Abstract
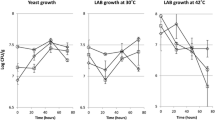
Nutrients can be made bioavailable in foods through fermentation of such foods either spontaneously or via starter cultures with consequent reduction in antinutrients. The effect of fermentation time on the microbiological properties, anti-nutritional and nutritional contents of malted acha (Digitaria exilis) flour fermented spontaneously and using starter culture was studied. Malted acha flour was fermented spontaneously and using starter culture for 72 and 48 h respectively. Two screened lactic acid bacteria with the best probiotic potential were employed from 11 bacteria isolates after they were identified using molecular method. Microbiological, antinutritional and nutritional analyses of the fermented products was performed using standard methods. There were decreases in aerobic bacteria and lactic acid bacteria counts after 72 h fermentation period with a converse increase in yeast count of the fermenting slurry during the same period. For spontaneously fermented acha flour, increases in values at P < 0.05 were recorded for crude protein (9.67 ± 0.03 to 10.80 ± 0.06%), crude fat (1.07 ± 0.03 to 1.23 ± 0.03%), moisture content (8.47 ± 0.09 to 8.53 ± 0.07%), and ash content (1.30 ± 0.06 to 1.37 ± 0.09%), within 48 h fermentation time and decreased by 72 h. Also, the mineral and vitamin contents increased with increase with fermentation time. However, decreases in values were recorded for carbohydrate content (77.30 ± 0.06 to 76.30 ± 0.11%) and crude fibre (2.20 ± 0.06 to 1.73 ± 0.03%) at 48 h and 72 h fermentation time respectively. The pH and antinutritional factors decreased with increase in fermentation time while the titratable acidity decreased. For starter culture fermentation, sample J which consist of the blend fermented with single starter (Lactobacillus plantarum), gave the highest yield for crude fat and moisture content (8.77 ± 0.09%) after 48 h fermentation period. The bioavailability of nutrients in the acha flour increased with fermentation time compared to the unfermented flour at 0 h fermentation time at P < 0.05. Starter fermentation of acha flour with lactic acid bacteria can be used to improve the proximate composition of acha flour which can be utilized as breakfast cereal.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Abedi, E., Hashemi, S.M.B.: Lactic acid production—producing microorganisms and substrates sources-state of art. Heliyon 6(10), e04974 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04974
Abiola Oso, A., Omotayo Ashafa, A.: Nutritional composition of grain and seed proteins. In: Grain and seed proteins functionality. IntechOpen (2021)
Adams, D.M., Yakubu, M.T.: Aqueous extract of Digitaria exilis grains ameliorate diabetes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic male Wistar rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 249, 112383 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2019.112383
Adebo, J.A., Njobeh, P.B., Gbashi, S., Oyedeji, A.B., Ogundele, O.M., Oyeyinka, S.A., Adebo, O.A.: Fermentation of cereals and legumes: impact on nutritional constituents and nutrient bioavailability. Fermentation 8(2), 63 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8020063
Adejuyitan, Otunola, J.A., Akande, E.T., Bolarinwa, E.A., Oladokun, I.F.: Some physicochemical properties of flour obtained from fermentation of tigernut (Cyperus esculentus) sourced from a market in Ogbomoso, Nigeria. Afr. J. Food Sci. 3(2), 51–055 (2009)
Ahn, J.Y., Kil, D.Y., Kong, C., Kim, B.G.: Comparison of oven-drying methods for determination of moisture content in feed ingredients. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 27(11), 1615–1622 (2014). https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.2014.14305
Akpoghelie, P.O., Edo, G.I., Akhayere, E.: Proximate and nutritional composition of beer produced from malted sorghum blended with yellow cassava. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 45, 102535 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2022.102535
Ariff, S., Saddiq, K., Khalid, J., Sikanderali, L., Tariq, B., Shaheen, F., et al.: Determinants of infant and young complementary feeding practices among children 6–23 months of age in urban Pakistan: a multicenter longitudinal study. BMC Nutr. 6(1), 75 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-020-00401-3
Aspri, M., Papademas, P., Tsaltas, D.: Review on non-dairy probiotics and their use in non-dairy based products. Fermentation 6(1), 30 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6010030
