Abstract
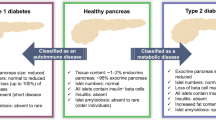
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles that are widely distributed in multiple cell types and circulating body fluids. They have a specific effect on the target cells by releasing different vesicle contents. They have recently been recognized as important means of intercellular communication, being involved, for example, in the development of diabetes by increasing β-cell apoptosis, activating autoimmunity, and regulating cytokines to affect islet β-cell function and insulin sensitivity. An in-depth study of the role of exosome in the pathogenesis of diabetes may therefore provide a novel means of diagnosing and treating diabetes. In this review, we detail how exosome is involved in the development of diabetes.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Pont C, Ascaso FJ, Grzybowski A, Huerva V (2020) Corneal endothelial cell density during diabetes mellitus and ocular diabetes complications treatment. J Fr Ophtalmol 43:794–798
Cole JB, Florez JC (2020) Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat Rev Nephrol 16:377–390
Zhang Y, Bi J, Huang J, Tang Y, Du S, Li P (2020) Exosome: a review of its classification, isolation techniques, storage, diagnostic and targeted therapy applications. Int J Nanomedicine 15:6917–6934
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS (2020) The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 367(6478):eaau6977
Bobrie A, Colombo M, Raposo G, Thery C (2011) Exosome secretion: molecular mechanisms and roles in immune responses. Traffic 12:1659–1668
Robbins PD, Morelli AE (2014) Regulation of immune responses by extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Immunol 14:195–208
Cai Z, Yang F, Yu L, Yu Z, Jiang L, Wang Q, Yang Y, Wang L, Cao X, Wang J (2012) Activated T cell exosomes promote tumor invasion via Fas signaling pathway. J Immunol 188:5954–5961
Quesenberry PJ, Aliotta JM (2010) Cellular phenotype switching and microvesicles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62:1141–1148
Timmers L, Lim SK, Hoefer IE, Arslan F, Lai RC, van Oorschot AA, Goumans MJ, Strijder C, Sze SK, Choo A, Piek JJ, Doevendans PA, Pasterkamp G, de Kleijn DP (2011) Human mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium improves cardiac function following myocardial infarction. Stem Cell Res 6:206–214
Chivet M, Hemming F, Pernet-Gallay K, Fraboulet S, Sadoul R (2012) Emerging role of neuronal exosomes in the central nervous system. Front Physiol 3:145
Teng Y, Ren Y, Hu X, Mu J, Samykutty A, Zhuang X, Deng Z, Kumar A, Zhang L, Merchant ML, Yan J, Miller DM, Zhang HG (2017) MVP-mediated exosomal sorting of miR-193a promotes colon cancer progression. Nat Commun 8:14448
Anel A, Gallego-Lleyda A, de Miguel D, Naval J, Martínez-Lostao L (2019) Role of exosomes in the regulation of T-cell mediated immune responses and in autoimmune disease. Cells 12(2):154
Matsuzaka Y, Yashiro R (2022) Regulation of extracellular vesicle-mediated immune responses against antigen-specific presentation. Vaccines (Basel) 10(10):1691
Zhang J (2022) Biomarkers of endothelial activation and dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases. Rev Cardiovasc Med 23(2):73
Akbar N, Azzimato V, Choudhury RP, Aouadi M (2019) Extracellular vesicles in metabolic disease. Diabetologia 62(12):2179–2187
Pardo F, Villalobos-Labra R, Sobrevia B, Toledo F, Sobrevia L (2018) Extracellular vesicles in obesity and diabetes mellitus. Mol Aspects Med 60:81–91
Krishnan P, Syed F, Jiyun Kang N, Mirmira RG, Evans-Molina C (2019) Profiling of RNAs from Human Islet-Derived Exosomes in a Model of Type 1 Diabetes. Int J Mol Sci 25(23):5903
Soltani S, Mansouri K, Emami Aleagha MS, Moasefi N, Yavari N, Shakouri SK, Notararigo S, Shojaeian A, Pociot F, Yarani R (2022) Extracellular vesicle therapy for type 1 diabetes. Front Immunol 13:865782
Jafari N, Kolla M, Meshulam T, Shafran JS, Qiu Y, Casey AN, Pompa IR, Ennis CS, Mazzeo CS, Rabhi N, Farmer SR, Denis GV (2021) Adipocyte-derived exosomes may promote breast cancer progression in type 2 diabetes. Sci Signal 14(710):eabj2807
Li G, Liu H, Ma C, Chen Y, Wang J, Yang Y (2019) Exosomes are the novel players involved in the beneficial effects of exercise on type 2 diabetes. J Cell Physiol 234(9):14896–14905
