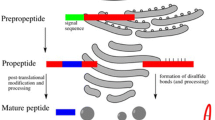
Abstract
In addition to classic phytohormones, such as auxin, cytokinin, ethylene, gibberellin, and abscisic acid, plant peptide hormones are also involved in various aspects of growth and development. This group of phytohormones is represented by short peptides, which are, as a rule, ligands for receptor kinases that initiate a signaling cascade, regulating plant development in response to stimuli from an external or internal environment. The review examines the peptide phytohormones known to date, their structure, synthesis features, receptors, and their role in plant development.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Pearce, G., Strydom, D., Johnson, S., and Ryan, C.A., A polypeptide from tomato leaves induces wound-inducible proteinase inhibitor proteins, Science, 1991, vol. 253, pp. 895–897.
Matsubayashi, Y. and Sakagami, Y., Phytosulfokine, sulfated peptides that induce the proliferation of single mesophyll cells of Asparagus officinalis L., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1996, vol. 93, pp. 7623–7627.
Fletcher, J.C., Brand, U., Running, M.P., Simon, R., and Meyerowitz, E.M., Signaling of cell fate decisions by CLAVATA3 in Arabidopsis shoot meristems, Science, 1999, vol. 283, pp. 1911–1914.
Ito, Y., Nakanomyo, I., Motose, H., Iwamoto, K., Sawa, S., Dohmae, N., and Fukuda, H., Dodeca-CLE peptides as suppressors of plant stem cell differentiation, Science, 2006, vol. 313, pp. 842–845.
Matsubayashi, Y., Posttranslationally modified small-peptide signals in plants, Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2014, vol. 65, pp. 385–413.
Lease, K.A. and Walker, J.C., The Arabidopsis unannotated secreted peptide database, a resource for plant peptidomics, Plant Physiol., 2006, vol. 142, pp. 831–838.
Schardon, K., Hohl, M., Graff, L., Pfannstiel, J., Schulze, W., Stintzi, A., and Schaller, A., Precursor processing for plant peptide hormone maturation by subtilisin-like serine proteinases, Science, 2016, vol. 354, pp. 1594–1597.
Tamaki, T., Betsuyaku, S., Fujiwara, M., Fukao, Y., Fukuda, H., and Sawa, S., SUPPRESSOR OF LLP1 1‑mediated C-terminal processing is critical for CLE19 peptide activity, Plant J., 2013, vol. 76, pp. 970–981.
Okamoto, S., Shinohara, H., Mori, T., Matsubayashi, Y., and Kawaguchi, M., Root-derived CLE glycopeptides control nodulation by direct binding to HAR1 receptor kinase, Nat. Commun., 2013, vol. 4: 2191.
Gorres, K.L. and Raines, R.T., Prolyl 4-hydroxylase, Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 2010, vol. 45, pp. 106–124.
Santiago, J., Brandt, B., Wildhagen, M., Hohmann, U., Hothorn, L.A., Butenko, M.A., and Hothorn, M., Mechanistic insight into a peptide hormone signaling complex mediating floral organ abscission, Elife, 2016, vol. 5: e15075.
Amano, Y., Tsubouchi, H., Shinohara, H., Ogawa, M., and Matsubayashi, Y., Tyrosine-sulfated glycopeptide involved in cellular proliferation and expansion in A-rabidopsis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2007, vol. 104, pp. 18333–18338.
Song, W., Liu, L., Wang, J., Wu, Z., Zhang, H., Tang, J., Lin, G., Wang, Y., Wen, X., Li, W., Han, Z., Guo, H., and Chai, J., Signature motif-guided identification of receptors for peptide hormones essential for root meristem growth, Cell Res., 2016, vol. 26, pp. 674–685.
Matsuzaki, Y., Ogawa-Ohnishi, M., Mori, A., and Matsubayashi, Y., Secreted peptide signals required for maintenance of root stem cell niche in Arabidopsis, Science, 2010, vol. 329, pp. 1065–1067.
Hirakawa, Y., Torii, K.U., and Uchida, N., Mechanisms and strategies shaping plant peptide hormones, Plant Cell Physiol., 2017, vol. 58, pp. 1313–1318.
Ma, X., Xu, G., He, P., and Shan, L., SERKing coreceptors for receptors, Trends Plant Sci., 2016, vol. 21, pp. 1017–1033.
