Abstract
Purpose of Review
The purpose of this review article is to analyze the current information about diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, and interventional therapies regarding pulmonary embolism (PE) treatment. In addition to review the outcomes obtained by pulmonary embolism response teams.
Recent Findings
Several important contributions in the PE management have been recently published. New scoring systems, such as the PERC rule and YEARS, are used to effectively rule out PE; and stratification scores such as Bova and Hestia were validated. New evidence was favorable to support the use of direct oral anticoagulants in morbidly obese and end-stage renal disease patients; although, not in patients with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. New studies of catheter-based thrombectomy for acute PE were also published. However, a new statement from the American Heart Association criticizes the lack of randomized trials to support the use of catheter-based interventions in acute PE. Contributions about the cardiopulmonary support in massive PE patients, including ventilation techniques, vasopressors, inhaled pulmonary vasodilators and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation are available. Finally, the advantages and disadvantages of the impact of Pulmonary Embolism Response Teams in the care of acute PE patients.
Summary
Nearly all aspects in the diagnosis, prognosis and care of PE are evolving. In this article, we discuss the epidemiology, diagnosis, risk stratification, and therapeutic approaches to PE. We provide additional focus on advanced therapeutic strategies such as catheter-based interventions, surgical approaches, and cardiopulmonary support. The impact of a multidisciplinary team approach to PE management is also discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
Beckman MG, Hooper WC, Critchley SE, Ortel TL. Venous Thromboembolism. A Public Health Concern. American Journal of Preventive Medicine. 2010;38(4):S495-501.
Goldhaber SZ. Venous thromboembolism: Epidemiology and magnitude of the problem. Best Practice and Research: Clinical Haematology. 2012;25(3):235–42.
Pineda LA, Hathwar VS, Grant BJB. Clinical suspicion of fatal pulmonary embolism. Chest. 2001;120(3):791–5.
Meignan M, Rosso J, Gauthier H, Brunengo F, Claudel S, Sagnard L, et al. Systematic lung scans reveal a high frequency of silent pulmonary embolism in patients with proximal deep venous thrombosis. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2000;160(2):159–64.
Schneider D, Lilienfeld DE, Im W. The epidemiology of pulmonary embolism: Racial contrasts in incidence and in-hospital case fatality. J Natl Med Assoc. 2006;98(12):1967.
Tang Y, Sampson B, Pack S, Shah K, Yon Um S, Wang D, et al. Ethnic differences in out-of-hospital fatal pulmonary embolism. Circulation. 2011;123(20):2219–25.
Heit JA, Silverstein MD, Mohr DN, Petterson TM, O’Fallon WM, Melton LJ. Risk Factors for Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160(6):809–15.
• Carroll BJ, Piazza G. (2018) Hypercoagulable states in arterial and venous thrombosis: When, how, and who to test? Vasc Med (United Kingdom). 23(4):388–99. This article explains how and when to perform a hypercoagulable work up in VTE patients.
Buckner TW, Key NS. (2012) Venous thrombosis in blacks. Circulation. 125(6):837–9
Giannakopoulos B, Passam F, Ioannou Y, Krilis SA. How we diagnose the antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood. 2009;113(5):985–94.
• Klok FA, Huisman M V. (2017) Management of incidental pulmonary embolism. The European respiratory journal. 49(6). This article discusses the management of asymptomatic incidentally found PE.
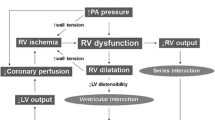
Wood KE. Major pulmonary embolism: Review of a pathophysiologic approach to the golden hour of hemodynamically significant pulmonary embolism. Chest. 2002;121(3):877–905.
Worsley DF, Alavi A, Aronchick JM, Chen JTT, Greenspan RH, Ravin CE. Chest radiographic findings in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: Observations from the PIOPED study. Radiology. 1993;189(1):133–6.