de Candia P, De Rosa V, Gigantino V, Botti G, Ceriello A, Matarese G (2017) Immunometabolism of human autoimmune diseases: from metabolites to extracellular vesicles. FEBS letters 591:3119–3134
Samuelson I, Vidal-Puig AJ (2018) Fed-EXosome: extracellular vesicles and cell-cell communication in metabolic regulation. Essays Biochem 62:165–175
Cianciaruso C, Phelps EA, Pasquier M, Hamelin R, Demurtas D, Alibashe Ahmed M, Piemonti L, Hirosue S, Swartz MA, De Palma M, Hubbell JA, Baekkeskov S (2017) Primary human and rat beta-cells release the intracellular autoantigens GAD65, IA-2, and proinsulin in exosomes together with cytokine-induced enhancers of immunity. Diabetes 66:460–473
Sheng H, Hassanali S, Nugent C, Wen L, Hamilton-Williams E, Dias P, Dai YD (2012) Insulinoma-released exosomes or microparticles are immunostimulatory and can activate autoreactive T cells spontaneously developed in nonobese diabetic mice. J Immunol 187:1591–1600
Bashratyan R, Sheng H, Regn D, Rahman MJ, Dai YD (2013) Insulinoma-released exosomes activate autoreactive marginal zone-like B cells that expand endogenously in prediabetic NOD mice. Eur J Immunol 43:2588–2597
Song M, Han L, Chen FF, Wang D, Wang F, Zhang L, Wang ZH, Zhong M, Tang MX, Zhang W (2018) Adipocyte-derived exosomes carrying sonic hedgehog mediate M1 macrophage polarization-induced insulin resistance via Ptch and PI3K pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem 48:1416–1432
Rahman MJ, Regn D, Bashratyan R, Dai YD (2014) Exosomes released by islet-derived mesenchymal stem cells trigger autoimmune responses in NOD mice. Diabetes 63:1008–1020
Guay C, Kruit JK, Rome S, Menoud V, Mulder NL, Jurdzinski A, Mancarella F, Sebastiani G, Donda A, Gonzalez BJ, Jandus C, Bouzakri K, Pinget M, Boitard C, Romero P, Dotta F, Regazzi R (2019) Lymphocyte-derived exosomal micrornas promote pancreatic beta cell death and may contribute to type 1 Diabetes Development. Cell Metab 29(348-361):e346
Marcelin G, Gautier EL, Clément K, Adipose tissue fibrosis in obesity (2022) Etiology and Challenges. Annu Rev Physiol 84:135–155
Ying W, Riopel M, Bandyopadhyay G, Dong Y, Birmingham A, Seo JB, Ofrecio JM, Wollam J, Hernandez-Carretero A, Fu W, Li P, Olefsky JM (2017) Adipose tissue macrophage-derived exosomal mirnas can modulate in vivo and in vitro insulin sensitivity. Cell 171(372-384):e312
Guay C, Menoud V, Rome S, Regazzi R (2015) Horizontal transfer of exosomal microRNAs transduce apoptotic signals between pancreatic beta-cells. Cell Commun Signal 13:17
Kiran S, Kumar V, Kumar S, Price RL, Singh UP (2021) Adipocyte, immune cells, and mirna crosstalk: a novel regulator of metabolic dysfunction and obesity. Cells 10(5):1004
Kranendonk ME, Visseren FL, van Balkom BW, Nolte-'t Hoen EN, van Herwaarden JA, de Jager W, Schipper HS, Brenkman AB, Verhaar MC, Wauben MH, Kalkhoven E (2014) Human adipocyte extracellular vesicles in reciprocal signaling between adipocytes and macrophages. Obesity (Silver Spring) 22:1296–1308
Ferrante SC, Nadler EP, Pillai DK, Hubal MJ, Wang Z, Wang JM, Gordish-Dressman H, Koeck E, Sevilla S, Wiles AA, Freishtat RJ (2015) Adipocyte-derived exosomal miRNAs: a novel mechanism for obesity-related disease. Pediatr Res 77(3):447–454
Zhang Y, Shi L, Mei H, Zhang J, Zhu Y, Han X, Zhu D (2015) Inflamed macrophage microvesicles induce insulin resistance in human adipocytes. Nutr Metab (Lond) 12:21
Osmai M, Osmai Y, Bang-Berthelsen CH, Pallesen EM, Vestergaard AL, Novotny GW, Pociot F, Mandrup-Poulsen T (2016) MicroRNAs as regulators of beta-cell function and dysfunction. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 32(4):334–349
Saint-Pol J, Gosselet F, Duban-Deweer S, Pottiez G, Karamanos Y (2020) Targeting and crossing the blood-brain barrier with extracellular vesicles. Cells 9(4):851
Hezel MEV, Nieuwland R, Bruggen RV, Juffermans NP (2017) The ability of extracellular vesicles to induce a pro-inflammatory host response. Int J Mol Sci 18(6):1285
Palmisano G, Jensen SS, Le Bihan MC, Laine J, McGuire JN, Pociot F, Larsen MR (2012) Characterization of membrane-shed microvesicles from cytokine-stimulated beta-cells using proteomics strategies. Mol Cell Proteomics 11(8):230–243
Kang C, Qin J, Osei W, Hu K (2017) Regulation of protein kinase C-epsilon and its age-dependence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 482(4):1201–1206