Yamaguchi, Y.L., Ishida, T., and Sawa, S., CLE peptides and their signaling pathways in plant development, J. Exp. Bot., 2016, vol. 67, pp. 4813–4826.
Kucukoglu, M. and Nilsson, O., CLE peptide signaling in plants—the power of moving around, Physiol. Plant., 2015, vol. 155, pp. 74–87.
Schoof, H., Lenhard, M., Haecker, A., Mayer, K.F., Jürgens, G., and Laux, T., The stem cell population of Arabidopsis shoot meristems in maintained by a regulatory loop between the CLAVATA and WUSCHEL genes, Cell, 2000, vol. 100, pp. 635–644.
Stahl, Y., Wink, R.H., Ingram, G.C., and Simon, R., A signaling module controlling the stem cell niche in Arabidopsis root meristems, Curr. Biol., 2009, vol. 19, pp. 909–914.
Pi, L., Aichinger, E., van der Graaff, E., Llavata-Peris, C.I., Weijers, D., Hennig, L., Groot, E., and Laux, T., Organizer-derived WOX5 signal maintains root columella stem cells through chromatin-mediated repression of CDF4 expression, Dev. Cell, 2015, vol. 33, pp. 576–588.
Kondo, Y. and Fukuda, H., The TDIF signaling network, Curr. Opin. Plant Biol., 2015, vol. 28, pp. 106–110.
Kondo, Y., Hirakawa, Y., Kieber, J.J., and Fukuda, H., CLE peptides can negatively regulate protoxylem vessel formation via cytokinin signaling, Plant Cell Physiol., 2011, vol. 52, pp. 37–48.
Fiers, M., Hause, G., Boutilier, K., Casamitjana-Martinez, E., Weijers, D., Offringa, R., van der Geest, L., van Lookeren Campagne, M., and Liu, C.M., M-is‑expression of the CLV3/ESR-like gene CLE19 in Arabidopsis leads to a consumption of root meristem, Gene, 2004, vol. 327, pp. 37–49.
Gancheva, M.S., Dodueva, I.E., Lebedeva, M.A., Tvorogova, V.E., Tkachenko, A.A., and Lutova, L.A., Identification, expression, and functional analysis of CLE genes in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) storage root, BMC Plant Biol., 2016, vol. 16, suppl. 1: 7.
Shinohara, H., Moriyama, Y., Ohyama, K., and Matsubayashi, Y., Biochemical mapping of a ligand-binding domain within Arabidopsis BAM1 reveals diversified ligand recognition mechanisms of plant LRR-RKS, Plant J., 2012, vol. 70, pp. 845–854.
Osipova, M.A., Mortier, V., Demchenko, K.N., Tsyganov, V.E., Tikhonovich, I.A., Lutova, L.A., Dolgikh, E.A., and Goormachtig, S., WUSCHEL-RELATED HOMEOBOX5 gene expression and interaction of CLE peptides with components of the systemic control add two pieces to the puzzle of autoregulation of nodulation, Plant Physiol., 2012, vol. 158, pp. 1329–1341.
Araya, T., Miyamoto, M., Wibowo, J., Suzuki, A., Kojima, S., Tsuchiya, Y.N., Sawa, S., Fukuda, H., von Wiren, N., and Takahashi, H., CLE-CLAVATA1 peptide-receptor signaling module regulates the expansion of plant root systems in a nitrogen-dependent manner, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2014, vol. 111, pp. 2029–2034.
Samorodova, A.P., Tvorogova, V.E., Tkachenko, A.A., Potsenkovskaya, E.A., Lebedeva M.A., Tikhono-vich, I.A., and Lutova, L., Agrobacterial tumors interfere with nodulation and demonstrate the expression of nodulation-induced CLE genes in pea, J. Plant Physiol., 2017, vol. 221, pp. 94–100.
Wang, X., Mitchum, M.G., Gao, B., Li, C., Diab, H., Baum, T.J., Hussey, R.S., and Davis, E.L., A parasitism gene from a plant–parasitic nematode with function similar to CLAVATA3/ESR (CLE) of Arabidopsis thaliana, Mol. Plant Pathol., 2005, vol. 6, pp. 187–191.
