofluid flow over a permeable stretching sheet with suction. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Num. Simul. 17, 249–257 (2016)
Kh.S. Mekheimer, W.M. Hasona, R.E. Abo-Elkhair, A.Z. Zaher, Peristaltic blood flow with gold nanoparticles as a third grade nanofluid in catheter: Application ofcancer therapy. Phys. Lett. A 382, 85–93 (2018)
M. Marin, M.M. Maskeen, A. Zeeshan, O.U. Mehmood, M. Hassan, Hydromagnetic transport of iron nanoparticle aggregates suspended in water. Indian J. Phys. 93(1), 53–59 (2019)
N.S. Akbar, M. Mustafa, Ferromagnetic effects for nanofluid venture through composite permeable stenosed arteries with different nanosize particles. AIP Adv. 5, 077–102 (2015)
S.I. Abdelsalam, M.M. Bhatti, The impact of impinging TiO2 nanoparticles in Prandtl nanofluid along with endoscopic and variable magnetic field effects on peristaltic blood flow. Multidiscipl. Model. Mater. Struct. 14, 530–548 (2018)
I. Shahzadi, S. Suleman, S. Saleem, S. Nadeem, Utilization of Cu-nanoparticles as medication agent to reduce atherosclerotic lesions of a bifurcated artery having compliant walls. Computer Methods Programs Biomed. 184, 105–123 (2020)
A. Zeeshan, M.M. Maskeen, O.U. Mehmood, Hydromagnetic nanofluid flow past a stretching cylinder embedded in non-Darcian Forchheimer porous media. Neural Comput. Appl. 30, 3479–3489 (2018)
S. Uddin, M. Mohamad, M.A.H. Mohmad, O.U. Mehmood, M. Kamardan, R. Roslan, Natural heat transfer phenomenon in MHD fractional second grade fluid. Univ. J. Mech. Eng. 7(6C), 32–36 (2019). https://doi.org/10.13189/ujme.2019.071605
M. Hameed, A.K. Ambreen, R. Ellahi, M. Raza, Study of magnetic and heat transfer on the peristaltic transport of a fractional second grade fluid in a vertical tube. Eng. Sci. Technol., Int. J. 18, 496–502 (2015)
S. Nadeem, General periodic flows of fractional Oldroyd-B fluid for an edge. Phys. Lett. A 368, 181–187 (2007)
W.C. Tan, W.X. Pan, M.Y. Xu, A note on unsteady flows of a viscoelastic fluid with the fractional Maxwell model between two parallel plates. Int. J. Non Linear Mech. 38(5), 645–650 (2003)
W. Tan, Xu Mingyu, Unsteady flows of a generalized second grade fluid with the fractional derivative model between two parallel plates. Acta Mechan. Sinica 20(5), 471–476 (2004)
V.P. Rathod, A. Tuljappa, Slip effect on the peristaltic flow of a fractional second grade fluid through a cylindrical tube. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 6(3), 101–111 (2015)
Y. Kang, C. Yang, X. Huang, Electroosmotic flow in a capillary annulus with high zeta potentials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 253(2), 85–294 (2002)
S. Ghosal, Electrokinetic flow and dispersion in capillary electrophoresis. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 38, 309–338 (2006)
U. Ghosh, S. Chakraborty, Electroosmosis of viscoelastic fluids over charge modulated surfaces in narrow confinements. Phys. Fluids 27(6), 062004 (2015)
Kh.S. Mekheimer, W.M. Hasona, A.A. El-Shekhipy, A.Z. Zaher, Electrokinetics of dielectric non-newtonian bio fluids with heat transfer through a flexible channel: numerical study. Comput. Methods in Sci. Technol. 23, 331–341 (2017)
H. Keramati, A. Sadeghi, M.H. Saidi, S. Chakraborty, Analytical solutions for thermo-fluidic transport in electroosmotic flow through rough micro-tubes. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 92, 244–251 (2016)
N. Shehzad, A. Zeeshan, R. Ellahi, Electroosmotic flow of MHD Power law Al2O3-PVC nanofluid in a horizontal channel: Couette-Poiseuille flow model. Commun. Theor. Phys. 69, 655 (2018)
P. Liang, S. Wang, M. Zhao, Numerical study of rotating electroosmotic flow of Oldroyd-B fluid in a microchannel with slip boundary condition. Chin. J. Phys. 65, 459–471 (2020)
M. Buren, Y. Jian, Electromagnetohydrodynamic (EMHD) flow between two transversely wavy micro parallel plates. Electrophoresis 36, 1539–1548 (2015)
M.M. Bhatti, A. Zeeshan, R. Ellahi, O. Anwar Bég, A. Kadir, Effects of coagulation on the two-phase peristaltic pumping of magnetized Prandtl biofluid through an endoscopic annular geometry containing a porous medium. Chin. J. Phys. 58, 222–234 (2019)
M.M. Bhatti, A. Zeeshan, N. Ijaz, O. Anwar Bég, A. Kadir, Mathematical modelling of nonlinear thermal radiation effects on EMHD peristaltic pumping of viscoelastic dusty fluid through a porous medium duct. Eng. Sci. Technol., Int. J. 20, 1129 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2016.11.003
R.E. Abo-Elkhair, Kh.S. Mekheimer, A.Z. Zaher, Electro-magnetohydrodynamic oscillatory flow of a dielectric fluid through a porous medium with heat transfer: Brinkman model. Bio Nano Science 8, 596–608 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-018-0515-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehmood, O.U., Bibi, S., Zeeshan, A. et al. Electroosmotic impacts on hybrid antimicrobial blood stream through catheterized stenotic aneurysmal artery. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 137, 585 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02783-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-02783-8