Abstract
Introduction
AL amyloidosis is caused by a clone of plasma cell. Due to the impact of the disease on patient survival, careful evaluation of organ involvement is essential and treatment should be tailored to single patient's risk. AIM: We analyzed the clinical, laboratory and histological characteristics of 21 elderly patients (pts) (mean age 74.7 ± 7.97 years, range 55–81) with AL amyloidosis, including 17 patients (81%) with biopsy-proven renal involvement, who were ineligible for bone marrow transplantation, and evaluated the impact of renal impairment on survival.
Results
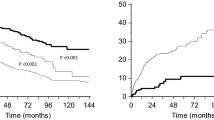
Cardiac and renal involvement was found in 14 (67%) cases. Among the 17 patients with renal involvement, 12 had renal failure with proteinuria, and one showed isolated renal failure and vascular amyloid deposition. Hematological response occurred in 57.1% after first line therapy (75% after three cycles). In six of the patients with renal involvement, proteinuria decreased from 4.2 to 1.1 g/24 h (range 0.2–3 g/24 h), serum Creatinina (sCr) levels declined or stabilized. Severe renal failure at diagnosis was found to directly influence patient survival, while the Staging System for Renal Outcome in AL Amyloidosis did not associate with outcomes.
Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge this is the first case series in which the whole cohort of patients with urinary or functional abnormalities underwent a histological evaluation. None of the patients were eligible for bone marrow transplantation. Hematologic response was 57.1%, while renal response was much lower (35%). Of note, the Staging System did not completely apply to this peculiar setting of patients in whom renal involvement was not presumptive but biopsy-proven. More aggressive approaches may be needed in these patients to avoid the inexorable progression of the disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palladini G, Merlini G (2016) What is new in diagnosis and management of light chain amyloidosis? Blood 128(2):159–168
Blancas-Mejia LM, Misra P, Dick CJ, Cooper SA, Redhage KR, Bergman MR, Jordan TL, Maar K, Ramirez-Alvarado M (2018) Immunoglobulin light chain amyloid aggregation. Chem Commun Camb 54(76):10664–10674. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc04396e
Sanchorawala V (2006) Light-chain (AL) amyloidosis: diagnosis and treatment. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1(6):1331–1341
Pinney JH, Lachmann HJ, Bansi L, Wechalekar AD, Gilbertson JA, Rowczenio D, Sattianayagam PT, Gibbs SD, Orlandi E, Wassef NL, Bradwell AR, Hawkins PN, Gillmore JD (2011) Outcome in renal Al amyloidosis after chemotherapy. J ClinOncol 29(6):674–681. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.30.5235
Pinney JH, Whelan CJ, Petrie A, Dungu J, Banypersad SM, Sattianayagam P, Wechalekar A, Gibbs SD, Venner CP, Wassef N, McCarthy CA, Gilbertson JA, Rowczenio D, Hawkins PN, Gillmore JD, Lachmann HJ (2013) Senile systemic amyloidosis: clinical features at presentation and outcome. J Am Heart Assoc 2(2):e000098. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.113.000098
Nuvolone M, Milani P, Palladini G, Merlini G (2018) Management of the elderly patient with AL amyloidosis. Eur J Intern Med 58:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2018.05.00
Palumbo A, Rajkumar SV, San Miguel JF et al (2014) International Myeloma Working Group consensus statement for the management, treatment, and supportive care of patients with myeloma not eligible for standard autologous stem-cell transplantation. J ClinOncol 32:587–600. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.48.7934
Milani P, Palladini G, Merlini G (2016) Serum-free light-chain analysis in diagnosis and management of multiple myeloma and related conditions. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl 245:S113–S118. https://doi.org/10.1080/00365513.2016.121033
Prokaeva T, Spencer B, Sun F, O’Hara RM, Seldin DC, Connors LH, Sanchorawala V (2016) Immunoglobulin heavy light chain test quantifies clonal disease in patients with AL amyloidosis and normal serum free light chain ratio. Amyloid 23(4):214–220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-015-1827-8
