Abstract
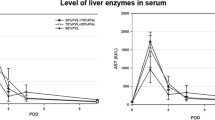
Resection of liver for primary and metastatic tumors and living donor liver transplantation has become a common clinical practice. The success of recovery depends on the regeneration and functions of the remnant liver. However, information on the regenerative potential of liver with steatosis and steatohepatitis, a common clinical problem in this country, is incomplete. Therefore, we evaluated regeneration after two-thirds partial hepatectomy (PH) in male F-344 rats with marked steatosis and mild steatohepatitis induced by feeding choline-deficient diet. Choline-deficient rats and control rats were killed at 24, 36, 48, 72, and 96 h after PH. Liver regeneration was determined by measuring mitotic activity and bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) labeling in hepatocytes. Livers of rats maintained on the choline-deficient diet showed marked steatosis and mild steatohepatitis. In these animals the levels of serum and liver triacylglycerols (TG) were low and very high, respectively, when compared to controls. In control rats mitotic and BrdU labeling indices were maximal at 24 h followed by a rapid decline, whereas in choline-deficient rats both these indices increased significantly at 36 h and decreased gradually over the next 60 h. By 96 h the size of livers in both groups was comparable. The results of this study indicate that regeneration in the liver of rats with marked steatosis is not impaired.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Brown RS, Lake JR: Liver transplantation. Curr Hepatol 16:353–406, 1997
Fong Y, Salo J: Surgical therapy of hepatic colorectal metastasis. Semin Oncol 26:514–523, 1995
Nakagami M, Morimoto T, Itoh K, Arima Y, Yamamoto Y, Ikai I, Yamaoka Y: Patterns of restoration of remnant liver volume after graft harvesting in donors for living related liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 30: 191–199, 1998
Uemoto S, Inomata Y, Sakurai T, Egawa H, Fujita S, Kiuchi T, Hayashi M, Yasutomi M, Yamabe H, Tanaka K: Living donor liver transplantation for fulminant hepatic failure. Transplantation 70:152–157, 2000
Michalopoulos GK, DeFrances MC: Liver regeneration. Science 276:60–66, 1997
Yamanaka N, Okamoto E, Kawamura E, Kato T, Oriyama T, Fujimoto J, Furukawa K, Tanaka T, Tomoda F, Tanaka W: Dynamics of normal and injured human liver regeneration after hepatectomy as assessed on the basis of computed tomography and liver function. Hepatology 18:79–85, 1993
Bucher NLR. Liver regeneration. Then and now. In Liver regeneration and Carcinogenesis. RL Jirtle (ed). New York, Academic Press, 1995; pp 1–25
Diehl AM: Nutrition, hormones, metabolism, and liver regeneration. Semin Liver Dis 11:315–340, 1995
Sandgren EP, Luetteke NC, Palmiter RD, Brinster L, Lee DC: Overexpression of TGF-a in transgenic mice: Induction of epithelial hyperplasia, pancreatic metaplasia and carcinoma of the breast. Cell 61:1121–1135, 1990
Fausto N: Lessons from genetically engineered animal models. V. Knocking out genes to study liver regeneration: Present and future. Am J Physiol 277:G917–G921, 1999
Chou MW, Shaddock JG, Kong J, Hart RW, Casciano DA: Effect of dietary restriction on partial hepatectomy-induced liver regeneration of aged F344 rats. Cancer Lett 91:191–197, 1995
Burt AD, Mutton A, Day CP: Diagnosis and interpretation of steatosis and steatohepatitis. Semin Diag Pathol 15:246–258, 1998
Fong DG, Nehra V, Lindor KD, Buchman AL: Metabolic and nutritional considerations in nonalcoholic fatty liver. Hepatology 32:3–9, 2000
Kuczmarski RJ, Carroll MD, Flegal KM, Troiano RP: Varying body mass index cutoff points to describe overweight prevelance among US adults. NHANES 111 (1988-1994). Obes Res 5:542–548, 1997
Bellentani S, Saccocio G, Masutti, Croce LS, Brandi G, Sasso F, Cristanini G: Prevalence of and risk factors for hepatic steatosis in northern Italy. Ann Intern Med 132:112–117, 2000