Averianova, L.A., Balabanova, L.A., Son, O.M., Podvolotskaya, A.B., Tekutyeva, L.A.: Production of vitamin B2 (riboflavin) by microorganisms: an overview. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. (2020). https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.570828
Babarinde, G.O., Adeyanju, J.A., Ogunleye, K.Y., Adegbola, G.M., Ebun, A.A., Wadele, D.: Nutritional composition of gluten-free flour from blend of fonio (Digitaria iburua) and pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan) and its suitability for breakfast food. J. Food Sci. Technol. 57(10), 3611–3620 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04393-7
Bartzatt, R., Wol, T.: Detection and assay of vitamin B-2 (riboflavin) in alkaline borate buffer with UV/Visible spectrophotometry. Int. Scholarly Res. Notices 2014, 1–7 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/453085
Bazine, T., Arslanoğlu, ŞF.: Tiger nut (cyperus esculentus); morphology, products, uses and health benefits. BSJ Agric. 3(4), 324–328 (2020)
Becerra, S.C., Roy, D.C., Sanchez, C.J., Christy, R.J., Burmeister, D.M.: An optimized staining technique for the detection of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria within tissue. BMC. Res. Notes 9(1), 216 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-016-1902-0
Campana, R., van Hemert, S., Baffone, W.: Strain-specific probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria and their interference with human intestinal pathogens invasion. Gut Pathogens 9(1), 12 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13099-017-0162-4
Cannas, D., Loi, E., Serra, M., Firinu, D., Valera, P., Zavattari, P.: Relevance of essential trace elements in nutrition and drinking water for human health and autoimmune disease risk. Nutrients 12(7), 2074 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12072074
Çatak, J.: Determination of niacin profiles in some animal and plant based foods by high performance liquid chromatography: association with healthy nutrition. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 61(3), 138–146 (2019). https://doi.org/10.5187/jast.2019.61.3.138
Chadare, F.J., Idohou, R., Nago, E., Affonfere, M., Agossadou, J., Fassinou, T.K., et al.: Conventional and food-to-food fortification: an appraisal of past practices and lessons learned. Food Sci. Nutr. 7(9), 2781–2795 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.1133
Danchik, C., Casadevall, A.: Role of cell surface hydrophobicity in the pathogenesis of medically-significant fungi. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2020.594973
Darkoh, C., Chappell, C., Gonzales, C., Okhuysen, P.: A rapid and specific method for the detection of indole in complex biological samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81(23), 8093–8097 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02787-15
Das, A.K., Islam, M.N., Faruk, M.O., Ashaduzzaman, M., Dungani, R.: Review on tannins: extraction processes, applications and possibilities. S. Afr. J. Bot. 135, 58–70 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2020.08.008
Dereje, B., Girma, A., Mamo, D., Chalchisa, T.: Functional properties of sweet potato flour and its role in product development: a review. Int. J. Food Prop. 23(1), 1639–1662 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2020.1818776
Deriu, A.G., Vela, A.J., Ronda, F.: Techno-functional and gelling properties of acha (Fonio) (Digitaria exilis stapf) flour: a study of its potential as a new gluten-free starch source in industrial applications. Foods 11(2), 183 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11020183
Dimidi, E., Cox, S., Rossi, M., Whelan, K.: Fermented foods: definitions and characteristics, impact on the gut microbiota and effects on gastrointestinal health and disease. Nutrients 11(8), 1806 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11081806
Edo, G.I.: Antibacterial, phytochemical and GC-MS analysis of Thevetia peruviana extracts: an approach in drug formulation. Nat. Resour. Human Health. (2022a). https://doi.org/10.53365/nrfhh/146543
Edo, G.I.: Effects of paraquat dichloride on adult male wistar rat: an approach in the toxicity of body weights and hematological tissues. J. Anal. Pharm Res. 11(1), 1–7 (2022b). https://doi.org/10.15406/japlr.2022.11.00394
Edo, G.I., Makinde, M.G., Nwosu, L.C., Ozgor, E., Akhayere, E.: Physicochemical and pharmacological properties of palm oil: an approach for quality, safety, and nutrition evaluation of palm oil. Food Anal. Methods (2022a). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-022-02293-4
Edo, G.I., Onoharigho, F.O., Akpoghelie, P.O., Emakpor, O.L., Ozgor, E., Akhayere, E.: Physicochemical, phytochemical, antioxidant, and inhibition properties of key enzymes linked to raw and regular honey. Chemistry Africa (2022b). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-022-00401-9
