Abstract
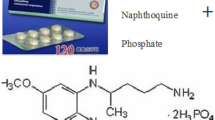
Naphthoquine is a 4-aminoquinoline antimalarial drug first synthesised in China in 1986 but which was not developed for clinical use until the late 1990s. Early in vitro parasite sensitivity and in vivo efficacy data, together with a long terminal elimination half-life (up to 23 days), suggested that it could be used as monotherapy for uncomplicated falciparum and vivax malaria, but is now marketed as a single-dose, fixed co-formulation with artemisinin in a milligram per kilogram ratio of 1:2.5. This form of artemisinin combination therapy (ACT) has also shown high cure rates, especially in two randomised trials in which, consistent with World Health Organization recommendations for all ACTs, it was administered daily for 3 days rather than as single dose for Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax infections (28-day adequate clinical and parasitological response ≥98.4 %). Although detailed safety monitoring has been performed in a minority of subjects, >4000 healthy volunteers and patients with malaria have been exposed to naphthoquine without any documented significant toxicity. As with other 4-aminoquinolines, naphthoquine is associated with prolongation of the electrocardiographic QT interval but not with cardiac or neurological events. It has been administered to children as young as 4 months of age but, due to a lack of pharmacokinetic, efficacy and toxicity data in young infants and in pregnant/lactating women, it should not be used in these vulnerable patient groups.With the emergence of parasite resistance to other ACTs, naphthoquine partnered with a potent artemisinin derivative may prove a viable alternative treatment for uncomplicated malaria.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cui L, Su XZ. Discovery, mechanisms of action and combination therapy of artemisinin. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2009;7(8):999–1013.
Muregi FW. Antimalarial drugs and their useful therapeutic lives: rational drug design lessons from pleiotropic action of quinolines and artemisinins. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2010;7(4):280–316.
Wang JY, Cao WC, Shan CQ, Zhang M, Li GF, Ding DB, et al. Naphthoquine phosphate and its combination with artemisinine. Acta Trop. 2004;89(3):375–81.
Deng RX. Recent progress in research on antimalarials in China. Chin J Pharm. 1989;20:372–6.
Law XX. Progress in clinical research on naphthoquine phosphate for treatment of malaria. Shanghai Pharm J. 2004;4(25):160–1.
Wang JY, Shan CQ, Fu DD, Sun ZW, Ding DB. Efficacy of naphthoquine, artemisinine and a combination of the two drugs in the treatment of falciparum malaria. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis. 2003;21(3):131–3.
Shan CQ, Wang JY, Ding DB, Sun ZW. Efficacy of naphthoquine phosphate, artemisinine and a combination of the two drug in the treatment of falciparum malaria. Acta Parasitologica et Medica Entomologica Sinica. 2005;12(2):90–2.
Li CF, Che LG, Yang CZ, Tao DZ. Effect of naphthoquine phosphate against malaria. J Pract Parasit Dis. 1998;6(2):58–9.
Li XL, Che LG, Li CF. Observation on the effectiveness of naphthoquine phosphate tablets on patients with vivax malaria and falciparum malaria. Chin Trop Med. 2003;3(5):608–9.
Li XL, Li CZ, He W, Dao QY. The treating effect of naphthoquine phosphates and artemether compound to P. falciparum. Chin J Pest Control. 2001;17(6):284–5.
Shan CQ, Liu GG, Jiao XQ. Primary observation on efficacy of naphthoquine phospate on the treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Acta Parasitologica et Medica Entomologica Sinica. 2003;10(4):198–201.
Shan CQ, Liu GG, Jiao XQ. Observation on efficacy of naphthoquine against vivax malaria. J Pathog Biol. 1998;11(4):275–6.
Guo WZ, Zheng Q, Li G, Ou FZ, Guo XB. A randomized-controlled study of naphthoquine and artesunate in the treatment of falciparum malaria. J Guangzhou Univ Tradit Chin Med. 2000;17(3):25–7.