Replogle, A., Wang, J., Paolillo, V., Smeda, J., Kinoshita, A., Durbak, A., Tax, F.E., Wang, X., Sawa, S., and Mitchum, M.G., Synergistic interaction of CLAVATA1, CLAVATA2, and RECEPTOR-LIKE PROTEIN KINASE 2 in cyst nematode parasitism of Arabidopsis, Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact., 2013, vol. 26, pp. 87–96.
Meng, L., Buchanan, B.B., Feldman, L.J., and Luan, S., CLE-like (CLEL) peptides control the pattern of root growth and lateral root development in Arabidopsis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2012, vol. 109, pp. 1760–1765.
Whitford, R., Fernandez, A., Tejos, R., Perez, A.C., Kleine-Vehn, J., Vanneste, S., Drozdzecki, A., Leitner, J., Abas, L., Aerts, M., Hoogewijs, K., Baster, P., de Groodt, R., Lin, Y.C., Storme, V., et al., GOLVEN secretory peptides regulate auxin carrier turnover during plant gravitropic responses, Dev. Cell, 2012, vol. 22, pp. 678–685.
Shinohara, H., Mori, A., Yasue, N., Sumida, K., and Matsubayashi, Y., Identification of three LRR-RKS involved in perception of root meristem growth factor in Arabidopsis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2016, vol. 113, pp. 3897–3902.
Yang, H., Matsubayashi, Y., Nakamura, K., and Sakagami, Y., Oryza sativa PSK gene encodes a precursor of phytosulfokine-α, a sulfated peptide growth factor found in plants, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1999, vol. 96, pp. 13560–13565.
Matsubayashi, Y., Morita, A., Matsunaga, E., Furuya, A., Hanai, N., and Sakagami, Y., Physiological relationships between auxin, cytokinin, and a peptide growth factor, phytosulfokine-α, in stimulation of asparagus cell proliferation, Planta, 1999, vol. 207, pp. 559–565.
Yu, L., Liu, Y., Liu, Y., Li, Q., Tang, G., and Luo, L., Overexpression of phytosulfokine-α induces male sterility and cell growth by regulating cell wall development in Arabidopsis, Plant Cell Rep., 2016, vol. 35, pp. 2503–2512.
Matsubayashi, Y., Ogawa, M., Kihara, H., Niwa, M., and Sakagami, Y., Disruption and overexpression of Arabidopsis phytosulfokine receptor gene affects cellular longevity and potential for growth, Plant Physiol., 2006, vol. 142, pp. 45–53.
Srivastava, R., Liu, J.X., and Howell, S.H., Proteolytic processing of a precursor protein for a growth-promoting peptide by a subtilisin serine protease in Arabidopsis, Plant J., 2008, vol. 56, pp. 219–227.
Sauter, M., Phytosulfokine peptide signalling, J. Exp. Bot., 2015, vol. 66, pp. 5161–5169.
Wang, J., Li, H., Han, Z., Zhang, H., Wang, T., Lin, G., Chang, J., Yang, W., and Chai, J., Allosteric receptor activation by the plant peptide hormone phytosulfokine, Nature, 2015, vol. 525, pp. 265–268.
Oehlenschlæger, C.B., Gersby, L.B.A., Ahsan, N., Pedersen, J.T., Kristensen, A., Solakova, T.V., Thelen, J.J., and Fuglsang, A.T., Activation of the LRR receptor-like kinase PSY1R requires transphosphorylation of residues in the activation loop, Front. Plant Sci., 2017, vol. 8: 2005.
Mosher, S. and Kemmerling, B., PSKR1 and PSY1R-mediated regulation of plant defense responses, Plant Signal. Behav., 2013, vol. 8: e24119. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.24119
Roberts, I., Smith, S., de Rybel, B., van den Broeke, J., Smet, W., de Cokere, S., Mispelaere, M., de Smet, I., and Beeckman, T., The CEP family in land plants: evolutionary analyses, expression studies, and role in Arabidopsis shoot development, J. Exp. Bot., 2013, vol. 64, pp. 5371–5381.
Tabata, R., Sumida, K., Yoshii, T., Ohyama, K., Shinohara, H., and Matsubayashi, Y., Perception of root-derived peptides by shoot LRR-RKS mediates systemic N-demand signaling, Science, 2014, vol. 346, pp. 343–346.