Ullman E, Brady WJ, Perron AD, Chan T, Mattu A. Electrocardiographic manifestations of pulmonary embolism. Am J Emerg Med. 2001;19(6):514–9.
Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, Stiell I, Dreyer JF, Barnes D, et al. Excluding pulmonary embolism at the bedside without diagnostic imaging: Management of patients with suspected pulmonary embolism presenting to the emergency department by using a simple clinical model and D-dimer. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135(2):98–107.
Le Gal G, Righini M, Roy PM, Sanchez O, Aujesky D, Bounameaux H, Perrier A. Prediction of pulmonary embolism in the emergency department: The revised geneva score. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144(3):165–71.
van der Hulle T, Cheung WY, Kooij S, Beenen LF, van Bemmel T, van Es J, et al. (2017) Simplified diagnostic management of suspected pulmonary embolism (the YEARS study): a prospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet. 390(10091):289–97. This article introduces a new scoring system to diagnose pulmonary embolism
Kline JA, Courtney DM, Kabrhel C, Moore CL, Smithline HA, Plewa MC, et al. Prospective multicenter evaluation of the pulmonary embolism rule-out criteria. J Thromb Haemost. 2008;6(5):772–80.
•• Kearon C, de Wit K, Parpia S, Schulman S, Afilalo M, Hirsch A, et al. (2019) Diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism with d -Dimer Adjusted to Clinical Probability. N Engl J Med. 381(22):2125–34. This article introduces a new scoring system to diagnose pulmonary embolism
Doğan H, de Roos A, Geleijins J, Huisman M, Kroft L. The role of computed tomography in the diagnosis of acute and chronic pulmonary embolism. Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology. 2015;21(4):307.
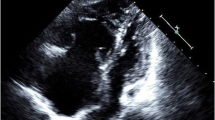
Dudzinski DM, Hariharan P, Parry BA, Chang Y, Kabrhel C. (2017) Assessment of Right Ventricular Strain by Computed Tomography Versus Echocardiography in Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Acad Emerg Med. 24(3):337–43. This article explains how to appropriately evaluate the right ventricle by echocardiogram and CT.
•• van der Hulle T, Cheung WY, Kooij S, Beenen LF, van Bemmel T, van Es J, et al. (2017) Simplified diagnostic management of suspected pulmonary embolism (the YEARS study): a prospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet. 390(10091):289–97. This article introduces a new scoring system to diagnose pulmonary embolism
Waxman AD, Bajc M, Brown M, Fahey FH, Freeman LM, Haramati LB, et al. (2017) Appropriate use criteria for ventilation-perfusion imaging in pulmonary embolism: Summary and excerpts. Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 58(5):13N-5N. This article explains how to use VQ scan to evaluate a patient for pulmonary embolism.
Dilorenzo MP, Bhatt SM, Mercer-Rosa L. How best to assess right ventricular function by echocardiography. Cardiol Young. 2015;25(8):1473.
Kucher N, Rossi E, De Rosa M, Goldhaber SZ. Prognostic role of echocardiography among patients with acute pulmonary embolism and a systolic arterial pressure of 90 mm Hg or higher. Arch Intern Med. 2005;165(15):1777–81.
Goliszek S, Wisniewska M, Kurnicka K, Lichodziejewska B, Ciurzyński M, Kostrubiec M, et al. Patent foramen ovale increases the risk of acute ischemic stroke in patients with acute pulmonary embolism leading to right ventricular dysfunction. Thromb Res. 2014;134(5):1052–6.
Jaff MR, McMurtry MS, Archer SL, Cushman M, Goldenberg N, Goldhaber SZ, et al. Management of massive and submassive pulmonary embolism, iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis, and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: A scientific statement from the american heart association. Circulation. 2011;123(16):1788–830.
Aujesky D, Obrosky DS, Stone RA, Auble TE, Perrier A, Cornuz J, et al. Derivation and validation of a prognostic model for pulmonary embolism. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172(8):1041–6.
