Abstract
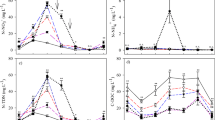
Liquid dairy cattle (Bos taurus) manure effect on corn (Zea mays L.) yield and nutrients’ uptake and soil fertility were studied, in comparison to the crop’s common and recommended inorganic fertilization, by means of a 5-year field experiment. The treatments applied each year in the same plots were: (i) manure, (ii) common inorganic fertilization, (iii) recommended inorganic fertilization, and (iv) no fertilization. Each year from each plot, surface soil samples were collected before sowing, corn aboveground biomass was collected at silage, they were analyzed, and grain yield was determined at harvest. Upon all kinds of fertilization, corn silage yield increased in comparison to control and ranged between 51 and 194, 50 and 190, and 39 and 189% for the manure, recommended, and common inorganic fertilization treatment, respectively. Similarly, grain yield and the macro- and micronutrients’ plant uptake were increased. Soil fertility improved regarding the NO3-N, which upon organic or inorganic fertilization increased 10–46% in comparison to the control. Manure application significantly increased K by 32–81%. However, in the case of P, an excessive increase was observed, which was two to three times higher than the inorganic fertilization (30–44 mg kg−1). Consequently, repeated annual applications of liquid cattle manure to soil can enhance crop yield, nutrients’ uptake, and soil fertility, at levels higher or similar to the common or recommended inorganic fertilization for the crop. However, the possibility of P build up should also be considered.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brady NC, Weil RR (2008) The nature and properties of soils, 14th edn. Pearson Prentice Hall, Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River
Bremner JM (1996) Nitrogen - total. In: Sparks DL (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 3, Chemical methods, SSSA book series no, vol 5. SSSA and ASA, Madison, pp 1085–1121
Cavalli D, Cabassi G, Borrelli L, Geromel G, Bechini L, Degano L, Gallina PM (2016) Nitrogen fertilizer replacement value of undigested liquid cattle manure and digestates. Eur J Agron 73:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2015.10.007
Cavalli D, Corti M, Baronchelli D, Bechini L, Gallina PM (2017) CO2 emissions and mineral nitrogen dynamics following application to soil of undigested liquid cattle manure and digestates. Geoderma 308:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.08.027
Dahnke WC, Johnson GV (1990) Testing soils for available nitrogen. In: Westerman RL (ed) Soil testing and plant analysis, SSSA Book Series No, vol 3, 3rd edn. SSSA, Madison, pp 127–139
Evans SD, Goodrich PR, Munter RC, Smith RE (1977) Effects of solid and liquid beef manure and liquid hog manure on soil characteristics and on growth, yield, and composition of corn. J Environ Qual 6:361–368. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq1977.00472425000600040006x
FAO (2019) Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FAOSTAT, http://www.fao.org/faostat/. Accessed 10 March 2020
Gasparatos D, Massas I, Godelitsas A (2019) Fe-Mn concentrations and nodules formation in redoximorphic soils and soil phosphorus dynamics: current knowledge and gaps. Catena 182:104106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104106
Golroudbary SR, Wali ME, Kraslawski A (2019) Environmental sustainability of phosphorus recycling from wastewater, manure and solid wastes. Sci Total Environ 672:515–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.439
Grigatti M, Boanini E, Cavani L, Ciavatta C, Marzadori C (2015) Phosphorus in digestate-based compost: chemical speciation and plant-availability. Waste Biomass Valoriz 6:481–493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-015-9383-2
Guan DX, Sun FS, Yu GH, Polizzotto ML, Liu YG (2018) Total and available metal concentrations in soils from six long-term fertilization sites across China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:31666–31678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3143-3
Haby YA, Russelle MP, Skogley EO (1990) Testing soils for potassium, calcium, and magnesium. In: Westerman RL (ed) Soil testing and plant analysis, SSSA Book Series No, vol 3, 3rd edn. SSSA, Madison, pp 181–227
Halajnia A, Hagnia GH, Fotovat A, Khorasani R (2009) Phosphorus fractions in calcareous soils amended with P fertilizer and cattle manure. Geoderma 150:209–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.02.010
Halvorson AD, Schweissing FC, Bartolo ME, Reule C (2005) Corn response to nitrogen fertilization in a soil with high residual nitrogen. Agron J 97:1222–1229. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2004.0279
Keren R (1996) Boron. In: Sparks DL (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 3, Chemical methods, SSSA book series no, vol 5. SSSA and ASA, Madison, pp 603–626
Kuo S (1996) Phosphorus. In: Sparks DL (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 3, Chemical methods, SSSA book series no, vol 5. SSSA and ASA, Madison, pp 869–919
Li J, Marschner P (2019) Phosphorus pools and plant uptake in manure-amended soil. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19:175–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00025-y
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:421–428. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1978.03615995004200030009x