Miyazaki K, Kawai S, Suzuki K (2015) Abdominal subcutaneous fat pad aspiration and bone marrow examination for the diagnosis of AL amyloidosis: the reliability of immunohistochemistry. Int J Hematol 02(3):289–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-015-1827-8
Muchtar E, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Buadi FK, Kapoor P, Hayman SR, Gonsalves W, Warsame R, Kourelis TV, Chakraborty R, Russell S, Lust JA, Lin Y, Go RS, Zeldenrust S, Rajkumar SV, Dingli D, Leung N, Kyle RA, Kumar SK, Gertz MA (2017) Overuse of organ biopsies in immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis (AL): the consequence of failure of early recognition. Ann Med 49(7):545–551. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890
Murakami Y, Hattori S, Sugiyama F, Yoshikawa K, Sugiura T, Matsushima H (2015) A case of primary (AL) amyloidosis with predominantly vascular amyloid deposition in the kidney. CEN Case Rep 4(2):151–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13730-014-0157-7
Weiss BM, Lund SH, Bjorkholm M et al (2016) Improved survival in AL amyloidosis: a population-based study on 1430 patients diagnosed in Sweden 1995–2013. Blood 128(22):4448
Lousada I, Comenzo RL, Landau H, Guthrie S, Merlini G (2015) Light chain amyloidosis: patients experience survey from the amyloidosis research consortium. Adv Ther 32(10):920–928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-015-0250-0
Falk RH, Dubrey SW (2014) Amyloid heart disease. Progress Cardiovasc Diseases Open J Clin Diagnostics 4(1):347–361
Kumar S, Dispenzieri A, Lacy M, Hayman S, Buadi FK, Colby C, Laumann K, Zeldenrust S, Leung N, Dingli D, Greipp P, Lust JA, Russell S, Kyle RA, Rajkumar V, Gertz MA (2012) Revised prognostic staging system for light chain amyloidosis incorporating cardiac biomarkers and serum free light chain measurements. J Clin Oncol 30(9):989–995. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2011.38.5724
Dispenzieri A (2014) Renal risk and response in amyloidosis. Blood 124(15):2315–2316. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-08-596338
Kastritis E, Gavriatopoulou M, Rossou M et al (2017) Renal outcome in patients with AL amyloidosis: prognostic factors. Am J Hematol 92(7):632–639. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.24738
Fuah KW, Lim CTS (2018) Renal-limited AL amyloidosis—a diagnostic and management dilemma. BMC Nephrol 19(1):307. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-018-1118-8
Sasatomi Y, Kiyoshi Y, Uesugi N, Hisano S, Takebayashi S (2001) Prognosis of renal amyloidosis: a clinic-pathological study using cluster analysis. Nephron 87:42–49
Kalle A, Gudipati A, Raju SB, Kalidindi K, Guditi S, Taduri G, Uppin MS (2018) Revisiting renal amyloidosis with clinicopathological characteristics, grading, and scoring: a single-institutional experience. J Lab Phys 10(2):226–231. https://doi.org/10.4103/JLP.JLP_148_17
Rezk T, Lachmann HJ, Fontana M, Sachchithanantham S, Mahmood S, Petrie A, Whelan CJ, Pinney JH, Foard D, Lane T, Youngstein T, Wechalekar AD, Bass P, Hawkins PN, Gillmore JD (2017) Prolonged renal survival in light chain amyloidosis: speed and magnitude of light chain reduction is the crucial factor. Kidney Int 92(6):1476–1483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2017.05.004
Palladini G, Hegenbart U, Milani P, Kimmich C, Foli A, Ho AD et al (2014) A staging system for renal outcome and early markers of renal response to chemotherapy in AL amyloidosis. Blood 124:2325–2332. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-04-570010
Kyle RA, Greipp PR, O’Fallon WM (1986) Primary systemic amyloidosis: multivariate analysis for prognostic factors in 168 cases. Blood 68:220–224
Sethi S, Theis JD (2018) Pathology and diagnosis of renal non-AL amyloidosis. J Nephrol 31(3):343–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-017-0426-6
Grogan M, Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA (2017) Light-chain cardiac amyloidosis: strategies to promote early diagnosis and cardiac response. Heart 103(14):1065–1072. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2016-310704