•• Bova C, Vanni S, Prandoni P, Morello F, Dentali F, Bernardi E, et al. A prospective validation of the Bova score in normotensive patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Thromb Res. 2018. May 1;165:107–11. This article validates a new scoring system for pulmonary embolism risk stratification
Zondag W, Mos ICM, Creemers-Schild D, Hoogerbrugge ADM, Dekkers OM, Dolsma J, et al. Outpatient treatment in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: The Hestia Study. J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9(8):1500–7.
Vanni S, Jimenez D, Nazerian P, Gigli C, Parisi M, Morello F, et al. Prognostic value of plasma lactate in acute pulmonary embolism: the multicentre Thrombo-Embolism Lactate Outcome study. Eur Heart J. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2012.10.022.
Ruíz-Giménez N, Suárez C, González R, Nieto JA, Todolí JA, Samperiz ÁL, et al. Predictive variables for major bleeding events in patients presenting with documented acute venous thromboembolism. Findings from the RIETE Registry. Thromb Haemost. 2008;100(07):26–31.
Ludwig R. Therapeutic Use of Heparin beyond Anticoagulation. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2009;6(4):281–9.
Patel JP, Roberts LN, Arya R. Anticoagulating obese patients in the modern era. British Journal of Haematology. 2011;155(2):137–49.
Cuker A, Gimotty PA, Crowther MA, Warkentin TE. Predictive value of the 4Ts scoring system for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood. 2012;120(20):4160–7.
• Cuker A, Arepally GM, Chong BH, Cines DB, Greinacher A, Gruel Y, et al. (2018) American Society of Hematology 2018 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood Advances. 120(20):4160–7. This article provides recommendations for management of heparin induced thrombocytopenia.
Simonneau G, Sors H, Charbonnier B, Page Y, Laaban J-P, Azarian R, et al. A Comparison of Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin with Unfractionated Heparin for Acute Pulmonary Embolism. N Engl J Med. 1997;337(10):663–9.
Lee AYY, Levine MN, Baker RI, Bowden C, Kakkar AK, Prins M, et al. Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin versus a Coumarin for the Prevention of Recurrent Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(2):146–53.
Lee AYY, Bauersachs R, Janas MS, Jarner MF, Kamphuisen PW, Meyer G, et al. CATCH: A randomised clinical trial comparing long-term tinzaparin versus warfarin for treatment of acute venous thromboembolism in cancer patients. BMC Cancer. 2013;13(1):1–3.
Martel N, Lee J, Wells PS. Risk for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with unfractionated and low-molecular-weight heparin thromboprophylaxis: A meta-analysis. Blood. 2005;106(8):2710–5.
Investigators Matisse. Subcutaneous Fondaparinux versus Intravenous Unfractionated Heparin in the Initial Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(18):1695–702.
Bhatt VR, Aryal MR, Shrestha R, Armitage JO. Fondaparinux-associated heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Eur J Haematol. 2013;91(5):437–41.
Linkins L-A, Dans AL, Moores LK, Bona R, Davidson BL, Schulman S, et al. Treatment and Prevention of Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia. Chest. 2012;141(2):e495S-530S.
Lee CJ, Ansell JE. Direct thrombin inhibitors. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 2011;72(4):581–92.
Stone GW, McLaurin BT, Cox DA, Bertrand ME, Lincoff AM, Moses JW, et al. Bivalirudin for Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(21):2203–16.
Warkentin TE, Greinacher A, Koster A, Lincoff AM. Treatment and prevention of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (8th edition). Chest. 2008;133(6):340S-80S.
Wardrop D, Keeling D. The story of the discovery of heparin and warfarin. British Journal of Haematology. 2008;141(6):757–63.
Whitlon DS, Sadowski JA, Suttie JW, Sadowski JA. Mechanism of Coumarin Action: Significance of Vitamin K Epoxide Reductase Inhibition. Biochemistry. 1978;17(8):1371–7.