Lithourgidis AS, Matsi T, Barbayiannis N, Dordas CA (2007) Effect of liquid cattle manure on corn yield, composition, and soil properties. Agron J 99:1041–1047. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2006.0332
Marchezan C, Ferreira PAA, Silva LS, Bacca A, Krug AV, Nicoloso FT, Tarouco CP, Tiecher TL, Brunetto G, Ceretta CA (2020) Nitrogen availability and physiological response of corn after 12 years with organic and mineral fertilization. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00185-2
Martinez E, Domingo F, Rosello A, Serra J, Boixadera J, Lloveras J (2017) The effects of dairy cattle manure and mineral N fertilizer on irrigated maize and soil N and organic C. Eur J Agron 83:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2016.10.002
Marzi M, Shahbazi K, Kharazi N, Rezai M (2020) The influence of organic amendment source on carbon and nitrogen mineralization in different soils. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:177–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00116-w
Matsi T, Lithourgidis AS, Gagianas A (2003) Effects of injected liquid cattle manure on growth and yield of winter wheat and soil characteristics. Agron J 95:592–596. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2003.5920
Matsi T, Lithourgidis AS, Barbayiannis N (2015) Effect of liquid cattle manure on soil chemical properties and corn growth in northern Greece. Exp Agric 51:435–450. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0014479714000404
McCallister D, Larson JA, Walters DT, Marx DB, Gossin C (2010) Soil phosphorus distribution as affected by manure compost phosphorus concentration and incorporation. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 41:721–734. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620903563956
Mills HA, Benton-Jones J Jr (1996) Plant analysis handbook II. Micro-Macro Publishing, Athens
Mulvaney RL (1996) Nitrogen - inorganic forms. In: Sparks DL (ed) Methods of soil analysis, part 3. Chemical methods, SSSA Book Series No, vol 5. SSSA and ASA, Madison, pp 1123–1184
Nikoli T, Matsi T (2011) Influence of liquid cattle manure on micronutrients content and uptake by corn and their availability in a calcareous soil. Agron J 103:113–118. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2010.0273
Schlegel AJ, Aseefa Y, Bond HD, Haag LA, Stone LR (2017) Changes in soil nutrients after 10 years of cattle manure and swine effluent application. Soil Tillage Res 172:48–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2017.05.004
Sims JT, Johnson GV (1991) Micronutrient soil tests. In: Mortvedt JJ et al (eds) Micronutrients in agriculture, SSSA Book Series No, vol 4, 2nd edn. SSSA, Madison, pp 427–476
Skoulou V, Zabaniotou A (2007) Investigation of agricultural and animal wastes in Greece and their allocation to potential application for energy production. Renew Sust Energ Rev 11:1698–1719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2005.12.011
Thomas GW (1982) Exchangeable cations. In: Page AL et al (eds) Methods of soil analysis, Part 2. Chemical and microbiological methods, 2nd edn. SSSA and ASA, Madison, pp 159–165
Thomas GW, Peaslee DE (1973) Testing soils for phosphorus. In: Walsh LM, Beaton JD (eds) Soil testing and plant analysis, SSSA Book Series No, vol 3. SSSA, Madison, pp 115–132
Vlyssides A, Mai S, Barampouti EM (2015) Energy generation potential in Greece from agricultural residues and livestock manure by anaerobic digestion technology. Waste Biomass Valoriz 6:747–757. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-015-9400-5
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci 37:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-193401000-00003
Wang Y, Zhu Y, Zhang S, Wang Y (2018) What could promote farmers to replace chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers? J Clean Prod 199:882–890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.07.222
Yang Q, Tian H, Li X, Ren W, Zhang B, Zhang X, Julie W (2016) Spatiotemporal patterns of livestock manure nutrient production in the conterminous United States from 1930 to 2012. Sci Total Environ 541:1592–1602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.10.044
Yolcu H, Gunes A, Dasci M, Turan M, Serin Y (2010) The effects of solid, liquid and combined cattle manure applications on the yield, quality and mineral contents of common vetch and barley intercropping mixture. Ekoloji 75:71–81. https://doi.org/10.5053/ekoloji.2010.7510
Zhang W, Wang C, Dong M, Jin S, Huan L (2018) Dynamics of soil fertility and maize growth with lower environment impacts depending on a combination of organic and mineral fertilizer. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 18:556–575. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162018005001701
Zhao Y, Yan Z, Qin J, Xiao Z (2014) Effects of long-term cattle manure application on soil properties and soil heavy metals in corn seed production in Northwest China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:7586–7595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-2671-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samara, E., Matsi, T., Barbayiannis, N. et al. Liquid Cattle Manure Effect on Corn Yield and Nutrients’ Uptake and Soil Fertility, in Comparison to the Common and Recommended Inorganic Fertilization. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20, 2283–2293 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00294-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-020-00294-y