Abstract
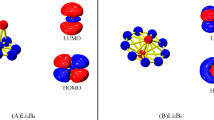
This paper reports a systematic study on the doping of two potassium atoms in small-sized neutral boron clusters. The CALYPSO software in conjunction with DFT was used to anticipate the low-energy structures, optimize their geometry, and adjust their energies. With increasing size, the structural development of the K2Bn (n = 1–12) clusters was revealed, and we discovered that the majority of their ground-state structural isomers structurally inherited well from the corresponding ground-state isomers of pure B clusters. A fresh finding was made after confirming the NPA (natural population analysis) of the low-lying K2Bn (n = 1–12): every doped K atom in the structure has a positive charge. According to relative stability analysis, the most stable K2B8 cluster within the parameters of our investigation has a HOMO–LUMO gap of 3.31 eV. Strong interactions between K-4s and B-2P AO were also discovered through an additional examination of the molecular orbitals and bonds of K2B8 clusters. These interactions may be the primary cause of K2B8's exceptional stability. We hope that our research will be useful in the future for synthesizing and using doped boron-based nanomaterials.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.-G. Jang et al., Synthesis of dimesitylborane-substituted phenylcarbazoles as bipolar host materials and the variation of the green PHOLED performance with the substituent position of the boron atom. Dalton Trans. 43(21), 7712–7715 (2014)
M.-S. Lin et al., A diarylborane-substituted carbazole as a universal bipolar host material for highly efficient electrophosphorescence devices. J. Mater. Chem. 22(3), 870–876 (2012)
M.-M. Xue et al., De novo design of boron-based host materials for highly efficient blue and white phosphorescent OLEDs with low efficiency roll-off. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8(31), 20230–20236 (2016)
J.-I. Aihara, B13+ is highly aromatic. J. Phys. Chem. A 105(22), 5486–5489 (2001)
I. Boustani, Systematic lsd investigation on cationic boron clusters: B (n 2–14). Int. J. Quant. Chem. 52(4), 1081–1111 (1994)
L. Hanley, J.L. Whitten, S.L. Anderson, Collision-induced dissociation and ab initio studies of boron cluster ions: determination of structures and stabilities. J. Phys. Chem. 92(20), 5803–5812 (1988)
H.J. Zhai et al., Hepta-and octacoordinate boron in molecular wheels of eight-and nine-atom boron clusters: observation and confirmation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 42(48), 6004–6008 (2003)
B. Albert, H. Hillebrecht, Boron: elementary challenge for experimenters and theoreticians. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 48(46), 8640–8668 (2009)
J.-I. Aihara, H. Kanno, T. Ishida, Aromaticity of planar boron clusters confirmed. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127(38), 13324–13330 (2005)
A.N. Alexandrova et al., Electronic structure, isomerism, and chemical bonding in B7-and B7. J. Phys. Chem. A 108(16), 3509–3517 (2004)
A.N. Alexandrova et al., All-boron aromatic clusters as potential new inorganic ligands and building blocks in chemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 250(21–22), 2811–2866 (2006)
K.C. Lau, R. Pandeyl, The 2D–3D structural transition and chemical bonding in. Struct. Propert. Clusters Few Atoms Nanoparticles 5, 116 (2006)
H.-J. Zhai et al., Hydrocarbon analogues of boron clusters—planarity, aromaticity and antiaromaticity. Nat. Mater. 2(12), 827–833 (2003)
A.P. Sergeeva et al., All-boron analogues of aromatic hydrocarbons: B17− and B18−. J. Chem. Phys. 134(22), 224304 (2011)
A.P. Sergeeva et al., Understanding boron through size-selected clusters: structure, chemical bonding, and fluxionality. Acc. Chem. Res. 47(4), 1349–1358 (2014)
M.P. Johansson, On the strong ring currents in B20 and neighboring boron toroids. J. Phys. Chem. C 113(2), 524–530 (2009)
L.-S. Wang, Photoelectron spectroscopy of size-selected boron clusters: from planar structures to borophenes and borospherenes. Int. Rev. Phys. Chem. 35(1), 69–142 (2016)