Tideman PA, Tirimacco R, St. John A, Roberts GW. (2015) How to manage warfarin therapy. Aust Prescr. 2015;38(2):44.
Zareh M, Davis A, Henderson S. Reversal of warfarin-induced hemorrhage in the emergency department. Western Journal of Emergency Medicine. 2011;12(4):386.
Kakagia DD, Papanas N, Karadimas E, Polychronidis A. Warfarin-induced skin necrosis Ann Dermatol. 2014;26(1):96.
Investigators E. Oral rivaroxaban for symptomatic venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(26):2499–510.
Agnelli G, Buller HR, Cohen A, Curto M, Gallus AS, Johnson M, et al. Oral apixaban for the treatment of acute venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med [Internet]. 2013;369(9):799–808.
Bueller HR. Edoxaban versus warfarin for venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(1):80–1.
Schulman S, Kearon C, Kakkar AK, Mismetti P, Schellong S, Eriksson H, et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in the treatment of acute venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med [Internet]. 2009;361(24):2342–52.
Kearon C, Akl EA, Ornelas J, Blaivas A, Jimenez D, Bounameaux H, et al. Antithrombotic therapy for VTE disease: CHEST guideline and expert panel report. Chest. 2016;149(2):315–52.
Agnelli G, Becattini C, Meyer G, Muñoz A, Huisman M V., Connors JM, et al. (2020) Apixaban for the Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism Associated with Cancer. N Engl J Med. 382(17):1599–607. This article provides evidence of efficacy of the use of apixaban in cancer patients.
Raskob GE, van Es N, Verhamme P, Carrier M, Di Nisio M, Garcia D, et al. (2017) Edoxaban for the Treatment of Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism. N Engl J Med. 378(7):615–24. This article provides evidence of efficacy of the use of edoxaban in cancer patients.
Carrier M, Abou-Nassar K, Mallick R, Tagalakis V, Shivakumar S, Schattner A, et al. (2019) Apixaban to prevent venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. N Engl J Med. 380(8):711–9. This article provides evidence of efficacy of the use of apixaban to prevent VTE in cancer patients.
Martin K, Beyer-Westendorf J, Davidson BL, Huisman MV, Sandset PM, Moll S. Use of the direct oral anticoagulants in obese patients: guidance from the SSC of the ISTH. J Thromb Haemost. 2016;14(6):1308.
• Coons JC, Albert L, Bejjani A, Iasella CJ. (2020) Effectiveness and Safety of Direct Oral Anticoagulants versus Warfarin in Obese Patients with Acute Venous Thromboembolism. Pharmacotherapy. 40(3):204–10. This article provides evidence of efficacy of the use of DOACS in morbid obese patients.
Dias C, Moore KT, Murphy J, Ariyawansa J, Smith W, Mills RM, et al. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of single-dose rivaroxaban in chronic hemodialysis. Am J Nephrol. 2016;43(4):229–36.
Wang X, Tirucherai G, Marbury TC, Wang J, Chang M, Zhang D, et al. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and safety of apixaban in subjects with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;56(5):628–36.
•• Siontis KC, Zhang X, Eckard A, Bhave N, Schaubel DE, He K, et al. (2018) Outcomes associated with apixaban use in patients with end-stage kidney disease and atrial fibrillation in the United States. Circulation. 138(15):1519–29. This article provides evidence of efficacy of the use of apixaban in patients receiving hemodialysis.
Nigwekar SU, Thadhani R. (2018) Long-Term Anticoagulation for Patients Receiving Dialysis. Circulation. 1530–1533. This article provides evidence of efficacy of the use of DOACS in patients receiving hemodialysis.
Reed D, Palkimas S, Hockman R, Abraham S, Le T, Maitland H. (2018) Safety and effectiveness of apixaban compared to warfarin in dialysis patients. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2(2):291–8. This article provides evidence of efficacy of the use of apixaban in patients receiving hemodialysis.
