Abstract
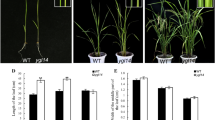
Yellow leaf mutants are useful genetic variants to explore the mechanism of chloroplast development. In this study, we developed and characterized a new rice (Orzya sativa L.) yellow leaf mutant, ygl54, with ethylmethane sulfonate (EMS) treatment on Zhenong 34, which exhibited leaf yellowing at early stage. By map-based cloning, OsYGL54 was located on long arm of chromosome 11 with a physical distance of 26 kb, and the substitution from G to A at the first exon of LOC_Os11g36440 was identified. Silent mutation in subsequent codon of ATG, disturbed the translation initiation, which caused lower expression level of OsYGL54 across the tissues. The histological analysis revealed that the chloroplast of mesophyll cells in ygl54 was disrupted with reduction in size of starch granules and higher number of plastoglobuli, which resulted in decreased chlorophyll contents, lower photosynthetic parameter, and lower expression level of genes associated with pigment metabolism and photosynthesis. The disruption in chloroplast caused higher accumulation of H2O2 and MDA contents. In conclusion, our results revealed the importance of sequence of second codon suggests that OsYGL54 was possibly involved in pigment metabolism and valuable for further study to explore the mechanism of chloroplast development.







Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Richards, R.A., Selectable traits to increase crop photosynthesis and yield of grain crops, J. Exp. Bot., 2000, vol. 51, p. 447.
Eckhardt, U., Grimm, B., and Hörtensteiner, S., Recent advances in chlorophyll biosynthesis and breakdown in higher plants, Plant Mol. Biol., 2004, vol. 56, p. 1.
Miyoshi, K., Ito, Y., Serizawa, A., and Kurata, N., OsHAP3 genes regulate chloroplast biogenesis in rice, Plant J., 2003, vol. 36, p. 532.
Mei, J., Li, F., Liu, X., Hu, G., Fu, Y., and Liu, W., Newly identified CSP41b gene localized in chloroplasts affects leaf color in rice, Plant Sci., 2017, vol. 256, p. 39.
Zhou, K., Ren, Y., Lv, J., Wang, Y., Liu, F., Zhou, F., Zhao, S., Chen, S., Peng, C., Zhang, X., Guo, X., Cheng, Z., Wang, J., Wu, F., Jiang, L., et al., Young Leaf Chlorosis 1, a chloroplast-localized gene required for chlorophyll and lutein accumulation during early leaf development in rice, Planta, 2013, vol. 237, p. 279.
Sakuraba, Y., Kim, E., Han, S.-H., Piao, W., An, G., Todaka, D., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K., and Paek, N., Rice Phytochrome-Interacting Factor-Like1 (OsPIL1) is involved in the promotion of chlorophyll biosynthesis through feed-forward regulatory loops, J. Exp. Bot., 2017, vol. 68, p. 4103.
Wan, C., Li, C., Ma, X., Wang, Y., Sun, C., Huang, R., Zhong, P., Gao, Z., Chen, D., Xu, Z., Zhu J., Gao, X., Wang, P., and Deng, X., GRY79 encoding a putative metallo-β-lactamase-trihelix chimera is involved in chloroplast development at early seedling stage of rice, Plant Cell Rep., 2015, vol. 34, p. 1353.
Wang, Y., Zhong, P., Zhang, X., Liu, J., Zhang, C., Yang, X., Wan, C., Liu, C., Zhou, H., Yang, B., Sun C., Deng, X., and Wang, P., GRA78 encoding a putative S‑sulfocysteine synthase is involved in chloroplast development at the early seedling stage of rice Plant Sci., 2019, vol. 280, p. 321.
Chen, N., Wang, P., Li, C., Wang, Q., Pan, J., Xiao, F., Wang, Y., Zhang, K., Li, C., Yang, B., Sun C., and Deng X., A single nucleotide mutation of the ispe gene participating in the MEP pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis causes a green-revertible yellow leaf phenotype in rice, Plant Cell Physiol., 2018, vol. 59, p. 1905.
Ma, X., Sun, X., Li, C., Huan, R., Sun, C., Wang, Y., Xiao, F., Wang, Q., Chen, P., Ma, F., et al., Map-based cloning and characterization of the novel yellow-green leaf gene ys83 in rice (Oryza sativa), Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2017, vol. 111, p. 1.
Zhou, K., Ren, Y., Zhou, F., Wang, Y., Zhang, L., Lyu, J., Wang, Y., Zhao, S., Ma, W., Zhang, H., Wang, L., Wang, C., Wu, F., Zhang, X., Guo X., et al., Young Seedling Stripe1 encodes a chloroplast nucleoid-associated protein required for chloroplast development in rice seedlings, Planta, 2017, vol. 245, p. 45.
Lyu, J., Wang, Y., Liu, L., Wang, C., Ren, Y., Peng, C., Liu, F., Wang, Y., Niu, M., Wang, D., Zheng, M., Zhou, K., Zhao, S., Wu, F., Wang, H., et al., A putative plastidial adenine nucleotide transporter, BRITTLE1-3, plays an essential role in regulating chloroplast development in rice (Oryza sativa L.), J. Plant Biol., 2017, vol. 60, p. 493.
