Abstract
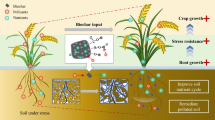
It is uncertain how soil amendments (organic manure and biochar-based fertilizer) affect soil water and salt movement below the root zone under brackish water irrigation. Two-year field experiments (freshwater irrigation + chemical fertilizer (CK), twice alternative irrigation with brackish water + chemical fertilizer (BCF), twice alternative irrigation with brackish water + organic manure (BOM), and twice alternative irrigation with brackish water + biochar-based fertilizer (BBF)) were carried out to investigate the effects of organic manure and biochar-based fertilizer on soil water and salt dynamics and crop yield. In BOM, soil pH decreased and soil aggregate content and stability increased, resulting in higher soil water (average water content 1.92% higher than BCF) and lower electrical conductivity of soil solution (0.45% lower than BCF) in the root zone (0–200 cm) during the second rotation. Soil salt excreted from the root zone and accumulated in the deep zone (200–400 cm), and the salt leaching amount in 0–400 cm was lowest (55.71 t·hm−2) in BOM. Soil pH, sodium adsorption ratio and total porosity increased in BBF, and micro-aggregate development was promoted. Additionally, soil salt was transported to a deeper layer (with the lowest salt storage of 38.50 t·hm−2 in the root zone) and the salinity of the entire profile was reduced (with the highest leaching amount of 69.17 t·hm−2). Organic manure and biochar-based fertilizer reduced soil salt in the root zone through different soil amendment mechanisms, resulting in different results of soil salt accumulation and leaching. In BOM, soil salt accumulated in the deep zone, while salt leaching occurred through 0–400 cm in BBF. These findings are beneficial for the safe utilization of brackish water and sustainable agriculture development.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahamed AA, Izzeldin SIM, Abdalla AMS (2019) The effect of irrigation frequency and farm yard manure on salt leaching under saline–sodic soil. Int J Acad Multidiscip Res (IJAMR) 3:36–44
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration Guidelines for computing crop water requirements-FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56. Fao, Rome 300: D05109
Assouline S, Russo D, Silber A, Or D (2015) Balancing water scarcity and quality for sustainable irrigated agriculture. Water Resour Res 51:3419–3436. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015WR017071
Ayars JE, Christen EW, Soppe RW, Meyer WS (2006) The resource potential of in situ shallow groundwater use in irrigated agriculture: a review. Irrig Sci 24:147–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-005-0003-y
Chaganti VN, Crohn M, JirkaŠimůnek D (2015) Leaching and reclamation of a biochar and compost amended saline-sodic soil with moderate SAR reclaimed water. Agric Water Manag 158:255–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2015.05.016
Chen L, Feng Q, Wang Y, Yu T (2012) Water and salt movement under saline water irrigation in soil with clay interlayer. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 28:44–51. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.08.007
Chen S, Shao L, Sun H, Zhang X, Li Y (2016) Effect of brackish water irrigation on soil salt balance and yield of both winter wheat and summer maize. Chin J Eco-Agric 24:1049–1058
Dane JH, Topp GC (2002) Methods of soil analysis, Part 4: physical methods. Soil Science Society of America Inc, Madison
Dong X, Li G, Lin Q, Zhao X (2017) Quantity and quality changes of biochar aged for 5 years in soil under field conditions. CATENA 159:136–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2017.08.008
Funakawa S, Kosaki T (2007) Potential risk of soil salinization in different regions of Central Asia with special reference to salt reserves in deep layers of soils. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 53:634–649. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0765.2007.00186.x
Hao X, Chang C (2003) Does long-term heavy cattle manure application increase salinity of a clay loam soil in semi-arid southern Alberta? Agric Ecosyst Environ 94:89–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8809(02)00008-7
He J, Den Q, Ma X, Su X, Ma X (2021) Soil salinization affected by hydrogeochemical processes of shallow groundwater in Cangzhou City, a coastal region in North China. Hydrol Res 52:1116–1131. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2021.183
Herencia JF, Maqueda C (2016) Effects of time and dose of organic fertilizers on soil fertility, nutrient content and yield of vegetables. J Agric Sci 154:1343–1361. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0021859615001136