•• Pengo V, Denas G, Zoppellaro G, Jose SP, Hoxha A, Ruffatti A, et al. (2018) Rivaroxaban vs warfarin in high-risk patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. Blood. 132(13). This article provides evidence of safety of the use of rivaroxaban in patients diagnosed with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome.
•• Pollack C V., Reilly PA, van Ryn J, Eikelboom JW, Glund S, Bernstein RA, et al. (2017) Idarucizumab for Dabigatran Reversal — Full Cohort Analysis. N Engl J Med. 377(5):431–41. This article provides evidence of effectiveness and safety of the use of Idarucizumab to reverse dabigatran
Siegal DM, Curnutte JT, Connolly SJ, Lu G, Conley PB, Wiens BL, et al. Andexanet Alfa for the Reversal of Factor Xa Inhibitor Activity. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(25):2413–24.
•• Connolly SJ, Crowther M, Eikelboom JW, Gibson CM, Curnutte JT, Lawrence JH, et al. (2019) Full Study Report of Andexanet Alfa for Bleeding Associated with Factor Xa Inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 380(14):1326–35. This article provides evidence of effectiveness and safety of the use of Andexanet to reverse anti Xa.
•• Kiser TH, Burnham EL, Clark B, Ho PM, Allen RR, Moss M, et al. (2018) Half-dose versus full dose alteplase for treatment of pulmonary embolism. Crit Care Med. 46(10):1617. This article provides evidence of the effectiveness of reduced doses of thrombolytics to treat pulmonary embolism.
•• Konstantinides S V, Meyer G, Becattini C, Bueno H, Geersing G-J, Harjola V-P, et al. (2019) 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration with the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Eur Heart J. 41(4):543–603. This article is the updated European guidelines to treat pulmonary embolism.
Meyer G, Vicaut E, Danays T, Agnelli G, Becattini C, Beyer-Westendorf J, et al. Fibrinolysis for Patients with Intermediate- Risk Pulmonary Embolism for the PEITHO Investigators*. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1402–11.
Marti C, John G, Konstantinides S, Combescur C, Sanchez O, Lankeit M, et al. Systemic thrombolytic therapy for acute pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. European Heart Journal. 2015;36(10):605–14.
Kucher N, Boekstegers P, Müller OJ, Kupatt C, Beyer-Westendorf J, Heitzer T, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of ultrasound-assisted catheter-directed thrombolysis for acute intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. Circulation. 2014;129(4):479–86.
Piazza G, Hohlfelder B, Jaff MR, Ouriel K, Engelhardt TC, Sterling KM, et al. A Prospective, Single-Arm, Multicenter Trial of Ultrasound-Facilitated, Catheter-Directed, Low-Dose Fibrinolysis for Acute Massive and Submassive Pulmonary Embolism: The SEATTLE II Study. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;8(10):1382–92.
• Tapson VF, Sterling K, Jones N, Elder M, Tripathy U, Brower J, et al. (2018) A Randomized Trial of the Optimum Duration of Acoustic Pulse Thrombolysis Procedure in Acute Intermediate-Risk Pulmonary Embolism: The OPTALYSE PE Trial. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 11(14):1401–10. This article presents the evidence of safety and effectiveness of multiple protocols to use catheter directed thrombolytics.
• Geller BJ, Adusumalli S, Pugliese SC, Khatana SAM, Nathan A, Weinberg I, et al. (2020) Outcomes of catheter-directed versus systemic thrombolysis for the treatment of pulmonary embolism: A real-world analysis of national administrative claims. Vasc Med (United Kingdom). 25(4):334–40. This article presents the evidence of safety and effectiveness of catheter directed thrombolytics vs systemic thrombolytics.
Patel N, Patel NJ, Agnihotri K, Panaich SS, Thakkar B, Patel A, et al. Utilization of catheter-directed thrombolysis in pulmonary embolism and outcome difference between systemic thrombolysis and catheter-directed thrombolysis. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions. 2015;86(7):1219–27.