Guo WZ, Guo XB, Zheng QJ, Tan B, Chen RJ, Ou FZ, et al. A randomized comparative study of naphtoquine, mefloquine and artsunate in the treatment of falciparum malaria. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2003;83(16):1406–8.
Deben D, inventor. Research Institute of Microbial Epidemiology, The Academy of Military Medical Science, assignee. Patent: process for preparing synergetic antimalarial-compound naphthoquine phosphate. 1998.
Wang S, Meng F, Shen H, Wen Y, Zhuo K, Zhu Q, et al. Therapeutic effect of dihydroartemisinin combined with naphthoquine phosphate in patients with falciparum malaria. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis. 2002;20(3):180–2.
Yang HL, Gao BH, Yang PF, Li CF, Li XL, Zhang ZY. Study on artesunate combined with naphthoquine delaying resistance of Plasmodium falciparum to artesunate in laboratory. Chin J Schistosomiasis Control. 2003;15(6):426–8.
Li XL, Yang HL, Yang PF, Li CF, Li L. Efficacy of artesunate-naphthoquine combination against falciparum malaria. Chin J Parasit Dis Control. 2003;16(4):208–9.
Wang JY, Shan CQ, Fu DD, Pang XJ, Lu YF, Su LF, et al. Clinical trial of co-naphthoquine in the treatment of falciparum malaria. Chin J Parasit Dis Control. 2003;16(3):134–6.
Shan CQ, Wang JY, Ding DB, Wu BA, Shi YL. Observation on efficacy of complex naphthoquine against Plasmodium vivax malaria. Acta Parasitologica et Medica Entomologica Sinica. 2004;11(1):8–10.
Yan Q, Gong Y, inventors. Guilin Pharmaceutical Corporation Ltd, assignee. Patent: Compound antimalarial three-layered tablets containing artemisinin or its derivatives and its preparing method. China. 2007.
Zhang GL, Zeng T, Gao XO, inventors; Kunming Pharmaceutical Group Co. Ltd, assignee. Patent: Compound naphthoquine phosphate pellets and preparation method thereof. China. 2012.
Li GQ, Song JP, inventors. Li GQ, Song JP, assignee. Patent: Malaria-resisting arteannuin naphthoquine compound composition. China. 2008.
Heng S, inventor. Heng, S, assignee. Patent: Novel compound antimalarial preparation method. China. 2004.
China Food and Drug Administration. Database of approved active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and API manufacturers in China. Information Center of the China Food and Drug Administration. 2015. http://app1.sfda.gov.cn/datasearcheng/face3/base.jsp?tableId=85&tableName=TABLE85&title=Database%20of%20approved%20Active%20Pharmaceutical%20Ingredients%20(APIs)%20and%20API%20manufacturers%20in%20China&bcId=136489131226659132460942000667. Accessed Jan 2016.
Yang HL, Li XL, Yang PF, Li CF, Wu C, Zhang ZY, et al. Preventive effect on naphthoquine against vivax malaria and drug resistant falciparum malaria in Yunnan, China. Chin J Parasit Dis Con. 2003;16(3):137–9.
Pang XJ, Wang GZ, Xing QL. Hundred one cases of Plasmodium falciparum treated with naphthoquine phosphate. Chin J Parasit Dis. 1999;17(1):20–2.
Kunming Pharmaceutical Company (KPC). ARCO® dosing guidelines. Kunming Pharmaceutical Company. 2010.
Wells TN. New medicines to combat malaria: an overview of the global pipeline of therapeutics. In: Staines HM, Krishna S, editors. Treatment and prevention of malaria: antimalarial drug chemistry, action and use. New York: Springer; 2012. p. 227–47.
Glusker A. WHO confronts Chinese company over malaria drug. BMJ. 2007;334(7593):553.
Zamiska N, McKay B. Global health, China’s pride on line in malaria clash. The Wall Street Journal, New York. 2007. http://www.wsj.com/articles/SB117286583468125138. Accessed Jan 2016.
World Health Organization. Prequalification of medicines by WHO. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs278/en/. Accessed Jan 2016.