Evanovich, E., de Souza Mendonça Mattos, P.J., Guerreiro, J.F.: Comparative genomic analysis of lactobacillus plantarum: an overview. Int. J. Genom. 2019, 1–11 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/4973214
Forsido, S.F., Hordofa, A.A., Ayelign, A., Belachew, T., Hensel, O.: Effects of fermentation and malt addition on the physicochemical properties of cereal based complementary foods in Ethiopia. Heliyon 6(7), e04606 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04606
Forte, E., Borisov, V.B., Falabella, M., Colaço, H.G., Tinajero-Trejo, M., Poole, R.K., et al.: The terminal oxidase cytochrome bd promotes sulfide-resistant bacterial respiration and growth. Sci. Rep. 6(1), 23788 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23788
Gan, L., Zhou, L.-L., Li, X.-X., Yue, Y.-R.: Dietary leucine requirement of Juvenile Nile tilapia,Oreochromis Niloticus. Aquacult. Nutr. 22(5), 1040–1046 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12353
Garibyan, L., Avashia, N.: Polymerase chain reaction. J. Investig. Dermatol. 133(3), 1–4 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2013.1
Gentili, R., Ambrosini, R., Montagnani, C., Caronni, S., Citterio, S.: Effect of soil pH on the growth, reproductive investment and pollen allergenicity of Ambrosia artemisiifolia L. Front. Plant Sci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01335
Gupta, N.: DNA extraction and polymerase chain reaction. J. Cytol. 36(2), 116 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4103/JOC.JOC_110_18
Hadwan, M.H.: Simple spectrophotometric assay for measuring catalase activity in biological tissues. BMC Biochem. 19(1), 7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12858-018-0097-5
Han, S., Lu, Y., Xie, J., Fei, Y., Zheng, G., Wang, Z., et al.: Probiotic gastrointestinal transit and colonization after oral administration: a long journey. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.609722
Handa, V., Kumar, V., Panghal, A., Suri, S., Kaur, J.: Effect of soaking and germination on physicochemical and functional attributes of horsegram flour. J. Food Sci. Technol. 54(13), 4229–4239 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-017-2892-1
Hassan, F., Edo, G.I., Nwosu, L.C., Jalloh, A.A., Onyibe, P.N., Itoje-akpokiniovo, L.O., Irogbo, P.U.: An inventory of medicinal plants used as sedative, analgesic and blood tonic in Abeokuta, Ogun State, Nigeria. Acta Ecol. Sinica. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chnaes.2021.11.003
Ibrahim, A., Alghannam, A., Eissa, A., Firtha, F., Kaszab, T., Kovacs, Z., Helyes, L.: Preliminary study for inspecting moisture content, dry matter content, and firmness parameters of two date cultivars using an NIR hyperspectral imaging system. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. (2021a). https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.720630
Ibrahim, S.A., Ayivi, R.D., Zimmerman, T., Siddiqui, S.A., Altemimi, A.B., Fidan, H., et al.: Lactic acid bacteria as antimicrobial agents: food safety and microbial food spoilage prevention. Foods 10(12), 3131 (2021b)
Jafarpour, D., Hashemi, S.M.B.: Pure and co-fermentation of quinoa seeds by Limosilactobacillus fermentum and Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus: bioactive content, antidiabetic and antioxidant activities. Fermentation 9(2), 80 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020080
Jideani, I.A., Jideani, V.A.: Developments on the cereal grains Digitaria exilis (acha) and Digitaria iburua (iburu). J. Food Sci. Technol. 48(3), 251–259 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-010-0208-9
Jin, Q., Kirk, M.F.: pH as a primary control in environmental microbiology: 1—thermodynamic perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2018.00021
KG, A., SD, K., GR, P.: Studies on formulation and quality evaluation of weaning food from sorghum malt. Pharma. Innov. 10(3), 107–113 (2021). https://doi.org/10.22271/tpi.2021.v10.i3b.5924
Khalid, N., Ahmed, A., Bhatti, M.S., Randhawa, M.A., Ahmad, A., Rafaqat, R.: A question mark on zinc deficiency in 185 million people in Pakistan—possible way out. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 54(9), 1222–1240 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2011.630541
Kibr, G.: A narrative review of nutritional malpractices, motivational drivers, and consequences in pregnant women: evidence from recent literature and program implications in Ethiopia. Sci. World J. 2021, 1–11 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5580039