Merlini G, Wechalekar AD, Palladini G (2013) Systemic light chain amyloidosis: an update for treating physicians. Blood 121(26):5124–5130. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2013-01-453001
Lim AY, Lee JH, Jung KS, Gwag HB, Kim DK, Kim S, Lee GY, Kim JS, Kim H-J, Lee S-Y, Lee JE, Jeon E-S, Kim K (2015) Clinical features and outcomes of systemic amyloidosis with gastrointestinal involvement: a single-center experience. Korean J Intern Med 30(4):496–505. https://doi.org/10.3904/kjim.2015.30.4.496
Thompson CA, Kyle R, Gertz M, Heit J, Pruthi R, Pardanani A (2010) Systemic AL amyloidosis with acquired factor X deficiency: a study of perioperative bleeding risk and treatment outcomes in 60 patients. Am J Hematol 85(3):171–173. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.21603
Sucker C, Hetzel GR, Grabensee B, Stockschlaeder M, Scharf RE (2006) Amyloidosis and bleeding: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and therapy. Am J Kidney Dis 47(6):947–955
Muchtar E, Buadi FK, Dispenzieri A, Gertz MA (2016) Immunoglobulin light-chain amyloidosis: from basics to new developments in diagnosis, prognosis and therapy. Acta Haematol 135:172–190. https://doi.org/10.1159/000443200
Gillmore JD, Wechalekar A, Bird J, Cavenagh J, Hawkins S, Kazmi M, Lachmann HL, Hawkins P, Pratt G (2014) Guidelines on the diagnosis and investigation of AL amyloidosis. John Wiley Sons Ltd Br J Haematol 168:207–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.13156
Lavatelli F, Albertini R, Di Fonzo A, Palladini G, Merlini G (2014) Biochemical markers in early diagnosis and management of systemic amyloidosis. Clin Chem Lab Med 52(11):1517–1531. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2014-0235
Angel-Korman A, Jaberi A, Sanchorawala V, Havasi A (2019) The utility of repeat kidney biopsy in systemic immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis. Amyloid 27(1):17–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/13506129.2019.1672650
Kastritis E, Kostopoulos IV, Terpos E, Paiva B, Fotiou D, Gavriatopoulou M, Kanellias N, Ziogas DC, Roussou M, Migkou M, Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou E, Trougakos IP, Tsitsilonis O, Dimopoulos MA (2018) Evaluation of minimal residual disease using next-generation flow cytometry in patients with AL amyloidosis. Blood Cancer J 8(5):46. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41408-018-0086-3
Eirin A, Irazabal MV, Gertz MA, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Kumar S, Sethi S, Nasr SH, Cornell LD, Fidler ME, Fervenza FC, Leung N (2012) Clinical features of patients with immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis (AL) with vascular-limited deposition in the kidney. Nephrol Dial Transpl 27(3):1097–1101. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfr381
Manwani R, Foard D, Mahmood S, Sachchithanantham S, Lane T, Quarta C et al (2018) Rapid hematological responses improve outcomes in patients with very advanced (Stage IIIb) cardiac immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis. Haematologica 103(4):e165–e168. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2017.178095
Sanchorawala V, Sarosiek S, Schulman A, Mistark M, Migre ME, Cruz R, Sloan JM, Brauneis D, Shelton AC (2020) Safety, tolerability, and response rates of daratumumab in relapsed AL amyloidosis: results of a Phase II Study. Blood. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2019004436
Arnall JR, Usmani SZ, Adamu H, Mishkin J, Bhutani M (2019) Daratumumab, pomalidomide, and dexamethasone as a bridging therapy to autologous stem cell transplantation in a case of systemic light-chain amyloidosis with advanced cardiac involvement. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 25(4):1021–1025. https://doi.org/10.1177/1078155218815305
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted retrospectively from data obtained for clinical purposes and it did not need ethical approval.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fenoglio, R., Baldovino, S., Ferro, M. et al. Outcome of patients with severe AL amyloidosis and biopsy-proven renal involvement ineligible for bone marrow transplantation. J Nephrol 34, 231–240 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-020-00748-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-020-00748-7