Ohkubo, Y., Tanaka, M., Tabata, R., Ogawa-Ohnishi, M., and Matsubayashi, Y., Shoot-to-root mobile polypeptides involved in systemic regulation of nitrogen acquisition, Nat. Plants, 2017, vol. 3: 17029.
Imin, N., Mohd-Radzman, N.A., Ogilvie, H.A., and Djordjevic, M.A., The peptide-encoding CEP1 gene modulates lateral root and nodule numbers in Medicago truncatula, J. Exp. Bot., 2013, vol. 64, pp. 5395–5409.
Huault, E., Laffont, C., Wen, J., Mysore, K.S., Ratet, P., Duc, G., and Frugier, F., Local and systemic regulation of plant root system architecture and symbiotic nodulation by a receptor-like kinase, PLoS Genet., 2014, vol. 10: e1004891.
Bobay, B.G., DiGennaro, P., Scholl, E., Imin, N., Djordjevic, M.A., and Bird, D.McK., Solution NMR studies of the plant peptide hormone CEP inform function, FEBS Lett., 2013, vol. 587, pp. 3979–3985.
Vie, A.K., Najafi, J., Liu, B., Winge, P., Butenko, M.A., Hornslien, K.S., Kumpf, R., Aalen, R.B., Bones, A.M., and Brembu, T., The IDA/IDA-LIKE and PIP/PIP-LIKE gene families in Arabidopsis: phylogenetic relationship, expression patterns, and transcriptional effect of the PIPL3 peptide, J. Exp. Bot., 2015, vol. 66, pp. 5351–5365.
Stenvik, G.-E., Tandstad, N.M., Guo, Y., Shi, C.L., Kristiansen, W., Holmgren, A., Clark, S.E., Aalen, R.B., and Butenko, M.A., The EPIP peptide of INFLORESCENCE DEFICIENT IN ABSCISSION is sufficient to induce abscission in Arabidopsis through the receptor-like kinases HAESA and HAESA-LIKE2, Plant Cell, 2008, vol. 20, pp. 1805–1817.
Cho, S.K., Larue, C.T., Chevalier, D., Wang, H., Jinn, T.L., Zhang, S., and Walker, J.C., Regulation of floral organ abscission in Arabidopsis thaliana, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2008, vol. 105, pp. 15629–15634.
Butenko, M.A., Shi, C.L., and Aalen, R.B., KNAT1, KNAT2 and KNAT6 act downstream in the ID-A‑HAE/HSL2 signaling pathway to regulate floral organ abscission, Plant Signal. Behav., 2012, vol. 7, pp. 135–138.
Kumpf, R.P., Shi, C.L., Larrieu, A., Stø, I.M., Butenko, M.A., Péret, B., Riiser, E.S., Bennett, M.J., and Aalen, R.B., Floral organ abscission peptide IDA and its HAE/HSL2 receptors control cell separation during lateral root emergence, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2013, vol. 110, pp. 5235–5240.
Wang, X., Hou, S., Wu, Q., Lin, M., Acharya, B.R., Wu, D., and Zhang, W., IDL6-HAE/HSL2 impacts pectin degradation and resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv tomato DC3000 in Arabidopsis leaves, Plant J., 2017, vol. 89, pp. 250–263.
Hou, S., Wang, X., Chen, D., Yang, X., Wang, M., Turrà, D., di Pietro, A., and Zhang, W., The secreted peptide PIP1 amplifies immunity through receptor-like kinase 7, PLoS Pathog., 2014, vol. 10, no. 9. https://www. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4154866/, Accessed November 17, 2017.
Doblas, V.G., Smakowska-Luzan, E., Fujita, S., Alassimone, J., Barberon, M., Madalinski, M., Belkhadir, Y., and Geldner, N., Root diffusion barrier control by a vasculature-derived peptide binding to the SGN3 receptor, Science, 2017, vol. 355, pp. 280–284.
Nakayama, T., Shinohara, H., Tanaka, M., Baba, K., Ogawa-Ohnishi, M., and Matsubayashi, Y., A peptide hormone required for Casparian strip diffusion barrier formation in Arabidopsis roots, Science, 2017, vol. 355, pp. 284–286.