World Health OrganizationGlobal Malaria Programme. Guidelines for the treatment of malaria. Report. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015.
Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau. On the issuance of the “Principles and use of antimalarial regimen (revised)”. Shanghai. 2009. http://www.scdc.sh.cn/b/10156.shtml. Accessed Mar 2016.
Burrows JN, Chibale K, Wells TNC. The state of the art in anti-malarial drug discovery and development. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11(10):1226–54.
Crowe A, Ilett KF, Karunajeewa HA, Batty KT, Davis TM. Role of P glycoprotein in absorption of novel antimalarial drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50(10):3504–6.
Tun T, Tint HS, Lin K, Kyaw TT, Myint MK, Khaing W, et al. Efficacy of oral single dose therapy with artemisinin-naphthoquine phosphate in uncomplicated falciparum malaria. Acta Trop. 2009;111(3):275–8.
Sullivan DJ Jr, Gluzman IY, Russell DG, Goldberg DE. On the molecular mechanism of chloroquine’s antimalarial action. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93(21):11865–70.
Wei XL, Su RB, Wang JY, Shi YL. Effect of complex naphthoquine on DNA content and pH value of the lysosome in Plasmodium berghei. Bull Acad Mil Med Sci. 2002;26(3):191–6.
Shao P, Shi YL, Chen PH, Wang FY. The effect of naphthoquine phosphate on the DNA content of Plasmodium yoelii yoelii: an analysis by flow cytometry. Chin J Zoonoses. 2000;16(1):51–4.
Yuan J, Chen PQ, Du QY, Li GQ, Chen L, Lei WW, et al. Effect of compound naphthoquine on the ultrastructure of Plasmodium berghei ANKA strain in erythrocytic stage. J Guangzhou Univ Tradit Chin Med. 2000;1:46–50.
Wong RP, Lautu D, Tavul L, Hackett SL, Siba P, Karunajeewa HA, et al. In vitro sensitivity of Plasmodium falciparum to conventional and novel antimalarial drugs in Papua New Guinea. Trop Med Int Health. 2010;15(3):342–9.
Koleala T. In vitro drug susceptibility of Plasmodium falciparum isolates in Madang Province, PNG using an optimized fluorescence assay and investigation of the effect of strain multiplicity on the outcome of in vitro antimalarial drug susceptibility measurements. Madang: University of Papua New Guinea; 2013.
Wirjanata G, Sebayang BF, Chalfein F, Prayoga Handayuni I, Trianty L, et al. Potent ex vivo activity of naphthoquine and methylene blue against drug-resistant clinical isolates of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(10):6117–24.
Yang HL, Li XL, Gao BH, Yang PF, Zhang ZY. Surveillance of Plasmodium falciparum susceptibility to seven antimalarials, including artemether, in the western part of the Sino-Myanmar border area. J Pathog Biol. 2009;11:831–43.
Yang HL, Gao BH, Huang KG. Comparison of naphthoquine, metronidazole and norfloxacine to artesunate sensitive and resistant P. falciparum strains. J Pract Parasit Dis. 1999;2:52–3.
Koleala T, Karl S, Laman M, Moore BR, Benjamin J, Barnadas C, et al. Temporal changes in Plasmodium falciparum anti-malarial drug sensitivity in vitro and resistance-associated genetic mutations in isolates from Papua New Guinea. Malar J. 2015;14(1):37.
Chen C. Development of antimalarial drugs and their application in China: a historical review. Infect Dis Poverty. 2014;3(1):9.
Li FL, Wang LH, Ding DB, Yang JD, Gao XS. Studies on antimalarials synthesis of 4-arylamino-tert-butylaminomethyl phenols. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. 1982;1:77–9.
Basco LK, Ringwald P. In vitro activities of piperaquine and other 4-aminoquinolines against clinical isolates of Plasmodium falciparum in Cameroon. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003;47(4):1391–4.
