Abstract
In this paper, the geometric structure and physicochemical properties of Li2Bn0/− (n = 1–12) clusters were investigated using CALYPSO structure prediction software in combination with density functional theory at B3LYP/6-311G level. The results suggest that the doping of Li atoms has a significant effect on the ground state geometry of the Bn clusters. The stability changes with the increase in the number of boron atoms. Then two stable ground state structures, Li2B8 and Li2B9−, are selected for further analyzing their molecular orbitals and bonding properties. It is demonstrated that the stability of the Li2Bn0/− (n = 1–12) clusters originates from the s–p hybridization between B–B and Li–B. It is expected that this work can provide some references for future research on boron-based nanomaterials.
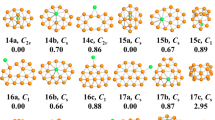
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
A.C. Reber, S.N. Khanna, Superatoms: electronic and geometric effects on reactivity. Acc. Chem. Res. 50(2), 255–263 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00464
W. Knight, Recent developments in cluster science. Phys. Scr. 1989(T29), 20 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/1989/T29/003
A. Castleman Jr., S. Khanna, Clusters, superatoms, and building blocks of new materials. J. Phys. Chem. C. 113(7), 2664–2675 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp806850h
P. Jena, Beyond the periodic table of elements: the role of superatoms. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 4(9), 1432–1442 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/jz400156t
P. Jena, Q. Sun, Super atomic clusters: design rules and potential for building blocks of materials. Chem. Rev. 118(11), 5755–5870 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00524
W.N. Lipscomb, The boranes and their relatives. Science 196(4294), 1047–1055 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.196.4294.1047
T. Jian, X. Chen, S.-D. Li, A.I. Boldyrev, J. Li, L.-S. Wang, Probing the structures and bonding of size-selected boron and doped-boron clusters. Chem. Soc. Rev. 48(13), 3550–3591 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CS00233B
I.-N. Chen, S.-Y. Wu, H.-T. Chen, Hydrogen storage in N-and B-doped graphene decorated by small platinum clusters: a computational study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 441, 607–612 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.106
L. Van Duong, N.T. Si, N.P. Hung, M.T. Nguyen, The binary boron lithium clusters B12Lin with n = 1–14: in search for hydrogen storage materials. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 23(43), 24866–24877 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP03682C
A.S. Rad, Application of B12N12 and B12P12 as two fullerene-like semiconductors for adsorption of halomethane: density functional theory study. Semiconductors 51, 134–138 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063782617010225
M.I. Eremets, V.V. Struzhkin, H.-K. Mao, R.J. Hemley, Superconductivity in boron. Science 293(5528), 272–274 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1062286
K. Yamamoto, T. Imaoka, M. Tanabe, T. Kambe, New horizon of nanoparticle and cluster catalysis with dendrimers. Chem. Rev. 120(2), 1397–1437 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00188
B. Zandkarimi, A.N. Alexandrova, Surface-supported cluster catalysis: ensembles of metastable states run the show. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Comput. Mol. Sci. 9(6), 1420 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/wcms.1420
A. Balogh, M. Dunlop, S. Cowley, D. Southwood, J. Thomlinson, K. Glassmeier, G. Musmann, H. Lühr, S. Buchert, M. Acuna, The cluster magnetic field investigation. Space Sci. Rev. 79, 65–91 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004970907748
J.C. Ordaz, E.C. Anota, M.S. Villanueva, M. Castro, Possibility of a magnetic [BN fullerene: B6 cluster]− nanocomposite as a vehicle for the delivery of dapsone. New J. Chem. 41(16), 8045–8052 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NJ01133D
K. Khan, A.K. Tareen, M. Aslam, M.F. Khan, Z. Shi, C. Ma, S.S. Shams, R. Khatoon, H. Zhang, Z. Guo, Synthesis, properties and novel electrocatalytic applications of the 2D-borophene Xenes. Prog. Solid State Chem. 59, 100283 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progsolidstchem.2020.100283
H.J. Zhai, A.N. Alexandrova, K.A. Birch, A.I. Boldyrev, L.S. Wang, Hepta-and octacoordinate boron in molecular wheels of eight-and nine-atom boron clusters: observation and confirmation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42(48), 6004–6008 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200351874
A.P. Sergeeva, D.Y. Zubarev, H.-J. Zhai, A.I. Boldyrev, L.-S. Wang, A photoelectron spectroscopic and theoretical study of B16− and B162−: an all-boron naphthalene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(23), 7244–7246 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja802494z