Jalali M, Ranjbar F (2009) Effects of sodic water on soil sodicity and nutrient leaching in poultry and sheep manure amended soils. Geoderma 153:194–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.08.004
Joseph S, Cowie AL, Zwieten LV, Bolan N, Budai A, Buss W, Cayuela ML, Graber ER, Ippolito JA, Kuzyakov Y, Luo Y, Ok YS, Palansooriya KN, Shepherd J, Stephens S, Weng ZH, Lehmann J (2021) How biochar works and when it doesn’t: a review of mechanisms controlling soil and plant responses to biochar. GCB Bioenergy 13:1731–1764. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12885
Khan MN, Mobin M, Abbas ZK, Alamri SA (2018) Fertilizers and their contaminants in soils, surface and groundwater. Encyclopaedia Anthropocene 5:225–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809665-9.09888-8
Lazarova V, Bahri A (2004) Water reuse for irrigation: agriculture, landscapes, and turfgrass. CRC Press
Lee X, Yang F, Xing Y, Huang Y, Xu L, Liu Z, Holtzman R, Kan I, Li Y, Zhang L, Zhou H (2022) Use of biochar to manage soil salts and water: effects and mechanisms. Catena 211:106018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2022.106018
Li H (2020) Effect and numerical simulation of saline/brackish water infiltration on soil permeability and solute transport Qingdao University
Liu X, Feike T, Chen S, Shao L, Sun H, Zhang X (2016) Effects of saline irrigation on soil salt accumulation and grain yield in the winter wheat-summer maize double cropping system in the low plain of North China. J Integr Agric 15:2886–2898. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(15)61328-4
Liu B, Wang S, Kong X, Liu X, Sun H (2019) Modeling and assessing feasibility of long-term brackish water irrigation in vertically homogeneous and heterogeneous cultivated lowland in the North China Plain. Agric Water Manag 211:98–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2018.09.030
Liu G (2004) A study on the effect of the long-term applying biological-organic fertilizer on the soil physical-chemical properties, China Agricultural University
Lu W, Zhang W, Li Y (2006) Effects of long-term brackish water irrigation on characteristics of agrarian soil. J Agro-Environ Sci 4:969–973
Ma Z, Tan J, Wei T (2019) The variation of salt-tolerance of crops in different regions irrigated with brackish water in China. J Irrig Drain 38:70–75
Mathinya VN, Rensburg LDV, Mavimbela SSW, Barnard JH (2019) Malt barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) water use and grain yield response to saline irrigation under shallow groundwater table conditions. Irrig Drain 68:867–880. https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.2389
Ortiz AC, Jin L (2021) Chemical and hydrological controls on salt accumulation in irrigated soils of southwestern U.S. Geoderma 391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2021.114976
Qian Y, Zhang Z, Fei Y, Chen J, Fe Z, Wang Z (2014) Sustainable exploitable potential of shallow groundwater in the North China Plain. Chin J Eco-Agric 22:890–897
Rhoades J, Kandiah A, Mashali A (1992) The use of saline waters for crop production-FAO irrigation and drainage paper 48. FAO, Rome, 133
Rillig MC, Aguilar-Trigueros CA, Bergmann J, Verbruggen E, Veresoglou SD, Lehmann A (2015) Plant root and mycorrhizal fungal traits for understanding soil aggregation. New Phytol 205:1385–1388. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13045
Sarker TS, Incerti G, Spaccini R, Piccolo A, Mazzoleni S, Bonanomi B (2018) Linking organic matter chemistry with soil aggregate stability: insight from 13C NMR spectroscopy. Soil Biol Biochem 117:175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.11.011
Singh A (2014) Poor quality water utilization for agricultural production: an environmental perspective. Land Use Policy 43:259–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2014.11.015
Singh A (2019) An overview of drainage and salinization problems of irrigated lands. Irrig Drain 68:551–558. https://doi.org/10.1002/ird.2344
Singh TB, Ali A, Prasad M, Yadav A, Shrivastav P, Goyal D, Dantu PK (2020) Role of organic fertilizers in improving soil fertility. Contaminants in agriculture. pp. 61–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-41552-5_3
Suarez DL, Wood JD, Lesch SM (2006) Effect of SAR on water infiltration under a sequential rain–irrigation management system. Agric Water Manag 86:150–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2006.07.010
Tedeschi A, Dell’Aquila R (2005) Effects of irrigation with saline waters, at different concentrations, on soil physical and chemical characteristics. Agric Water Manag 77:308–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2004.09.036