• Stępniewski J, Kopeć G, Musiałek P, Magoń W, Jonas K, Waligóra M, et al. (2021) Hemodynamic Effects of Ultrasound-Assisted, Catheter-Directed, Very Low-Dose, Short-Time Duration Thrombolysis in Acute Intermediate–High Risk Pulmonary Embolism (from the EKOS-PL Study). Am J Cardiol. 141:133–9. This article presents the evidence of safety and effectiveness of a low-dose protocol to use catheter directed thrombolytics.
• Avgerinos ED, Abou Ali A, Toma C, Wu B, Saadeddin Z, McDaniel B, et al. (2019) Catheter-directed thrombolysis versus suction thrombectomy in the management of acute pulmonary embolism. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. 7(5):623–8. This article compares two different catheter-based techniques to treat pulmonary embolism.
•• Giri J, Sista AK, Weinberg I, Kearon C, Kumbhani DJ, Desai ND, et al. (2019) Interventional Therapies for Acute Pulmonary Embolism: Current Status and Principles for the Development of Novel Evidence: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 140(20):e774–801. This article are the American Heart Association recommendations about the interventional therapies to treat pulmonary embolism.
Pasrija C, Kronfli A, Rouse M, Raithel M, Bittle GJ, Pousatis S, et al. (2018) Outcomes after surgical pulmonary embolectomy for acute submassive and massive pulmonary embolism: A single-center experience. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 155(3):1095–1106.e2. This article presents the single center outcomes of the use of surgical pulmonary embolectomy to treat massive pulmonary embolism.
Neely RC, Byrne JG, Gosev I, Cohn LH, Javed Q, Rawn JD, et al. Surgical embolectomy for acute massive and submassive pulmonary embolism in a series of 115 patients. Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 2015;100(4):1245–52.
Jenkins D. Pulmonary endarterectomy: The potentially curative treatment for patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. European Respiratory Review. 2015;24(136):263–71.
• Kline JA, Puskarich MA, Jones AE, Mastouri RA, Hall CL, Perkins A, et al. (2019) Inhaled nitric oxide to treat intermediate risk pulmonary embolism: A multicenter randomized controlled trial. Nitric Oxide - Biol Chem. 84:60–8. This article presents the efficacy and safety of the use of inhaled nitric oxide to treat acute pulmonary embolism.
Fuller BM, Mohr NM, Skrupky L, Fowler S, Kollef MH, Carpenter CR. The use of inhaled prostaglandins in patients with ARDS: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest. 2015;147(6):1510–22.
Kooter AJ, IJzerman RG, Kamp O, Boonstra AB, Smulders YM. No effect of epoprostenol on right ventricular diameter in patients with acute pulmonary embolism: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Pulm Med. 2010;10(1):1–9.
Boulain T, Lanotte R, Legras A, Perrotin D. Efficacy of epinephrine therapy in shock complicating pulmonary embolism. Chest. 1993;104(1):300–2.
Kerbaul F, Rondelet B, Motte S, Fesler P, Hubloue I, Ewalenko P, et al. Effects of norepinephrine and dobutamine on pressure load-induced right ventricular failure. Crit Care Med. 2004;32(4):1035–40.
Tanaka H, Tajimi K, Matsumoto A, Kobayashi K. Vasodilatory effects of milrinone on pulmonary vasculature in dogs with pulmonary hypertension due to pulmonary embolism: A comparison with those of dopamine and dobutamine. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1990;17(10):681–90.
Kerbaul F, Gariboldi V, Giorgi R, Mekkaoui C, Guieu R, Fesler P, et al. Effects of levosimendan on acute pulmonary embolism-induced right ventricular failure. Crit Care Med. 2007;35(8):1948–54.
• Zhao S, Friedman O. (2020) Management of Right Ventricular Failure in Pulmonary Embolism. Critical Care Clinics. 36(3):505–15. This article provides important guidelines to manage the acute heart failure in pulmonary embolism.