N. MinháTam, H. TanáPham, L. VanáDuong, M. PhuongáPham-Ho, M. ThoáNguyen, Fullerene-like boron clusters stabilized by an endohedrally doped iron atom: BnFe with n = 14, 16, 18 and 20. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(5), 3000–3003 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CP04279D
I. Boustani, Systematic ab initio investigation of bare boron clusters: determination of the geometryand electronic structures of Bn (n = 2–14). Phys. Rev. B. 55(24), 16426 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.55.16426
M. Atiş, C. Özdoşan, Z.B. Güvenç, Density functional study of physical and chemical properties of nano size boron clusters: Bn (n = 13–20). Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 22(4), 380 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-0068/22/04/380-388
B. Kiran, S. Bulusu, H.-J. Zhai, S. Yoo, X.C. Zeng, L.-S. Wang, Planar-to-tubular structural transition in boron clusters: B20 as the embryo of single-walled boron nanotubes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 102(4), 961–964 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0408132102
Q. Chen, T.-T. Chen, H.-R. Li, X.-Y. Zhao, W.-J. Chen, H.-J. Zhai, S.-D. Li, L.-S. Wang, B31− and B32−: chiral quasi-planar boron clusters. Nanoscale 11(19), 9698–9704 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NR01524H
X. Wu, L. Sai, S. Zhou, P. Zhou, M. Chen, M. Springborg, J. Zhao, Competition between tubular, planar and cage geometries: a complete picture of structural evolution of Bn (n = 31–50) clusters. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22(23), 12959–12966 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CP01256D
W.-J. Chen, Y.-Y. Ma, T.-T. Chen, M.-Z. Ao, D.-F. Yuan, Q. Chen, X.-X. Tian, Y.-W. Mu, S.-D. Li, L.-S. Wang, B48−: a bilayer boron cluster. Nanoscale 13(6), 3868–3876 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR09214B
L. Hanley, S.L. Anderson, Oxidation of small boron cluster ions (B+1–13) by oxygen. J. Chem. Phys. 89(5), 2848–2860 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.454989
H.-J. Zhai, L.-S. Wang, A.N. Alexandrova, A.I. Boldyrev, Electronic structure and chemical bonding of B5− and B5 by photoelectron spectroscopy and ab initio calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 117(17), 7917–7924 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1511184
A.N. Alexandrova, A.I. Boldyrev, H.-J. Zhai, L.-S. Wang, All-boron aromatic clusters as potential new inorganic ligands and building blocks in chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 250(21–22), 2811–2866 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2006.03.032
W. Huang, A.P. Sergeeva, H.-J. Zhai, B.B. Averkiev, L.-S. Wang, A.I. Boldyrev, A concentric planar doubly π-aromatic B19− cluster. Nat. Chem. 2(3), 202–206 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.534
H.-J. Zhai, Y.-F. Zhao, W.-L. Li, Q. Chen, H. Bai, H.-S. Hu, Z.A. Piazza, W.-J. Tian, H.-G. Lu, Y.-B. Wu, Observation of an all-boron fullerene. Nat. Chem. 6(8), 727–731 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1999
Z.A. Piazza, H.-S. Hu, W.-L. Li, Y.-F. Zhao, J. Li, L.-S. Wang, Planar hexagonal B36 as a potential basis for extended single-atom layer boron sheets. Nat. Commun. 5, 3113 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4113
K.A. Nguyen, K. Lammertsma, Structure, bonding, and stability of small boron-lithium clusters. J. Phys. Chem. A. 102(9), 1608–1614 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp972864l
Y. Li, D. Wu, Z.R. Li, C.C. Sun, Structural and electronic properties of boron-doped lithium clusters: Ab initio and DFT studies. J. Comput. Chem. 28(10), 1677–1684 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20637
M.A. Çipiloğlu, A. Özkurt, Theoretical investigation on molecular structure and electronic properties of BxLiy cluster for lithium-ion batteries with quantum ESPRESSO program. Molecules 25(14), 3266 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25143266
D. Lin, Y. Liu, Y. Cui, Reviving the lithium metal anode for high-energy batteries. Nat. Nanotechnol. 12(3), 194–206 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2017.16
W. Liu, Y. Zhao, Y. Li, Q. Jiang, E. Lavernia, Enhanced hydrogen storage on Li-dispersed carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. C. 113(5), 2028–2033 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp8091418
A.L. Arokiyanathan, N. Panjulingam, S. Lakshmipathi, Chemical properties of lithium cluster (Lix, x = 2–8) on Stone–Wales defect graphene sheet: a DFT study. J. Phys. Chem. C. 124(13), 7229–7237 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b11529
L. Yan, J. Shao, Y. Li, Electronic shell study of prolate Lin (n= 15–17) clusters: magnetic superatomic molecules. Chin. Phys. B. 29(12), 125101 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/abb669