Todo S, Demetris AJ, Makowka L, Teperman L, Podesta L, Shaver T, Tzakis A, Starzl TE: Primary nonfunction of hepatic allografts with preexisting fatty infiltration. Transplantation 47:903–905, 1989
Adam A, Reynes M, Johann M, Morino M, Astarcioglu I, Kafetzis I, Castaing D, Bismuth H: The outcome of steatotic grafts in liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 23:1538–1540, 1991
Teramoto K, Bowers JL, Khettry U, Palombo JD, Clouse ME: A rat fatty liver transplant model. Transplantation 55:737–741, 1993
Higgins GM, Anderson RM: Experimental pathology of the liver: Restoration of the liver in the white rat following partial removal. Arch Pathol 12:186–202, 1931
Hashimoto T, Cook WS, Qi C, Yeldandi AV, Reddy JK, Rao MS: Defect in peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α-inducible fatty acid oxidation determines the severity of hepatic steatosis in response to fasting. J Biol Chem 275:28918–28928, 2000
Ledda-Columbano GM, Pibiri, Loi R, Perra A, Shinozuka H, Columbano A: Early increase in cyclin-D1 expression and accelerated entry of mouse hepatocytes into S phase after administration of the mitogen 1,4-bis[2-(3,5-dichloropyridyloxy)] benzene. Am J Pathol 156:91–97, 2000
Behrns KE, Tsiotos GG, DeSouza NF, Krishna MK, Ludwig J, Nagorney M: Hepatic steatosis as a potential risk factor for major hepatic resection. J Gastrointest Surg 2:292–298, 1998
Selzner M, Clavien P: Failure of regeneration of the steatotic rat liver: Disruption at two different levels in the regeneration pathway. Hepatology 31:35–42, 2000
Zhang B, Weltman M, Farrell GC: Does steatohepatitis impair liver regeneration? A study in a dietary model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14:133–137, 1999
MacDonald RA, Rogers AE, Pechet G: Regeneration of the liver. Relation of regenerative response to size of partial hepatectomy. Lab Invest 11:544–548, 1962
Goshal AK, Ahluwalia M, Farber E: The rapid induction of liver cell death in rats fed a choline-deficient methionine-low diet. Am J Pathol 113:309–314, 1983
Ghoshal AK, Farber E: Choline deficiency, lipotrope deficiency and the development of liver disease including liver cancer: A new perspective. Lab Invest 68:255–260, 1993
Yao Z, Vance D: The active synthesis of phosphatidylcholine is required for very low density lipoprotein secretion from rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 263:2998–3004, 1988
Day CP, James OFW: Hepatic steatosis: Innocent bystander or guilty party? Hepatology 27:1463–1465, 1998.
Bloomstrand R, Kager L, Lautto O: Studies on the ethanol induced decrease of acid oxidation in rat and human liver slices. Life Sci 13:1131–1141, 1973
Rao MS, Reddy JK: Cell and tissue adaptation. In Cellular and Molecular Pathogenesis AE Sirica (ed). New York, Lippincott-Raven, publishers. 1996, pp 57–77
Sherlock S: Alcoholic liver disease. Lancet 345:227–229, 1995
Fromenty B, Pessayre D: Inhibition of mitochondrial beta oxidation as a mechanism of hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol Ther 67:101–154, 1995
Reddy JK, Mannaerts GP: Peroxisomal lipid metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 14:343–370, 1994
Rao MS, Reddy JK: The effect of microvesicular fatty change on liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy. Hepato-Gastroenterology 47:912–915, 2000
Yang SQ, Lin HZ, Yin M, Albrecht JH, Diehl AM: Effect of chronic ethanol consumption on cytokine regulation of liver regeneration. Am J Physiol 275:G696–G704, 1998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, M., Papreddy, K., Abecassis, M. et al. Regeneration of Liver with Marked Fatty Change Following Partial Hepatectomy in Rats. Dig Dis Sci 46, 1821–1826 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010654908938
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010654908938