H.-J. Zhai et al., Observation of an all-boron fullerene. Nat. Chem. 6(8), 727–731 (2014)
T.R. Galeev et al., Observation of the highest coordination number in planar species: decacoordinated Ta© B10− and Nb© B10− anions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51(9), 2101–2105 (2012)
W.-L. Li et al., Aluminum avoids the central position in AlB9–and AlB10–: photoelectron spectroscopy and ab Initio study. J. Phys. Chem. A 115(38), 10391–10397 (2011)
C. Romanescu et al., Aromatic metal-centered monocyclic boron rings: Co© B8− and Ru© B9−. Angew. Chem. 123(40), 9506–9509 (2011)
I.A. Popov et al., Complexes between planar boron clusters and transition metals: a photoelectron spectroscopy and ab initio study of CoB12–and RhB12–. J. Phys. Chem. A 118(37), 8098–8105 (2014)
A.N. Alexandrova et al., Molecular wheel B82-as a new inorganic ligand. Photoelectron spectroscopy and ab initio characterization of LiB8. Inorgan. Chem. 43(12), 3552–3554 (2004)
J.-B. Gu et al., Structural, electronic, and magnetic properties of boron cluster anions doped with aluminum: BnAl−(2≤ n≤ 9). Chin. Phys. B 21(4), 043102 (2012)
Z.-F. Liu et al., A density-functional theory for (BAs) n clusters (n= 1–14): structures, stabilities and electronic properties. Chin. Phys. B 20(2), 023101 (2011)
H.-J. Zhai et al., Electronic structure and chemical bonding of B 5− and B 5 by photoelectron spectroscopy and ab initio calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 117(17), 7917–7924 (2002)
J. Lv et al., Particle-swarm structure prediction on clusters. J. Chem. Phys. 137(8), 084104 (2012)
Y. Wang et al., Crystal structure prediction via particle-swarm optimization. Phys. Rev. B 82(9), 094116 (2010)
Y. Wang et al., CALYPSO: a method for crystal structure prediction. Comput. Phys. Commun. 183(10), 2063–2070 (2012)
D. Die et al., The ground-state structure, optical-absorption and photoelectron spectrum of silver clusters. Phys. E 117, 113805 (2020)
L.-P. Ding et al., Structures, mobilities, and electronic properties of functionalized silicene: Superhalogen BO2 adsorption. Inorg. Chem. 59(7), 5041–5049 (2020)
Y.-W. Fan, H.-Q. Wang, H.-F. Li, Structural and electronic properties of exohedrally doped neutral silicon clusters LnSi n (n= 5, 10; Ln= Sm, Eu, Yb). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 22(36), 20545–20552 (2020)
L. Lai et al., Growth mechanism and electronic and magnetic properties of AgnTi alloy clusters. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 148, 109757 (2021)
C.-G. Li et al., Analysis of the structures, stabilities and electronic properties of MB 16−(M= V, Cr, Mn, Fe Co, Ni) clusters and assemblies. New J. Chem. 44(13), 5109–5119 (2020)
C.-G. Li et al., A comparative study of Cu n X (X= Sc, Y; n= 1–10) clusters based on the structures, and electronic and aromatic properties. New J. Chem. 43(17), 6597–6606 (2019)
Z. Li et al., The selectivity of the transition metal encapsulated in fullerene-like B36 clusters. Chem. Phys. Lett. 757, 137876 (2020)
C. Lu, C. Chen, Indentation strengths of zirconium diboride: intrinsic versus extrinsic mechanisms. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12(11), 2848–2853 (2021)
C. Lu et al., Elucidating stress–strain relations of ZrB12 from first-principles studies. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 11(21), 9165–9170 (2020)
Y.R. Zhao et al., Probing the structural and electronic properties of neutral and anionic lanthanum-doped silicon clusters. J. Phys. Chem. C 123(47), 28561–28568 (2019)
S.M. Bouzzine et al., Density functional theory (B3LYP/6-31G*) study of oligothiophenes in their aromatic and polaronic states. J. Mol. Struct. (Thoechem.) 726(1–3), 271–276 (2005)
J.E. Del Bene, W.B. Person, K. Szczepaniak, Properties of hydrogen-bonded complexes obtained from the B3LYP functional with 6–31G (d, p) and 6–31+ G (d, p) basis sets: comparison with MP2/6-31+ G (d, p) results and experimental data. J. Phys. Chem. 99(27), 10705–10707 (1995)
