Abstract
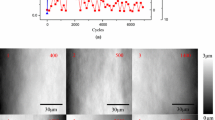
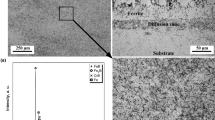
The tribological tests of brass and steel are carried out on an in-situ tribometer. The Stribeck curve illustrates that the roughness and the wear rate as a whole reflect the lubrication regimes. Under boundary lubrication, a mathematical model based on positive pressure and roughness is established. A good agreement between the measurement and the prediction is found. According to the analysis of worn surface morphology, the main wear mechanism of brass is adhesive wear under boundary lubrication, which results in relatively high values of tribological parameters. The oxides strengthening layer is hardly generated under boundary lubrication until the experiment enters the mixed lubrication (ML) and the hydrodynamic lubrication (HL) regimes.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Panagopoulos, C.N., Georgiou, E.P., and Simeonidis, K., Tribol. Int., 2012, vol. 50, pp. 1–5.
Perfilyev, V., Moshkovich, A., Lapsker, I., and Rapoport, L., Tribol. Int., 2010, vol. 43, pp. 1449–1456.
Elleuch, K., Elleuch, R., Mnif, R., Fridrici, V., and Kapsa, P., Tribol. Int., 2006, vol. 39, pp. 290–296.
Zhang, G., Wetzel, B., and Wang, Q., Tribol. Int., 2015, vol. 88, pp. 153–161.
Jenson, A.D., Roy, S., and Sundararajan, S., Tribol. Int., 2018, vol. 118, pp. 1–10.
Fukuda, K. and Morita, T., Wear, 2017, vols. 376–377, pp. 1528–1533.
Sullivan, J.L., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 1986, vol. 19, p. 1999.
Bosman, R. and Schipper, D.J., Tribol. Lett., 2011, vol. 42, pp. 169–178.
Hsu, S.M. and Gates, R.S., Tribol. Int., 2005, vol. 38, pp. 305–312.
Studt, P., Tribol. Int., 1989, vol. 22, pp. 111–119.
Gates, R.S., Jewett, K.L., and Hsu, S.M., ASLE Trans., 1989, vol. 32, pp. 423–430.
Belin, M., Martin, J.M., and Mansot, J.L., ASLE Trans., 1987, vol. 32, pp. 410–413.
Tonck, A., Kapsa, P., and Sabot, J., J. Tribol., 1986, vol. 108, pp. 117–122.
Hsu, S.M. and Klaus, E.E., ASLE Trans., 1979, vol. 22, pp. 135–145.
Stratmann, A., Hentschke, C., and Jacobs, G., Proc. World Tribology Congress 2013, Torino, September 8–13, 2013.
Morina, A. and Neville, A., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2007, vol. 40, p. 5476.
Stratmann, A., Jacobs, G., Hsu, C.-J., Gachot, C., and Burghardt, G., Tribol. Int., 2017, vol. 113, pp. 43–49.
Korres, S. and Dienwiebel, M., Rev. Sci. Instrum., 2010, vol. 81, p. 1545.
Nehl, E., Wear, 1986, vol. 107, pp. 329–341.
Nehl, E., Wear, 1986, vol. 107, pp. 329–341.
Korres, S., Feser, T., and Dienwiebel, M., Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60. pp. 420–429.
Bakoglidis, K.D., Nedelcu, I., Ivanov, I.G., Meeuwenoord, R., Schmidt, S., Janzén, E., et al., Tribol. Int., 2017, vol. 114, pp. 141–151.
Moshkovich, A., Perfilyev, V., Bendikov, T., Lapsker, I., Cohen, H., and Rapoport, L., Acta Mater., 2010, vol. 58, pp. 4685–4692.
Gelinck, E.R.M. and Schipper, D.J., Tribol. Int., 2000, vol. 33, pp. 175–181.
Archard, J.F., J. Appl. Phys., 2004, vol. 24, pp. 981–988.
Toledo, M.L.G.D., Freitas, M.A., Colosimo, E.A., and Gilardoni, G.L., Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf., 2015, vol. 140, pp. 107–115.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Special thanks are extended to Prof. Martin Dienwiebel at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology for their assistance with tribological experiments.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 51601021, 51671037, 51441001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Yang, C., Zhou, J. et al. Study on Wear Model and Adhesive Wear Mechanism of Brass under Boundary Lubrication. Prot Met Phys Chem Surf 57, 367–373 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205121010147
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2070205121010147