Usman A, Al-Wabel MI, Ok YS, Al-Harbi AR, Wahb-Allah MA, El-Naggar AH, Ahmad M, Al-Faraj A, Alomran A (2016) Conocarpus biochar induces changes in soil nutrient availability and tomato growth under saline irrigation. Pedosphere 26:27–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(15)60019-4
Wang J, Qi B, Zhang Y, Zhang A, Ning Y, Xu X, Zhang H, Ma H (2012a) Effects of long-term fertilization on pH buffer system of sandy loam calcareous fluvor-aquic soil. Chin J Appl Ecol 23:1031–1036
Wang S, Song X, Wang Q, Xiao G, Wang Z, Liu X, Wang P (2012b) Shallow groundwater dynamics and origin of salinity at two sites in salinated and water-deficient region of North China Plain, China. Environ Earth Sci 66:729–739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1280-9
Wang J (2020) Variation characteristics and influencing factors of soil aggregate-organic carbon fractions in agricultural soils from a Saline-Alkali soil region Jilin University
Weng ZH, Zwieten LV, Singh BP, Tavakkoli E, Joseph S, Macdonald LM, Rose TJ, Rose MT, Kimber SWL, Morris S, Cozzolino D, Araujo JR, Archanjo BS, Cowie A (2017) Biochar built soil carbon over a decade by stabilizing rhizodeposits. Nat Clim Chang 7:371–376. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate3276
Wichelns D, Qadir M (2014) Achieving sustainable irrigation requires effective management of salts, soil salinity, and shallow groundwater. Agric Water Manag 157:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2014.08.016
Wu Y, Xu G, Lü Y, Shao H (2014) Effects of biochar amendment on soil physical and chemical properties: current status and knowledge gaps. Adv Earth Sci 29:68–79
Wu Y (2005) Improvement of nitrogen fertilizer use efficiency by water-saving cultivation in winter wheat-summer maize production system in Northern China, China Agricultural University
Xiao L, Yuan G, Feng L, Shah GM, Wei J (2022) Biochar to reduce fertilizer use and soil salinity for crop production in the Yellow River Delta. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 22:1478–1489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00747-y
Yue Y, Guo WN, Lin QM, Li GT, Zhao X (2016) Improving salt leaching in a simulated saline soil column by three biochars derived from rice straw (Oryza sativa L.), sunflower straw (Helianthus annuus), and cow manure. J Soil Water Conserv 71:467–475. https://doi.org/10.2489/jswc.71.6.467
Zahra MB, Fayyaz B, Aftab ZEH, Haider MS (2021) Mitigation of degraded soils by using biochar and compost: a systematic review. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21:2718–2738. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-021-00558-1
Zhang X, Liu X, Chen S, Sun H, Shao L, Niu J (2016) Efficient utilization of various water sources in farmlands in the low plain nearby Bohai Sea. Chin J Eco-Agric 24:995–1004
Zhao H, Zhu C, Huang M, Ze Y, Zhai Y, Zheng J (2021) Amending soil with biochar to improve accumulation and translocation of dry matter after anthesis in winter wheat. J Irrig Drain 40:16–23
Zhao S, Yu F, Zhai C, Zhong R, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Zhang J, Meng Q (2022) Long-term effects of cattle manure application on the soil aggregate stability of salt-affected soil on the Songnen Plain of North-Eastern China. J Soils Sediments: 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-022-03317-6
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude for the support provided by the Nanpi Eco-Agricultural Station, CAS. We also thank Professor Leilei Min from the Center for Agricultural Resources Research, IGDB, CAS for his valuable advice on the manuscript and Jiali Lv from the Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, CAS for her assistance with language editing.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2021YFD1700500), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.42071053), the Open Project Program of Hebei Province Collaborative innovation center for sustainable utilization of water resources and optimization of industrial structure (No.XTZX202107), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (D2021503018) and the Key Research and Development Program of Hebei Province (21326411D).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Panpan Ni, Shiqin Wang, Bingxia Liu and Hongyong Sun. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Panpan Ni and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, P., Wang, S., Liu, B. et al. Effects of Organic Manure and Biochar-Based Fertilizer Application on Soil Water and Salt Transport in Brackish Water Irrigated Soil Profile. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 23, 3120–3136 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01310-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01310-7