Kusada, H., Morinaga, K., Tamaki, H.: Identification of bile salt hydrolase and bile salt resistance in a probiotic bacterium lactobacillus gasseri JCM1131T. Microorganisms 9(5), 1011 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9051011
Li, F., Xiong, X.-S., Yang, Y.-Y., Wang, J.-J., Wang, M.-M., Tang, J.W., et al.: Effects of NaCl concentrations on growth patterns, phenotypes associated with virulence, and energy metabolism in Escherichia coli BW25113. Front. Microbiol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.705326
Liptáková, D., Matejčeková, Z., Valík, L.: Lactic acid bacteria and fermentation of cereals and pseudocereals. In: Fermentation processes. InTech (2017)
Marjanovic, A., Djedjibegovic, J., Lugusic, A., Sober, M., Saso, L.: Multivariate analysis of polyphenolic content and in vitro antioxidant capacity of wild and cultivated berries from Bosnia and Herzegovina. Sci. Rep. 11(1), 19259 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98896-8
Mashau, M.E., Maliwichi, L.L., Jideani, A.I.O.: Non-alcoholic fermentation of Maize (Zea mays) in Sub-Saharan Africa. Fermentation 7(3), 158 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030158
Mendonça, A.A., de Paula Pinto-Neto, W., da Paixão, G.A., da Silva Santos, D., De Morais, M.A., De Souza, R.B.: Journey of the probiotic bacteria: survival of the fittest. Microorganisms 11(1), 95 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11010095
Moyo, M., Amoo, S.O., Aremu, A.O., Gruz, J., Šubrtová, M., Jarošová, M., et al.: Determination of mineral constituents, phytochemicals and antioxidant qualities of cleome gynandra, compared to Brassica oleracea and Beta vulgaris. Front. Chem. (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2017.00128
Naves, L.P., Rodrigues, P.B., Bertechini, A.G., Corrêa, A.D., de Oliveira, D.H., de Oliveira, E.C., Duarte, W.F., da Cunha, M.R.R.: Comparison of methodologies to quantify phytate phosphorus in diets containing phytase and excreta from broilers. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 27(7), 1003–1012 (2014). https://doi.org/10.5713/ajas.2013.13538
Niaz, K., Khan, F., Shah, M.A.: Analysis of carbohydrates (monosaccharides, polysaccharides). In: Recent advances in natural products analysis, pp. 621–633. Elsevier (2020)
Nkhata, S.G., Ayua, E., Kamau, E.H., Shingiro, J.-B.: Fermentation and germination improve nutritional value of cereals and legumes through activation of endogenous enzymes. Food Sci. Nutr. 6(8), 2446–2458 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.846
Nwaoha, M.: Production and quality assessment of gluten-free and nutrient-dense biscuit from acha, pigeon pea and sweet potato blends. Int. J. Food Nutr. Sci 2(4), 1–11 (2015). https://doi.org/10.15436/2377-0619.15.030
Nwosu, L.C., Edo, G.I., Ozgor, E.: The phytochemical, proximate, pharmacological, GC-MS analysis of Cyperus esculentus (Tiger nut): a fully validated approach in health, food and nutrition. Food Biosci. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101551
Obafemi, Y.D., Oranusi, S.U., Ajanaku, K.O., Akinduti, P.A., Leech, J., Cotter, P.D.: African fermented foods: overview, emerging benefits, and novel approaches to microbiome profiling. NPJ Sci. Food 6(1), 15 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41538-022-00130-w
Ogodo, A.C., Ugbogu, O.C., Onyeagba, R.A., Okereke, H.C.: Microbiological quality, proximate composition and in vitro starch/protein digestibility of Sorghum bicolor flour fermented with lactic acid bacteria consortia. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 6(1), 7 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40538-019-0145-4
Ojide, M.G., Adegbite, S., Tran, T., Taborda, L.A., Chapuis, A., Lukombo, S., et al.: Processors’ experience in the use of flash dryer for cassava-derived products in Nigeria. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2021.771639
Olagunju, A.I., Arigbede, T.I., Makanjuola, S.A., Oyebode, E.T.: Nutritional compositions, bioactive properties, and in vivo glycemic indices of amaranth-based optimized multigrain snack bar products. Measurement: Food 7, 100039 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meafoo.2022.100039
Olayemi Raji, A.: Utilization of starch in food and allied industries in africa: challenges and prospects. In: Innovation in the food sector through the valorization of food and agro-food by-products. IntechOpen (2021)
Olsen, T., Øvrebø, B., Haj-Yasein, N., Lee, S., Svendsen, K., Hjorth, M., et al.: Effects of dietary methionine and cysteine restriction on plasma biomarkers, serum fibroblast growth factor 21, and adipose tissue gene expression in women with overweight or obesity: a double-blind randomized controlled pilot study. J. Transl. Med. 18(1), 122 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-020-02288-x