Zhang, F., Luo, X., Hu, B., Wan, Y., and Xie, J., YGL138(t), encoding a putative signal recognition particle 54 kDa protein, is involved in chloroplast development of rice, Rice, 2013, vol. 6, p. 7.
Wang, Z., Zhang, T., Xing, Y., Zeng, X., Wang, L., Liu, Z., Shi, J., Zhu, X., Ma, L., Li, Y.-F., Ling, Y.-H., Sang, X.-C., and He, G.-H., YGL9, encoding the putative chloroplast signal recognition particle 43 kDa protein in rice, is involved in chloroplast development, J. Integr. Agric., 2016, vol. 15, p. 944.
Arnon, D.I., Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts-polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris, Plant Physiol., 1949, vol. 24, p. 1.
Dong, H., Deng, Y., Mu, J., Lu, Q., Wang, Y., Xu, Y., Chu, C., Chong, K., Lu, C., and Zuo, J., The Arabidopsis Spontaneous Cell Death1 gene, encoding a ζ-carotene desaturase essential for carotenoid biosynthesis, is involved in chloroplast development, photoprotection and retrograde signaling, Cell Res., 2007, vol. 17, p. 458.
Stenström, C.M., Holmgren, E., and Isaksson, L.A., Cooperative effects by the initiation codon and its flanking regions on translation initiation, Gene, 2001, vol. 273, p. 259.
Karimi, Z., Nezafat, N., Negahdaripour, M., Berenjian, A., Hemmati, S., and Ghasemi, Y., The effect of rare codons following the ATG start codon on expression of human granulocyte-colony stimulating factor in Escherichia coli, Protein Expression Purif., 2015, vol. 114, p. 108.
Nilsson, L.O. and Mannervik, B., Improved heterologous expression of human glutathione transferase A4-4 by random silent mutagenesis of codons in the 5' region, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Gen. Subj., 2001, vol. 1528, p. 101.
Akkaya, Ö., Öztürk, S.İ., Bolhuis, A., and Gümüşel, F., Mutations in the translation initiation region of the pac gene resulting in increased levels of activity of penicillin G acylase, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2012, vol. 28, p. 2159.
Bédard, J., Trösch, R., Wu, F., Ling, Q., Flores-Pérez, Ú., Töpel, M., Nawaz, F., and Jarvis, P., Suppressors of the chloroplast protein import mutant reveal a genetic link between protein import and thylakoid biogenesis, Plant Cell, 2017, vol. 29, p. 1726.
Deng, L., Qin, P., Liu, Z., Wang, G., Chen, W., Tong, J., Xiao, L., Tu, B., Sun, Y., Yan, W., He H., Tan J., Chen X., Wang Y., Li S., et al., Characterization and fine-mapping of a novel premature leaf senescence mutant yellow leaf and dwarf 1 in rice, Plant Physiol. Biochem., 2017, vol. 111, p. 50.
Gang, H., Li, R., Zhao, Y., Liu, G., Chen, S., and Jiang, J., Loss of GLK1 transcription factor function reveals new insights in chlorophyll biosynthesis and chloroplast development, J. Exp. Bot., 2019, vol. 70, p. 3125.
Howitt, C.A. and Pogson, B.J., Carotenoid accumulation and function in seeds and non-green tissues, Plant, Cell Environ., 2006, vol. 29, p. 435.
Falcone-Ferreyra, M., Casas, M., Questa, J., Herrera, L., Deblasio, S., Wang, J., Jackson, D., Grotewold, E., and Casati, P., Evolution and expression of tandem duplicated maize flavonol synthase genes, Front. Plant Sci., 2012, vol. 3.
Yao, N. and Greenberg, J.T., Arabidopsis ACCELERATED CELL DEATH2 modulates programmed cell death, Plant Cell, 2006, vol. 18, p. 397.
Apel, K. and Hirt, H., Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction, Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2004, vol. 55, p. 373.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development of China (project no. 2017YFD0100305) and the Science and Technology Office of Zhejiang Province, China (project no. 2016C02050-6).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.K. and X.J. developed and designed the experiments. A.K. conducted the main experiments and wrote the manuscript. C.H.S identified and provided the populations of the ygl54 mutant for the genetic study and carried out the gene mapping. S.J., H.C., M.S., Y.T., Z.C. and J.C. helped to carry out the experiments. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Statement on the welfare of humans or animals. This article does not contain any studies involving animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Abbreviations: APX—ascorbate peroxidase; EMS—ethylmethane sulfonate; POD—peroxidase; ROS—reactive oxygen species; SOD— superoxide dismutase; TEM—transmission electron microscope; WT—wild type plants.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A., Jalil, S., Cao, H. et al. Identification and Fine Mapping of Candidate Gene for Yellow Leaf Mutant (ygl54) Exhibiting Yellow Leaf Colour in Rice. Russ J Plant Physiol 68, 1069–1078 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443721060078
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443721060078