Davis TM, Hamzah J, Ilett KF, Karunajeewa HA, Reeder JC, Batty KT, et al. In vitro interactions between piperaquine, dihydroartemisinin, and other conventional and novel antimalarial drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50(8):2883–5.
Cabrera M, Cui L. In vitro activities of primaquine-schizonticide combinations on asexual blood stages and gametocytes of Plasmodium falciparum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59(12):7650–6.
Wang JY, Ding DB, Li GF, Zhao JH. Therapeutic efficacy of naphthoquine phosphate combined with artemisinine against Plasmodium knowlesi. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis. 2008;26(6):442–4.
Wang JY, Li GF, Zhao JH, Zhang M, Ji XG. Study of synergetic effect of naphthoquine phosphate and its combination with artemisinin and its delaying effect on drug-resistace of Plasmodium berghei. Acta Parasitologica et Medica Entomologica Sinica. 2008;15(3):133–6.
Sunday OS, George AO. The antimalarial effect of differnt dosage regimen of artemisinin-naphthoquine on Plasmodium berghei infected mice. Int J Pharmacol Ther. 2013;3(1):67–77.
Zhang ZX. Current situation of clinical treatment of falciparum malaria in Yunnan. J Kunming Med Univ. 2009;8:26–34.
World Health Organization. Assessment and monitoring of antimalarial drug efficacy for the treatment of uncomplicated falciparum malaria. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2003.
Yang HL, Yang PF, Li CF, Li XL, Li L, Yang CJ. Curative effect on artesunate-naphthoquine combination in treatment of malaria. Chin J Parasit Dis Control. 2004;17(2):87–9.
Liu H, Li CF, Nie RH, Sun YH, Li GS, Shen X. Treatment of malariae malaria with artesunate and naphthoquine phosphate: a report of two cases. Chin J Schistosomiasis Control. 2009;21(2):135.
Krudsood S, Chalermrut K, Pengruksa C, Srivilairit S, Silachamroon U, Treeprasertsuk S, et al. Comparative clinical trial of two-fixed combinations dihydroartemisinin-napthoquine-trimethoprim (DNP®) and artemether-lumefantrine (Coartem®/Riamet®) in the treatment of acute uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2003;34(2):316.
Song JP, Xu Y, Ou FZ, Peng NZ, Li GQ, Jin TS. Dosage verification of compound naphthoquine for falciparum malaria. J Guangzhou Univ Tradit Chin Med. 2001;18(1):19–24.
Hu AH, Li XM, Wang JH. Cost-minimization analysis on 3 kinds of medicines in the treatment of falciparum malaria. Strait Pharm J. 2011;4:199–201.
Meremikwu MM, Odey F, Oringanje C, Oyo-Ita A, Effa E, Esu EB, et al. Open-label trial of three dosage regimens of fixed-dose combination of artemisinin and naphthoquine for treating uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Calabar, Nigeria. Malar J. 2012;11:413.
Udoh E, Meremikwu M, Odey F, Oringanje C, Oduwole O, Oyo-ita A. Artemisinin-naphthoquine versus artemether-lumefantrine for treating uncomplicated plasmodium falciparum malaria in children: A randomized controlled trial of efficacy and safety. Niger J Paediatr. 2014;41(3):170–4.
Liu H, Yang HL, Xu JW, Wang JZ, Nie RH, Li CF. Artemisinin-naphthoquine combination versus chloroquine-primaquine to treat vivax malaria: an open-label randomized and non-inferiority trial in Yunnan Province, China. Malar J. 2013;12:409.
Laman M, Moore BR, Benjamin JM, Yadi G, Bona C, Warrel J, et al. Artemisinin-naphthoquine versus artemether-lumefantrine for uncomplicated malaria in Papua New Guinean children: an open-label randomized trial. PLoS Med. 2014;11(12):e1001773.
Laman M, Benjamin JM, Moore BR, Salib M, Tawat S, Davis WA, et al. Artemether-lumefantrine versus artemisinin-naphthoquine in Papua New Guinean children with uncomplicated malaria: a six months post-treatment follow-up study. Malar J. 2015;14:121.