Olson, R., Gavin-Smith, B., Ferraboschi, C., Kraemer, K.: Food fortification: the advantages, disadvantages and lessons from sight and life programs. Nutrients 13(4), 1118 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041118
Onuoha, O.G., Chibuzo, E., Badau, M.: Studies on the potential of malted Digitaria exilis, Cyperus esculentus and Colocasia esculenta flour blends as weaning food formulation. Niger. Food J. 32(2), 40–47 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0189-7241(15)30116-8
Ospina-Rojas, I.C., Pozza, P.C., Rodrigueiro, R.J.B., Gasparino, E., Khatlab, A.S., Murakami, A.E.: High leucine levels affecting valine and isoleucine recommendations in low-protein diets for broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 99(11), 5946–5959 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2020.08.053
Pereira, N., Alegria, C., Aleixo, C., Martins, P., Gonçalves, E.M., Abreu, M.: Selection of autochthonous LAB strains of unripe green tomato towards the production of highly nutritious lacto-fermented ingredients. Foods 10(12), 2916 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10122916
Pisoschi, A.M., Danet, A.F., Kalinowski, S.: Ascorbic acid determination in commercial fruit juice samples by cyclic voltammetry. J. Autom. Methods Manage. Chem. 2008, 1–8 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/937651
Revuelta, J.L., Buey, R.M., Ledesma-Amaro, R., Vandamme, E.J.: Microbial biotechnology for the synthesis of (pro)vitamins, biopigments and antioxidants: challenges and opportunities. Microb. Biotechnol. 9(5), 564–567 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12379
Ruiz, L., Margolles, A., Sánchez, B.: Bile resistance mechanisms in Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Front. Microbiol. (2013). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2013.00396
Samtiya, M., Aluko, R.E., Dhewa, T.: Plant food anti-nutritional factors and their reduction strategies: an overview. Food Product. Process. Nutr. 2(1), 6 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43014-020-0020-5
Sharma, R., Garg, P., Kumar, P., Bhatia, S.K., Kulshrestha, S.: Microbial fermentation and its role in quality improvement of fermented foods. Fermentation 6(4), 106 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6040106
Shvartsman, E., Richmond, M.E.I., Schellenberg, J.J., Lamont, A., Perciani, C., Russell, J.N.H., et al.: Comparative analysis of DNA extraction and PCR product purification methods for cervicovaginal microbiome analysis using cpn60 microbial profiling. PLoS ONE 17(1), e0262355 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0262355
Smith, L.C., Haddad, L.: Reducing child undernutrition: past drivers and priorities for the post-MDG era. World Dev. 68, 180–204 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2014.11.014
Somashekaraiah, R., Shruthi, B., Deepthi, B.V., Sreenivasa, M.Y.: Probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from neera: a naturally fermenting coconut palm nectar. Front. Microbiol. (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01382
Stefańska, I., Kwiecień, E., Jóźwiak-Piasecka, K., Garbowska, M., Binek, M., Rzewuska, M.: Antimicrobial susceptibility of lactic acid bacteria strains of potential use as feed additives—the basic safety and usefulness criterion. Front. Vet. Sci. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2021.687071
Succi, M., Tremonte, P., Reale, A., Sorrentino, E., Grazia, L., Pacifico, S., Coppola, R.: Bile salt and acid tolerance of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains isolated from Parmigiano Reggiano cheese. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 244(1), 129–137 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2005.01.037
Syed-Ab-Rahman, S.F., Carvalhais, L.C., Chua, E., Xiao, Y., Wass, T.J., Schenk, P.M.: Identification of soil bacterial isolates suppressing different phytophthora spp. and promoting plant growth. Front. Plant Sci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01502
Tamang, J.P., Shin, D.-H., Jung, S.-J., Chae, S.-W.: Functional properties of microorganisms in fermented foods. Front. Microbiol. (2016). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00578
Thiex, N.J., Anderson, S., Gildemeister, B., Adcock, W., Boedigheimer, J., Bogren, E., et al.: Crude fat, diethyl ether extraction, in feed, cereal grain, and forage (randall/soxtec/submersion method): collaborative study. J. AOAC Int. 86(5), 888–898 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoac/86.5.888