Pearce, G., Systemin, hydroxyproline-rich systemin and the induction of protease inhibitors, Curr. Protein Pept. Sci., 2011, vol. 12, pp. 399–408.
Higashiyama, T., Peptide signaling in pollen–pistil interactions, Plant Cell Physiol., 2010, vol. 51, pp. 177–189.
Qu, L.J., Li, L., Lan, Z., and Dresselhaus, T., Peptide signalling during the pollen tube journey and double fertilization, J. Exp. Bot., 2015, vol. 66, pp. 5139–5150.
Stotz, H.U., Thomson, J.G., and Wang, Y., Plant defensins: defense, development and application, Plant Signal. Behav., 2009, vol. 4, pp. 1010–1012.
Olsen, A.N., Mundy, J., and Skriver, K., Peptomics, identification of novel cationic Arabidopsis peptides with conserved sequence motifs, In Silico Biol., 2002, vol. 2, pp. 441–451.
Dressano, K., Ceciliato, P.H.O., Silva, A.L., Guerrero-Abad, J.C., Bergonci, T., Ortiz-Morea, F.A., Bürger, M., Silva-Filho, M.C., and Moura, D.S., BAK1 is involved in AtRALF1-induced inhibition of root cell expansion, PLoS Genet., 2017, vol. 13: e1007053.
Murphy, E. and de Smet, I., Understanding the RALF family: a tale of many species, Trends Plant Sci., 2014, vol. 19, pp. 664–671.
Murphy E., Vu L.D., van den Broeck L., Lin Z., Ramakrishna P., van de Cotte B., Gaudinier A., Goh T., Slane D., Beeckman T., Inzé D., Brady S.M., Fukaki H., and de Smet, I. RALFL34 regulates formative cell divisions in Arabidopsis pericycle during lateral root initiation, J. Exp. Bot., 2016, vol. 67, pp. 4863–4875.
Thynne, E., Saur, I.M.L., Simbaqueba, J., Ogilvie, H.A., Gonzalez-Cendales, Y., Mead, O., Taranto, A., Catanzariti, A.-M., McDonald, M.C., Schwessinger, B., Jones, D.A., Rathjen, J.P., and Solomon, P.S., Fungal phytopathogens encode functional homologues of plant rapid alkalinization factor (RALF) peptides, Mol. Plant Pathol., 2017, vol. 18, pp. 811–824.
Sugano, S.S., Shimada, T., Imai, Y., Okawa, K., Tamai, A., Mori, M., and Hara-Nishimura, I., Stomagen positively regulates stomatal density in Arabidopsis, Nature, 2010, vol. 463, pp. 241–244.
Shimada, T., Sugano, S.S., and Hara-Nishimura, I., Positive and negative peptide signals control stomatal density, Cell. Mol. Life Sci., 2011, vol. 68, pp. 2081–2088.
Murphy, E., Smith, S., and de Smet, I., Small signaling peptides in Arabidopsis development: how cells communicate over a short distance, Plant Cell, 2012, vol. 24, pp. 3198–3217.
Kondo, T., Kajita, R., Miyazaki, A., Hokoyama, M., Nakamura-Miura, T., Mizuno, S., Masuda, Y., Irie, K., Tanaka, Y., Takada, S., Kakimoto, T., and Sakagami, Y., Stomatal density is controlled by a mesophyll-derived signaling molecule, Plant Cell Physiol., 2010, vol. 51, pp. 1–8.
Lin, G., Zhang, L., Han, Z., Yang, X., Liu, W., Li, E., Chang, J., Qi, Y., Shpak, E.D., and Chai, J., A receptor-like protein acts as a specificity switch for the regulation of stomatal development, Genes Dev., 2017, vol. 31, pp. 927–938.
Jewaria, P.K., Hara, T., Tanaka, H., Kondo, T., Betsuyaku, S., Sawa, S., Sakagami, Y., Aimoto, S., and Kakimoto, T., Differential effects of the peptides Stomagen, EPF1 and EPF2 on activation of MAP kinase MPK6 and the SPCH protein level, Plant Cell Physiol., 2013, vol. 54, pp. 1253–1262.