H. Kruse, L. Goerigk, S. Grimme, Why the standard B3LYP/6-31G* model chemistry should not be used in DFT calculations of molecular thermochemistry: understanding and correcting the problem. J. Org. Chem. 77(23), 10824–10834 (2012)
J. Tirado-Rives, W.L. Jorgensen, Performance of B3LYP density functional methods for a large set of organic molecules. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 4(2), 297–306 (2008)
T.M. Krygowski, J.E. Zachara, H. Szatylowicz, Molecular geometry as a source of chemical information. 3. How H-bonding affects aromaticity of the ring in the case of phenol and p-nitrophenol complexes: A B3LYP/6–311+ G** study. J. Org. Chem. 69(21), 7038–7043 (2004)
X. Li et al., Pentaatomic tetracoordinate planar carbon,[CAl4] 2−: a new structural unit and its salt complexes. Angew. Chem. 112(20), 3776–3778 (2000)
Z. Liu, T. Lu, Q. Chen, An sp-hybridized all-carboatomic ring, cyclo [18] carbon: Electronic structure, electronic spectrum, and optical nonlinearity. Carbon 165, 461–467 (2020)
F. Weigend, Accurate Coulomb-fitting basis sets for H to Rn. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 8(9), 1057–1065 (2006)
F. Weigend, R. Ahlrichs, Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: Design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 7(18), 3297–3305 (2005)
M. Frisch et al., in Gaussian 09, revision D. 01. 2009, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT (2009)
M.E. Frisch et al., in Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT. Wallingford CT (2009).
T. Lu, F.-W. Chen, Meaning and functional form of the electron localization function. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 27(12), 2786–2792 (2011)
D.Y. Zubarev, A.I. Boldyrev, Developing paradigms of chemical bonding: adaptive natural density partitioning. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 10(34), 5207–5217 (2008)
L. Cheng, B14: an all-boron fullerene. J. Chem. Phys. 136(10), 104301 (2012)
R. Kawai, J. Weare, Instability of the B12 icosahedral cluster: rearrangement to a lower energy structure. J. Chem. Phys. 95(2), 1151–1159 (1991)
A. Jalbout, S. Fernandez, Part II. Gaussian, complete basis set and density functional theory stability evaluation of the singlet states of Cn (n= 1–6): energy differences, HOMO–LUMO band gaps, and aromaticity. J. Mol. Struct. Theochem. 584(1–3), 169–182 (2002)
J.-I. Aihara, Weighted HOMO-LUMO energy separation as an index of kinetic stability for fullerenes. Theoret. Chem. Acc. 102, 134–138 (1999)
R. Rakhi, C.H. Suresh, A DFT study on dihydropyrazine annulated linear polyacenes: aromaticity, stability and HOMO–LUMO energy modulation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18(35), 24631–24641 (2016)
S. Neukermans et al., Extremely stable metal-encapsulated AlPb 10+ and AlPb 12+ clusters: mass-spectrometric discovery and density functional theory study. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92(16), 163401 (2004)
S. Burkart et al., Experimental verification of the high stability of Al13H: a building block of a new type of cluster material? Chem. Phys. Lett. 301(5–6), 546–550 (1999)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Innovation Fund of Postgraduate Sichuan University of Science & Engineering (Grant No. y2021008, Y2022013, Y2022014), the Cultivating Program of Young and Middle-aged Backbone Teachers of Chengdu University of Technology (No. 10912-JXGG2022-09146), and the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program of Sichuan Province (Grant No. S202110622032). This work was supported by Sichuan University of Science & Engineering High Performance Computing Center provided computational.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, G.L., Yuan, Y.Q., Wang, C.P. et al. Structural and electronic properties of neutral boron clusters doped with two potassium atoms. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 82, 1171–1179 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-023-00789-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-023-00789-8