Hombhanje FW, Huang Q. Artemisinin–naphthoquine Combination (ARCO®): an overview of the progress. Pharmaceuticals. 2010;3(12):3581–93.
Wu DL, Wang GX, Tang DH. Observation on the effect of naphthoquine phosphate on the control of malaria in Qiongzhong County, Hainan Province. China Trop Med. 2001;1(3):216–7.
Wang H, Bei ZC, Wang JY, Cao WC. Plasmodium berghei K173: selection of resistance to naphthoquine in a mouse model. Exp Parasitol. 2011;127(2):436–9.
Sun YH, Zhou JL, Liu H, Wang HY, Yang HL. In vitro culture of naphthoquione-resistant Plasmodium falciparum strains in Yunnan Province. J Pathog Biol. 2010;2(124–6):33.
Qu HY, Gao HZ, Hao GT, Li YY, Li HY, Hu JC, et al. Single-dose safety, pharmacokinetics, and food effects studies of compound naphthoquine phosphate tablets in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;50(11):1310–8.
Batty KT, Salman S, Moore BR, Benjamin J, Lee ST, Page-Sharp M, et al. Artemisinin-naphthoquine combination therapy for uncomplicated pediatric malaria: a pharmacokinetic study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56(5):2472–84.
Li PF. Study on the determination of artemisinin/naphthoquine phosphate in human and pharmacokinetics [masters thesis, Jilin University, China]. 2006.
Wang JY, Zuo B, Xu ZH, Sun GZ, Zhang M, Wang C, et al. Long-term toxicity of co-naphthoquine in beagle dogs. Bull Acad Mil Med Sci. 2003;27(3):196–8.
Sunday OS, George AO. Effect of dosage regimen of Artemisinin-naphthoquine combination on biochemical parameters in Plasmodium berghei infected mice. J Med Res Pract. 2013;2(5):129–33.
Fowler JSL. Data interpretation. In: Duffus JG, Worth HGJ, editors. Fundamental toxicology. Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry; 2006. p. 53.
Benjamin J, Moore B, Lee ST, Senn M, Griffin S, Lautu D, et al. Artemisinin-naphthoquine combination therapy for uncomplicated pediatric malaria: a tolerability, safety, and preliminary efficacy study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56(5):2465–71.
White NJ. Cardiotoxicity of antimalarial drugs. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7(8):549–58.
El-Beshbishi SN, Taman A, El-Malky M, Azab MS, El-Hawary AK, El-Tantawy DA. First insight into the effect of single oral dose therapy with artemisinin-naphthoquine phosphate combination in a mouse model of Schistosoma mansoni infection. Int J Parasitol. 2013;43(7):521–30.
del Villar Perez. L, Burguillo FJ, Lopez-Aban J, Muro A. Systematic review and meta-analysis of artemisinin based therapies for the treatment and prevention of schistosomiasis. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45867.
Utzinger J, Xiao SH, Tanner M, Keiser J. Artemisinins for schistosomiasis and beyond. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2007;8(2):105–16.
El-Beshbishi SN, El Bardicy S, Tadros M, Ayoub M, Taman A. Spotlight on the in vitro effect of artemisinin-naphthoquine phosphate on Schistosoma mansoni and its snail host Biomphalaria alexandrina. Acta Trop. 2015;141(Pt A):37–45.
World Health Organization. Guidelines for the treatment of malaria. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2006.
Naing C, Whittaker MA, Mak JW, Aung K. A systematic review of the efficacy of a single dose artemisinin-naphthoquine in treating uncomplicated malaria. Malar J. 2015;14(1):392.
Isba R, Zani B, Gathu M, Sinclair D. Artemisinin-naphthoquine for treating uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;2:CD011547.
Price RN, Uhlemann AC, van Vugt M, Brockman A, Hutagalung R, Nair S, et al. Molecular and pharmacological determinants of the therapeutic response to artemether-lumefantrine in multidrug-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42(11):1570–7.