Makdisi G, Wang IW. Extra Corporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) review of a lifesaving technology. Journal of Thoracic Disease. 2015;7(7):E166.
Maggio P, Hemmila M, Haft J, Bartlett R. Extracorporeal life support for massive pulmonary embolism. J Trauma - Inj Infect Crit Care. 2007;62(3):570–6.
Murphy DA, Hockings LE, Andrews RK, Aubron C, Gardiner EE, Pellegrino VA, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation-hemostatic complications. Transfusion Medicine Reviews. 2015;29(2):90–101.
Meneveau N, Guillon B, Planquette B, Piton G, Kimmoun A, Gaide-Chevronnay L, et al. (2018) Outcomes after extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for the treatment of high-risk pulmonary embolism: A multicentre series of 52 cases. Eur Heart J. 39(47):4196–204. This article presents the European outcomes of the use of ECMO to treat massive pulmonary embolism.
Pasrija C, Kronfli A, George P, Raithel M, Boulos F, Herr DL, et al. (2018) Utilization of Veno-Arterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Massive Pulmonary Embolism. Ann Thorac Surg. 105(2):498–504. This article presents the single center outcomes of the use of ECMO to treat massive pulmonary embolism.
Rivera-Lebron B, McDaniel M, Ahrar K, Alrifai A, Dudzinski DM, Fanola C, et al. (2019) Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow Up of Acute Pulmonary Embolism: Consensus Practice from the PERT Consortium. Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis. 25:1076029619853037. This article presents the recommendations to treat acute pulmonary embolism by the PERT Consortium.
• Jen WY, Kristanto W, Teo L, Phua J, Yip HS, MacLaren G, et al. (2020) Assessing the Impact of a Pulmonary Embolism Response Team and Treatment Protocol on Patients Presenting With Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Hear Lung Circ. 29(3):345–53. This article analyzes the impact of the creation of PERT in the outcomes of pulmonary embolism patients.
•• Rosovsky R, Chang Y, Rosenfield K, Channick R, Jaff MR, Weinberg I, et al. (2019) Changes in treatment and outcomes after creation of a pulmonary embolism response team (PERT), a 10-year analysis. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 47(1):31–40. This article analyzes the impact of the creation of PERT in the outcomes of pulmonary embolism patients.
Kuo WT, Banerjee A, Kim PS, DeMarco FJ, Levy JR, Facchini FR, Unver K, Bertini MJ, Sista AK, Hall MJ, Rosenberg JK, De Gregorio MA. Pulmonaryembolism response to fragmentation embolectomy and catheter thrombolysis (PERFECT). Chest. 2015;148(3):667–73. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.15-0119.
Tu T, Toma C, Tapson VF, Adams C, Jaber WA, Silver M, et al. (2019) A Prospective, Single-Arm, Multicenter Trial of Catheter-Directed Mechanical Thrombectomy for Intermediate-Risk Acute Pulmonary Embolism: The FLARE Study. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 12(9):859–69. This article presents the effectiveness and safety of catheter based thrombectomy to treat acute pulmonary embolism.
• Sista AK, Horowitz JM, Tapson VF, Rosenberg M, Elder MD, Schiro BJ, et al. (2021) Indigo Aspiration System for Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism: Results of the EXTRACT-PE Trial. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 14(3):319–29. This article presents the effectiveness and safety of catheter based thrombectomy to treat acute pulmonary embolism.
Funding
N/A
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Ronson Madathil MD declares he has no conflict of interest. John Anagnostakos MD declares he has no conflict of interest. Gabriel Pereira MD declares he has no conflict of interest. Michael Hall MD declares he has no conflict of interest. Rafael S. Cires-Drouet MD declares he has no conflict of interest
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical collection on Vasular systems.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madathil, R., Anagnostakos, J., Pereira, G. et al. Current Management of Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Curr Surg Rep 9, 16 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40137-021-00293-7
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40137-021-00293-7