Yang, S.L., Jiang, L., Puah, C.S., Xie, L.F., Zhang, X.Q., Chen, L.Q., Yang, W.C., and Ye, D., Overexpression of TAPETUM DETERMINANT1 alters the cell fates in the Arabidopsis carpel and tapetum via genetic interaction with excess microsporocytes1/extra sporogenous cells, Plant Physiol., 2005, vol. 139, pp. 186–191.
Huang, J., Zhang, T., Linstroth, L., Tillman, Z., Otegui, M.S., Owen, H.A., and Zhao, D., Control of anther cell differentiation by the small protein ligand TPD1 and its receptor EMS1 in Arabidopsis, PLoS Genet., 2016, vol. 12: e1006147.
Li, Z., Wang, Y., Huang, J., Ahsan, N., Biener, G., Paprocki, J., Thelen, J.J., Raicu, V., and Zhao, D., Two SERK receptor-like kinases interact with EMS1 to control anther cell fate determination, Plant Physiol., 2017, vol. 173, pp. 326–337.
Wheeler, M.J., de Graaf, B.H.J., Hadjiosif, N., Perry, R.M., Poulter, N.S., Osman, K., Vatovec, S., Harper, A., Franklin, F.C.H., and Franklin-Tong, V.E., Identification of the pollen self-incompatibility determinant in Papaver rhoeas, Nature, 2009, vol. 459, pp. 992–995.
Lin, Z., Eaves, D.J., Sanchez-Moran, E., Fran-klin, F.C.H., and Franklin-Tong, V.E., The Papaver rhoeas S determinants confer self-incompatibility to Arabidopsis thaliana in planta, Science, 2015, vol. 350, pp. 684–687.
Tang, W., Kelley, D., Ezcurra, I., Cotter, R., and McCormick, S., LeSTIG1, an extracellular binding partner for the pollen receptor kinases LEPRK1 and LEPRK2, promotes pollen tube growth in vitro, Plant J., 2004, vol. 39, pp. 343–353.
Huang, W.J., Liu, H.K., McCormick, S., and Tang, W.H., Tomato pistil factor STIG1 promotes in vivo pollen tube growth by binding to phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and the extracellular domain of the pollen receptor kinase LePRK2, Plant Cell, 2014, vol. 26, pp. 2505–2523.
Márton, M.L., Cordts, S., Broadhvest, J., and Dresselhaus, T., Micropylar pollen tube guidance by egg apparatus 1 of maize, Science, 2005, vol. 307, pp. 573–576.
Uebler, S., Márton, M.L., and Dresselhaus, T., Classification of EA1-box proteins and new insights into their role during reproduction in grasses, Plant Reprod., 2015, vol. 28, pp. 183–197.
Okuda, S., Tsutsui, H., Shiina, K., Sprunck, S., Takeuchi, H., Yui, R., Kasahara, R.D., Hamamura, Y., Mizukami, A., Susaki, D., Kawano, N., Sakakibara, T., Namiki, S., Itoh, K., Otsuka, K., et al., Defensin-like polypeptide LUREs are pollen tube attractants secreted from synergid cell, Nature, 2009, vol. 458, pp. 357–361.
Takeuchi, H. and Higashiyama, T., Tip-localized receptors control pollen tube growth and LURE sensing in Arabidopsis, Nature, 2016, vol. 531, pp. 245–248.
Chae, K. and Lord, E.M., Pollen tube growth and guidance: roles of small, secreted proteins, Ann. Bot., 2011, vol. 108, pp. 627–636.
Tousheh, M., Miroliaei, M., Asghar Rastegari, A., Ghaedi, K., Esmaeili, A., and Matkowski, A., Computational evaluation on the binding affinity of non-specific lipid-transfer protein-2 with fatty acids, Comput. Biol. Med., 2013, vol. 43, pp. 1732–1738.
Sprunck, S., Rademacher, S., Vogler, F., Gheyselinck, J., Grossniklaus, U., and Dresselhaus, T., Egg cell-secreted EC1 triggers sperm cell activation during double fertilization, Science, 2012, vol. 338, pp. 1093–1097.
Mori, T. and Igawa, T., Gamete attachment process revealed in flowering plant fertilization, Plant Signal. Behav., 2014, vol. 9: e977715.