Tsafrakidou, P., Michaelidou, A.-M., Biliaderis, C.G.: Fermented cereal-based products: nutritional aspects, possible impact on gut microbiota and health implications. Foods 9(6), 734 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9060734
Tsegay, Z.T.: Total titratable acidity and organic acids of wines produced from cactus pear (Opuntia-ficus-indica) fruit and Lantana camara (L. Camara) fruit blended fermentation process employed response surface optimization. Food Sci. Nutr. 8(8), 4449–4462 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.1745
Venturini Copetti, M.: Yeasts and molds in fermented food production: an ancient bioprocess. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 25, 57–61 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2019.02.014
Verni, M., Rizzello, C.G., Coda, R.: Fermentation biotechnology applied to cereal industry by-products: nutritional and functional insights. Front. Nutr. (2019). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2019.00042
Verni, M., Pontonio, E., Montemurro, M., Giuseppe Rizzello, C.: Fermentation as strategy for improving nutritional, functional, technological, and sensory properties of legumes. In: Legumes, volume 2 [working title]. IntechOpen (2022)
Wang, R., Hartel, R.W.: Citric acid and heating on gelatin hydrolysis and gelation in confectionery gels. Food Hydrocoll. 129, 107642 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107642
Wang, Y., Wu, J., Lv, M., Shao, Z., Hungwe, M., Wang, J., et al.: Metabolism characteristics of lactic acid bacteria and the expanding applications in food industry. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2021.612285
Wang, N., Xiong, Y., Wang, X., Guo, L., Lin, Y., Ni, K., Yang, F.: Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on fermentation quality and anti-nutritional factors of paper mulberry silage. Fermentation 8(4), 144 (2022a). https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040144
Wang, W., Tan, Z., Gu, L., Ma, H., Wang, Z., Wang, L., et al.: Dynamics changes of microorganisms community and fermentation quality in soybean meal prepared with lactic acid bacteria and artemisia argyi through fermentation and aerobic exposure processes. Foods 11(6), 795 (2022b)
Whitfield, K.C., Bourassa, M.W., Adamolekun, B., Bergeron, G., Bettendorff, L., Brown, K.H., et al.: Thiamine deficiency disorders: diagnosis, prevalence, and a roadmap for global control programs. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1430(1), 3–43 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.13919
Xu, M., Li, J., Shu, Q., Tang, M., Zhang, X., Yang, T., et al.: Enhancement of l -arginine production by increasing ammonium uptake in an AmtR-deficient Corynebacterium crenatum mutant. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 46(8), 1155–1166 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-019-02204-3
Yakubu, C.M., Sharma, R., Sharma, S., Singh, B.: Influence of alkaline fermentation time on in vitro nutrient digestibility, bio- & techno-functionality, secondary protein structure and macromolecular morphology of locust bean (Parkia biglobosa) flour. LWT 161, 113295 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113295
Zhang, W., Liu, M., Dai, X.: Biological characteristics and probiotic effect of Leuconostoc lactis strain isolated from the intestine of black porgy fish. Braz. J. Microbiol. 44(3), 685–691 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822013005000053
Ziarno, M., Cichońska, P.: Lactic acid bacteria-fermentable cereal- and pseudocereal-based beverages. Microorganisms 9(12), 2532 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9122532
Zulkhairi, A.M., Razali, M., Umikalsum, M.B., Norfaizal, G.M., Athirah, A.A., Aisyah, M.N.S.: Determination of oxalates in corms of selected taro (Colocasia esculenta) varieties in malaysia using ultra high-performance liquid chromatography. Asian J. Chem. Sciences 1, 28–37 (2020). https://doi.org/10.9734/ajocs/2020/v7i319023
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HH, PO, GE, FO, JO were responsible for the conception and design of the study. PO, GE, HH, performed data collection. FO, GE, PO performed data analysis and drafted the article. GE, HH supervised the study, contributed to data analysis, interpretation, and critical revisions. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hwabejire, H.O., Akpoghelie, P.O., Edo, G.I. et al. Microbiological properties, anti-nutritional and nutritional composition of spontaneously and starter culture fermented malted acha flour. Proc.Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 90, 55–74 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43538-023-00219-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43538-023-00219-0