Abstract
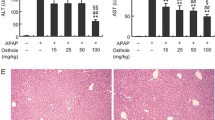
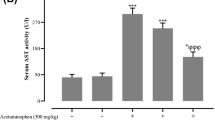
Acetaminophen-induced drug-induced acute liver injury is a liver disease which is one of the most serious human health diseases. Dehydroandrographolide is a natural product found in Andrographis paniculata (Burm.f.) Wall., Acanthaceae, with therapeutical uses such as analgesic and hepatoprotective. The present study was designed to analyze the effect of dehydroandrographolide on acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. The results showed that dehydroandrographolide attenuated the damage caused by acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure in C57BL/6 mice through a decreased level of serum aspartate aminotransferase and glutamic-pyruvic transaminase. In addition, dehydroandrographolide increased the levels of glutathione and significantly increased serum superoxide dismutase. In vitro, dehydroandrographolide significantly activating nuclear-related factor 2, glutamate-cysteine ligase, glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier, heme oxygenase-1, and NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 proteins promoted the phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and 5′ adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase (α and β), inhibited the phosphorylation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase, serine/threonine kinase, and mammalian target of rapamycin. These results suggest that dehydroandrographolide can improve acetaminophen-induced drug-induced acute liver failure in mice.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, [F. H], upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmedy OA, Salem HH, Sayed NH, Ibrahim SM (2022) Naringenin affords protection against lipopolysaccharide/d-galactosamine-induced acute liver failure: role of autophagy. Arch Biochem Biophys 717:109121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2022.109121
Allaire M, Rautou PE, Codogno P, Lotersztajn S (2019) Autophagy in liver diseases: time for translation? J Hepatol 70:985–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.01.026
Bernal W, Auzinger G, Dhawan A, Wendon J (2010) Acute liver failure. Lancet 376:190–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60274-7
Brodsky M, Hirsh S, Albeck M, Sredni B (2009) Resolution of inflammation-related apoptotic processes by the synthetic tellurium compound, AS101 following liver injury. J Hepatol 51:491–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2009.04.024
Cai W, Wen H, Zhou Q, Wu L, Chen Y, Zhou H, Jin M (2020) 14-Deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide inhibits apoptosis in influenza A(H5N1) virus-infected human lung epithelial cells via the caspase-9-dependent intrinsic apoptotic pathway which contributes to its antiviral activity. Antiviral Res 181:104885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104885
Carvalho NR, Tassi CC, Dobraschinski F, Amaral GP, Zemolin AP, Golombieski RM, Dalla Corte CL, Franco JL, Mauriz JL, Gonzalez-Gallego J, Soares FA (2017) Reversal of bioenergetics dysfunction by diphenyl diselenide is critical to protection against the acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Life Sci 180:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.05.012
Chaikijurajai T, Tang WHW (2020) Myeloperoxidase: a potential therapeutic target for coronary artery disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets 24:695–705. https://doi.org/10.1080/14728222.2020.1762177
Chao X, Wang H, Jaeschke H, Ding WX (2018) Role and mechanisms of autophagy in acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Liver Int 38:1363–1374. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.13866
Fisher ES, Curry SC (2019) Evaluation and treatment of acetaminophen toxicity. Adv Pharmacol 85:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apha.2018.12.004
Fruman DA, Meyers RE, Cantley LC (1998) Phosphoinositide kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 67:481–507. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.481
Hsieh MJ, Chen JC, Yang WE, Chien SY, Chen MK, Lo YS, Hsi YT, Chuang YC, Lin CC, Yang SF (2017) Dehydroandrographolide inhibits oral cancer cell migration and invasion through NF-kappaB-, AP-1-, and SP-1-modulated matrix metalloproteinase-2 inhibition. Biochem Pharmacol 130:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2017.01.011
Jadhav AK, Karuppayil SM (2021) Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f) Wall ex Nees: Antiviral properties. Phytother Res 35:5365–5373. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7145
Jaeschke H, Williams CD, Mcgill MR, Xie Y, Ramachandran A (2013) Models of drug-induced liver injury for evaluation of phytotherapeutics and other natural products. Food Chem Toxicol 55:279–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.12.063
Jaeschke H, Akakpo JY, Umbaugh DS, Ramachandran A (2020) Novel therapeutic approaches against acetaminophen-induced liver injury and acute liver failure. Toxicol Sci 174:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfaa002
Jiang Z, Yang X, Han Y, Li J, Hu C, Liu C, Xiao W (2022) Sarmentosin promotes USP17 and regulates Nrf2-mediated mitophagy and cellular oxidative stress to alleviate APAP-induced acute liver failure. Phytomedicine 104:154337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154337
Lee DH, Park JS, Lee YS, Han J, Lee DK, Kwon SW, Han DH, Lee YH, Bae SH (2020) SQSTM1/p62 activates NFE2l2/NRF2 via ULK1-mediated autophagic KEAP1 degradation and protects mouse liver from lipotoxicity. Autophagy 16:1949–1973. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1712108