M. Yousofizadeh, E. Shakerzadeh, M. Bamdad, Electronic and nonlinear optical characteristics of the LiBn (n = 4–11) nanoclusters: a theoretical study. Microelectron. Eng. 183, 64–68 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2017.10.011
X. Dong, S. Jalife, A. Vásquez-Espinal, J. Barroso, M. Orozco-Ic, E. Ravell, J. Cabellos, W. Liang, Z. Cui, G. Merino, Li2B24: the simplest combination for a three-ring boron tube. Nanoscale 11(5), 2143–2147 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR09173K
W.-L. Li, X. Chen, T. Jian, T.-T. Chen, J. Li, L.-S. Wang, From planar boron clusters to borophenes and metalloborophenes. Nat. Rev. Chem. 1(10), 0071 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-017-0071
Y. Wang, J. Lv, L. Zhu, Y. Ma, Crystal structure prediction via particle-swarm optimization. Phys. Rev. B. 82(9), 094116 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.82.094116
J. Lv, Y. Wang, L. Zhu, Y. Ma, Particle-swarm structure prediction on clusters. J. Chem. Phys. 137(8), 084104 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4746757
Y. Wang, J. Lv, L. Zhu, Y. Ma, CALYPSO: a method for crystal structure prediction. Comput. Phys. Commun. 183(10), 2063–2070 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpc.2012.05.008
M. Frisch, G. Trucks, H. Schlegel, G. Scuseria, M. Robb, J. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, B. Mennucci, G. Petersson, Gaussian 09, Revision D. 01, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT. See also: URL: http://www.gaussian.com. (2009).
Y. Wang, J. Lv, L. Zhu, S. Lu, K. Yin, Q. Li, H. Wang, L. Zhang, Y. Ma, Materials discovery via CALYPSO methodology. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter. 27(20), 203203 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/0953-8984/27/20/203203
C.-G. Li, Z.-G. Shen, J. Zhang, Y.-Q. Cui, J.-J. Li, H.-Y. Xue, H.-F. Li, B.-Z. Ren, Y.-F. Hu, Analysis of the structures, stabilities and electronic properties of MB16−(M = V, Cr, Mn, Fe Co, Ni) clusters and assemblies. New J. Chem. 44(13), 5109–5119 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NJ06335H
B. Gao, P. Gao, S. Lu, J. Lv, Y. Wang, Y. Ma, Interface structure prediction via CALYPSO method. Sci. Bull. 64(5), 301–309 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2019.02.009
E.I. Moreira, B. Brito, G.-Q. Hai, L. Cândido, Electron correlation effects in boron clusters BQn (for Q =− 1, 0, 1 and n ≤ 13) based on quantum Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 24(5), 3119–3128 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CP04737J
S. Alexander, R. Orbach, Density of states on fractals:«fractons». J. Physique Lett. 43(17), 625–631 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1051/jphyslet:019820043017062500
J. Mintmire, C. White, Universal density of states for carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81(12), 2506 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.2506
T. Lu, F. Chen, Multiwfn: a multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 33(5), 580–592 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.22885
M. Torrent-Sucarrat, J.M. Luis, M. Duran, M. Solà, On the validity of the maximum hardness and minimum polarizability principles for nontotally symmetric vibrations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123(32), 7951–7952 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja015737i
L.R. Murphy, T.L. Meek, A.L. Allred, L.C. Allen, Evaluation and test of pauling’s electronegativity scale. J. Phys. Chem. A. 104(24), 5867–5871 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp000288e
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Innovation Fund of Postgraduate Sichuan University of Science & Engineering (Grant No. y2021008, Y2022014), the Opening Project of Sichuan Province University Key Laboratory of Bridge Non-destruction Detecting and Engineering Computing (Grant No. 2020QYJ02), and the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of Sichuan Province (Grant No. S202110622032). This work was supported by Sichuan University of Science & Engineering High Performance Computing Center provided computational.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YYW: Investigation, writing-original draft. YQY: Investigation, methodology. YYL: Writing—review and editing, investigation, software. HY: Supervision, funding acquisition. JHG: Investigation, visualization. GLC: Conceptualization, funding acquisition. YFH: Software, funding acquisition. JY: Data curation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y.Y., Yuan, Y.Q., Li, Y.Y. et al. Theoretical study of geometry and electronic properties of medium-sized doped clusters Li2Bn0/− (n = 1–12). Eur. Phys. J. D 77, 114 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00668-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epjd/s10053-023-00668-8