Amaratunga C, Lim P, Suon S, Sreng S, Mao S, Sopha C, et al. Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Cambodia: a multisite prospective cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2016;16:357–65.
Basco LK. Field application of in vitro assays for the sensitivity of human malaria parasites to antimalarial drugs. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2007.
Rujumba J, Mworozi EA, Manganda AK, Kiguba R, Rwakimali B, Nsobya S. A comparative study of Arco and Coartem in the treatment of uncomplicated malaria in patients aged 4 months to 16 years attending Mulago hospital, Kapala, Uganda [abstract]. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14(Suppl 1):e332.
D’Alessandro U, Ubben D, Hamed K, Ceesay SJ, Okebe J, Taal M, et al. Malaria in infants aged less than six months—is it an area of unmet medical need? Malar J. 2012;11:400.
Davis TM, Mueller I, Rogerson SJ. Prevention and treatment of malaria in pregnancy. Future Microbiol. 2010;5(10):1599–613.
Skinner TS, Manning LS, Johnston WA, Davis TM. In vitro stage-specific sensitivity of Plasmodium falciparum to quinine and artemisinin drugs. Int J Parasitol. 1996;26(5):519–25.
Shanks GD, Edstein MD, Jacobus D. Evolution from double to triple-antimalarial drug combinations. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2015;109(3):182–8.
Delves M, Plouffe D, Scheurer C, Meister S, Wittlin S, Winzeler EA, et al. The activities of current antimalarial drugs on the life cycle stages of Plasmodium: a comparative study with human and rodent parasites. PLoS Med. 2012;9(2):e1001169.
Hombhanje FW, Linge D, Saweri A, Kuanch C, Jones R, Toraso S, et al. Artemisinin-naphthoquine combination (ARCO) therapy for uncomplicated falciparum malaria in adults of Papua New Guinea: a preliminary report on safety and efficacy. Malar J. 2009;8:196.
Toure OA, Penali LK, Yapi JD, Ako BA, Toure W, Djerea K, et al. A comparative, randomized clinical trial of artemisinin/naphtoquine twice daily one day versus artemether/lumefantrine six doses regimen in children and adults with uncomplicated falciparum malaria in Cote d’Ivoire. Malar J. 2009;8:148.
Nour BYM, Hamed NMM, Habour AB, Elkariem AAA, Mohamadani AA, Saeed OK. Efficacy and safety of artemisinin–naphthoquine (ARCO®) in the treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum among Sudanese adults. Glob Adv Res J Med Med Sci. 2014;3(1):1–7.
Tjitra E, Hasugian AR, Siswantoro H, Prasetyorini B, Ekowatiningsih R, Yusnita EA, et al. Efficacy and safety of artemisinin-naphthoquine versus dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine in adult patients with uncomplicated malaria: a multi-centre study in Indonesia. Malar J. 2012;11:153.
Kinde-Gazard D, Ogouyemi-Hounto A, Capo-Chichi L, Gbaguidi J, Massougbodji A. A randomized clinical trial comparing the effectiveness and tolerability of artemisinine-naphthoquine (Arco®) and artemether-lumefantrine (Coartem®) in the treatment of uncomplicated malaria in Benin. Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 2012;105(3):208–14.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Yue Wu for assistance in translating the Chinese-language publications.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No specific funding was obtained for the present review, but Brioni R. Moore is supported by a National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC) Early Career Fellowship (#1036951) and Timothy M. E. Davis is supported by an NHMRC Practitioner Fellowship (#1058260).
Conflicts of interest
Francis Hombhanje has received funding from Kunming Pharmaceutical Corporation for conducting clinical trials of ARCO®. Brioni R. Moore, Moses Laman, Sam Salman, Kevin T. Batty, Madhu Page-Sharp, Laurens Manning and Timothy M. E. Davis have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, B.R., Laman, M., Salman, S. et al. Naphthoquine: An Emerging Candidate for Artemisinin Combination Therapy. Drugs 76, 789–804 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-016-0572-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-016-0572-5