Li Y, Lu L, Luo N, Wang YQ, Gao HM (2017) Inhibition of PI3K/AKt/mTOR signaling pathway protects against D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide-induced acute liver failure by chaperone-mediated autophagy in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 92:544–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.037
Li C, Ming Y, Wang Z, Xu Q, Yao L, Xu D, Tang Y, Lei X, Li X, Mao Y (2019) GADD45alpha alleviates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by promoting AMPK activation. Cell Mol Life Sci 76:129–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-018-2912-y
Lu Z, Xie P, Zhang D, Sun P, Yang H, Ye J, Cao H, Huo C, Zhou H, Chen Y, Ye W, Yu L, Liu J (2018) 3-Dehydroandrographolide protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 158:305–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2018.10.034
Papackova Z, Heczkova M, Dankova H, Sticova E, Lodererova A, Bartonova L, Poruba M, Cahova M (2018) Silymarin prevents acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. PLoS One 13:e0191353. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191353
Rumack BH, Bateman DN (2012) Acetaminophen and acetylcysteine dose and duration: past, present and future. Clin Toxicol 50:91–98. https://doi.org/10.3109/15563650.2012.659252
Shen B, Zhao C, Wang Y, Peng Y, Cheng J, Li Z, Wu L, Jin M, Feng H (2019) Aucubin inhibited lipid accumulation and oxidative stress via Nrf2/HO-1 and AMPK signalling pathways. J Cell Mol Med 23:4063–4075. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14293
Stravitz RT, Lee WM (2019) Acute liver failure. Lancet 394:869–881. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31894-X
Sui Y, Wu F, Lv J, Li H, Li X, Du Z, Sun M, Zheng Y, Yang L, Zhong L, Zhang X, Zhang G (2015) Identification of the novel TMEM16A inhibitor dehydroandrographolide and its anticancer activity on SW620 cells. PLoS One 10:e0144715. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0144715
Towler MC, Hardie DG (2007) Amp-activated protein kinase in metabolic control and insulin signaling. Circ Res 100:328–341. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000256090.42690.05
Wang L, Zhang S, Cheng H, Lv H, Cheng G, Ci X (2016) Nrf2-mediated liver protection by esculentoside A against acetaminophen toxicity through the AMPK/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 101:401–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.11.009
Wong A, Graudins A (2017) Risk prediction of hepatotoxicity in paracetamol poisoning. Clin Toxicol 55:879–892. https://doi.org/10.1080/15563650.2017.1317349
Wu CT, Deng JS, Huang WC, Shieh PC, Chung MI, Huang GJ (2019) Salvianolic acid C against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by attenuating inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis through inhibition of the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:9056845. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9056845
Xiong W, Yuan Z, Wang T, Wu S, Xiong Y, Yao Y, Yang Y, Wu H (2021) Quercitrin attenuates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by maintaining mitochondrial complex I activity. Front Pharmacol 12:586010. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.586010
Yamada N, Karasawa T, Kimura H, Watanabe S, Komada T, Kamata R, Sampilvanjil A, Ito J, Nakagawa K, Kuwata H, Hara S, Mizuta K, Sakuma Y, Sata N, Takahashi M (2020) Ferroptosis driven by radical oxidation of n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids mediates acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Cell Death Dis 11:144. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2334-2
Yan M, Huo Y, Yin S, Hu H (2018) Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its implications for therapeutic interventions. Redox Biol 17:274–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.04.019
Zhang Y, Zhang F, Wang K, Liu G, Yang M, Luan Y, Zhao Z (2016) Protective effect of allyl methyl disulfide on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Chem Biol Interact 249:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2016.03.008
Zhao H, Jiang Z, Chang X, Xue H, Yahefu W, Zhang X (2018) 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid prevents acute APAP-induced liver injury by increasing phase II and antioxidant enzymes in mice. Front Pharmacol 9:653. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00653
Zong H, Ren JM, Young LH, Pypaert M, Mu J, Birnbaum MJ, Shulman GI (2002) AMP kinase is required for mitochondrial biogenesis in skeletal muscle in response to chronic energy deprivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:15983–15987. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.252625599
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31970507, No. 32273059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LD and YW: writing—original draft preparation, preliminary revision. WT and HF: conceptualization, supervision. HY, LZ and JC: methodology and suggestions. The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. All authors have approved the final revised manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
All mice studies conformed to the US National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and were authorized by the ethnical regulations of Jilin University (Number: ALKT202112003).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, L., Tan, W., Wei, Y. et al. Dehydroandrographolide Improvement of Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Failure. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 33, 523–533 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-023-00376-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43450-023-00376-9