Kranendonk ME, Visseren FL, van Herwaarden JA, Nolte-'t Hoen EN, de Jager W, Wauben MH, Kalkhoven E (2014) Effect of extracellular vesicles of human adipose tissue on insulin signaling in liver and muscle cells. Obesity (Silver Spring) 22(10):2216–2223
Delic D, Eisele C, Schmid R, Baum P, Wiech F, Gerl M, Zimdahl H, Pullen SS, Urquhart R (2016) Urinary exosomal miRNA signature in type II diabetic nephropathy patients. PLoS One 11(3):e0150154
Eissa S, Matboli M, Aboushahba R, Bekhet MM, Soliman Y (2016) Urinary exosomal microRNA panel unravels novel biomarkers for diagnosis of type 2 diabetic kidney disease. J Diabetes Complications 30(8):1585–1592
Sohrabi B, Dayeri B, Zahedi E, Khoshbakht S, Nezamabadi Pour N, Ranjbar H, Davari Nejad A, Noureddini M, Alani B (2022) Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes as novel vehicles for delivery of miRNAs in cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther 29(8-9):1105–1116
Xin H, Li Y, Buller B, Katakowski M, Zhang Y, Wang X, Shang X, Zhang ZG, Chopp M (2012) Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-133b from multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells to neural cells contributes to neurite outgrowth. Stem Cells 30(7):1556–1564
Tomasoni S, Longaretti L, Rota C, Morigi M, Conti S, Gotti E, Capelli C, Introna M, Remuzzi G, Benigni A (2013) Transfer of growth factor receptor mRNA via exosomes unravels the regenerative effect of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 22(5):772–780
Sun Y, Liu G, Zhang K, Cao Q, Liu T, Li J (2021) Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Stem Cell Res Ther 12(1):561
Zhang F, Yang Y, Chen X, Liu Y, Hu Q, Huang B, Liu Y, Pan Y, Zhang Y, Liu D, Liang R, Li G, Wei Q, Li L, Jin L (2021) The long non-coding RNA β Faar regulates islet β-cell function and survival during obesity in mice. Nat Commun 12(1):3997
Garcia-Contreras M, Brooks RW, Boccuzzi L, Robbins PD, Ricordi C (2017) Exosomes as biomarkers and therapeutic tools for type 1 diabetes mellitus. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21(12):2940–2956
Ruan H, Dong LQ (2016) Adiponectin signaling and function in insulin target tissues. J Mol Cell Biol 8(2):101–109
Guay C, Jacovetti C, Nesca V, Motterle A, Tugay K, Regazzi R (2012) Emerging roles of non-coding RNAs in pancreatic beta-cell function and dysfunction. Diabetes Obes Metab 14(Suppl 3):12–21
Javeed N, Sagar G, Dutta SK, Smyrk TC, Lau JS, Bhattacharya S, Truty M, Petersen GM, Kaufman RJ, Chari ST, Mukhopadhyay D (2015) Pancreatic Cancer-Derived Exosomes Cause Paraneoplastic beta-cell Dysfunction. Clin Cancer Res 21(7):1722–1733
Korc M (2015) Pancreatic cancer-associated diabetes is an “exosomopathy”. Clin Cancer Res 21(7):1508–1510
Kloting N, Bluher M (2014) Adipocyte dysfunction, inflammation and metabolic syndrome. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 15(4):277–287
McGown C, Birerdinc A, Younossi ZM (2014) Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Clin Liver Dis 18(1):41–58
Zhao H, Shang Q, Pan Z, Bai Y, Li Z, Zhang H, Zhang Q, Guo C, Zhang L, Wang Q (2018) Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells attenuate adipose inflammation and obesity through polarizing M2 macrophages and beiging in white adipose tissue. Diabetes 67(2):235–247
Herzig S, Shaw RJ, AMPK (2018) guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 19(2):121–135
Villalobos-Labra R, Silva L, Subiabre M, Araos J, Salsoso R, Fuenzalida B, Saez T, Toledo F, Gonzalez M, Quezada C, Pardo F, Chiarello DI, Leiva A, Sobrevia L (2017) Akt/mTOR Role in Human Foetoplacental Vascular Insulin Resistance in Diseases of Pregnancy. J Diabetes Res 2017:5947859
Sun T, Zhang K, Li W, Liu Y, Pangeni RP, Li A, Arvanitis L, Raz DJ (2022) Transcription factor AP2 enhances malignancy of non-small cell lung cancer through upregulation of USP22 gene expression. Cell Commun Signal 20(1):147 Published 2022 Sep 19
Ertunc ME, Sikkeland J, Fenaroli F, Griffiths G, Daniels MP, Cao H, Saatcioglu F, Hotamisligil GS (2015) Secretion of fatty acid binding protein aP2 from adipocytes through a nonclassical pathway in response to adipocyte lipase activity. J Lipid Res 56(2):423–434
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, F., Yu, Y. & Xu, H. How does exosome cause diabetes?. Hormones (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-024-00525-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-024-00525-2