Costa, L.M., Marshall, E., Tesfaye, M., Silverstein, K.A.T., Mori, M., Umetsu, Y., Otterbach, S.L., Papareddy, R., Dickinson, H.G., Boutiller, K., Vandenbosch, K.A., Ohki, S., and Gutierrez-Marcos, J.F., Central cell-derived peptides regulate early embryo patterning in flowering plants, Science, 2014, vol. 344, pp. 168–172.
Musielak, T.J. and Bayer, M., YODA signalling in the early Arabidopsis embryo, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 2014, vol. 42, pp. 408–412.
Corrado, G., Sasso, R., Pasquariello, M., Iodice, L., Carretta, A., Cascone, P., Ariati, L., Digilio, M.C., Guerrieri, E., and Rao, R., Systemin regulates both systemic and volatile signaling in tomato plants, J. Chem. Ecol., 2007, vol. 33, pp. 669–681.
Li, C., Liu, G., Xu, C., Lee, G.I., Bauer, P., Ling, H.Q., Ganal, M.W., and Howe, G.A., The tomato Suppressor of prosystemin-mediated responses2 gene encodes a fatty acid desaturase required for the biosynthesis of jasmonic acid and the production of a systemic wound signal for defense gene expression, Plant Cell, 2003, vol. 15, pp. 1646–1661.
Yamaguchi, Y., Huffaker, A., Bryan, A.C., Tax, F.E., and Ryan, C.A., PEPR2 is a second receptor for the Pep1 and Pep2 peptides and contributes to defense responses in Arabidopsis, Plant Cell, 2010, vol. 22, pp. 508–522.
Wang, Y., Wang, L., Zou, Y., Chen, L., Cai, Z., Zhang, S., Zhao, F., Tian, Y., Jiang, Q., Ferguson, B.J., Gresshoff, P.M., and Li, X., Soybean miR172c targets the repressive AP2 transcription factor NNC1 to activate ENOD40 expression and regulate nodule initiation, Plant Cell, 2014, vol. 26, pp. 4782–4801.
Batut, J., Mergaert, P., and Masson-Boivin, C., Peptide signalling in the rhizobium–legume symbiosis, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 14, pp. 181–187.
Wen, J., Lease, K.A., and Walker, J.C., DVL, a novel class of small polypeptides: overexpression alters Ar-abidopsis development, Plant J., 2004, vol. 37, pp. 668–677.
Ikeuchi, M., Yamaguchi, T., Kazama, T., Ito, T., Horiguchi, G., and Tsukaya, H., ROTUNDIFOLIA4 regulates cell proliferation along the body axis in Ar-abidopsis shoot, Plant Cell Physiol., 2011, vol. 52, pp. 59–69.
Valdivia, E.R., Chevalier, D., Sampedro, J., Taylor, I., Niederhuth, C.E., and Walker, J.C., DVL genes play a role in the coordination of socket cell recruitment and differentiation, J. Exp. Bot., 2012, vol. 63, pp. 1405–1412.
Liu, J., Mehdi, S., Topping, J., Friml, J., and Lindsey, K., Interaction of PLS and PIN and hormonal crosstalk in Arabidopsis root development, Front. Plant Sci., 2013, vol. 4: 75.
Chilley, P.M., Casson, S.A., Tarkowski, P., Hawkins, N., Wang, K.L.-C., Hussey, P.J., Beale, M., Ecker, J.R., Sandberg, G.K., and Lindsey, K., The POLARIS peptide of Arabidopsis regulates auxin transport and root growth via effects on ethylene signaling, Plant Cell, 2006, vol. 18, pp. 3058–3072.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The research was supported by grants from the Russian Science Foundation (project no. 16-16-1001), and the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project nos. 18-04-01017, 15-29-02737, and 18-34-00020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by M. Shulskaya
Supplementary materials are available for this article at 10.1134/S1021443719010072.
Abbreviations: AA—amino acid; CRP—cysteine-rich peptides; LRR-RLK—Leucin Reach Repeats containing Receptor-Like Kinase; NSSP—nonsecreted signal peptides; PTMP—posttranslationally modified peptides; TF—transcription factor.
Supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gancheva, M.S., Malovichko, Y.V., Poliushkevich, L.O. et al. Plant Peptide Hormones. Russ J Plant Physiol 66, 171–189 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443719010072
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443719010072