Abstract
Objective
Studies suggest that LncRNA maternally expressed 8, small nucleolar RNA host gene (MEG8) contributes to inflammatory regulation, while the function and potential mechanisms of MEG8 in Parkinson’s disease (PD) are unknown. This study aimed to assess the clinical value and biological function of MEG8 in PD.
Methods
One hundred and two PD patients, eighty-six AD patients, and eighty healthy controls were enrolled in this study. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced microglia BV2 constructs an in vitro cell model. RT-qPCR was conducted to quantify the levels of MEG8, miR-485-3p, and FBXO45 in serum and cells. ROC curve was employed to examine the diagnostic value of MEG8 in PD. Serum and cellular pro-inflammatory factor secretion were quantified by ELISA. Dual-luciferase reporter and RIP assay to validate the targeting relationship between miR-485-3p and FBXO45.
Results
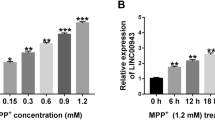
MEG8 and FBXO45 were significantly decreased in the serum of PD patients and LPS-induced bv2, while miR-485-3p was increased (P < 0.05). ROC curve confirmed that serum MEG8 has high sensitivity and specificity to identify PD patients from healthy controls and AD patients, respectively. Elevated MEG8 alleviated LPS-induced inflammatory factor overproduction compared with LPS-induced BV2 (P < 0.05), but this alleviating effect was eliminated by miR-485-3p (P < 0.05). The LPS-induced inflammatory response was suppressed by the low expression of miR-485-3p but significantly reversed by silencing of FBXO45. MEG8 was a sponge for miR-485-3p and inhibited its levels and promoted FBXO45 expression (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Elevated MEG8 is a potential diagnostic biomarker for PD and may mitigate inflammatory damage in PD via the miR-485-3p/FBXO45 axis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The data used and analyzed can be obtained from the corresponding author under a reasonable request.
References
Geng X, Zou Y, Li S, Qi R, Yu H, Li J (2023) MALAT1 mediates alpha-synuclein expression through miR-23b-3p to induce autophagic impairment and the inflammatory response in microglia to promote apoptosis in dopaminergic neuronal cells. Mediators Inflamm 2023:4477492
Asadi MR, Abed S, Kouchakali G, Fattahi F, Sabaie H, Moslehian MS et al (2023) Competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) networks in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review. Front Cell Neurosci 17:1044634
Varma P, Narayan L, Alty J, Painter V, Padmakumar C (2021) An innovative personalised management program for older adults with Parkinson’s disease: new concepts and future directions. J Pers Med. 11:1
Peng S, Jia J, Sun J, Xie Q, Zhang X, Deng Y et al (2019) LXW7 attenuates inflammation via suppressing Akt/nuclear factor kappa B and mitogen-activated protein kinases signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Int Immunopharmacol 77:105963
Kuo MC, Liu SC, Hsu YF, Wu RM (2021) The role of noncoding RNAs in Parkinson’s disease: biomarkers and associations with pathogenic pathways. J Biomed Sci 28(1):78
Liu L, Zhou T, Li T, Liang Z, Luo X (2022) LncRNA DLX6-AS1 promotes microglial inflammatory response in Parkinson’s disease by regulating the miR-223-3p/NRP1 axis. Behav Brain Res 431:113923
Abrishamdar M, Jalali MS, Rashno M (2022) MALAT1 lncRNA and Parkinson’s disease: the role in the pathophysiology and significance for diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Mol Neurobiol 59(9):5253–5262
Li K, Wang Z (2023) lncRNA NEAT1: key player in neurodegenerative diseases. Ageing Res Rev 86:101878
Li YZ, Zhu HC, Du Y, Zhao HC, Wang L (2022) Silencing lncRNA SLC16A1-AS1 induced ferroptosis in renal cell carcinoma through miR-143-3p/SLC7A11 signaling. Technol Cancer Res Treat 21:15330338221077804
Lin X, Wang R, Li R, Tao T, Zhang D, Qi Y (2022) Diagnostic performance of miR-485-3p in patients with Parkinson’s disease and its relationship with neuroinflammation. Neuromolecular Med 24(2):195–201
Xie W, Jiang L, Huang X, Shang H, Gao M, You W et al (2021) lncRNA MEG8 is downregulated in osteoarthritis and regulates chondrocyte cell proliferation, apoptosis and inflammation. Exp Ther Med 22(4):1153
Xu D, Dai R, Chi H, Ge W, Rong J (2021) Long non-coding RNA MEG8 suppresses hypoxia-induced excessive proliferation, migration and inflammation of vascular smooth muscle cells by regulation of the miR-195-5p/RECK axis. Front Mol Biosci 8:697273
Buccarelli M, Lulli V, Giuliani A, Signore M, Martini M, D’Alessandris QG et al (2020) Deregulated expression of the imprinted DLK1-DIO3 region in glioblastoma stemlike cells: tumor suppressor role of lncRNA MEG3. Neuro Oncol 22(12):1771–1784
Tan MC, Widagdo J, Chau YQ, Zhu T, Wong JJ, Cheung A et al (2017) The activity-induced long non-coding RNA Meg3 modulates AMPA receptor surface expression in primary cortical neurons. Front Cell Neurosci 11:124
Zhao XY, Lu MH, Yuan DJ, Xu DE, Yao PP, Ji WL et al (2019) Mitochondrial dysfunction in neural injury. Front Neurosci 13:30
Sui S, Sun L, Zhang W, Li J, Han J, Zheng J et al (2021) LncRNA MEG8 attenuates cerebral ischemia after ischemic stroke through targeting miR-130a-5p/VEGFA signaling. Cell Mol Neurobiol 41(6):1311–1324
Zheng Y, Sun S, Yu M, Fu X (2019) Identification of potential hub-lncRNAs in ischemic stroke based on Subpathway-LNCE method. J Cell Biochem 120(8):12832–12842
Daniel SE, Lees AJ (1993) Parkinson’s disease society brain bank, London: overview and research. J Neural Transm Suppl 39:165–172
Zhang J, Yang Y, Zhou C, Zhu R, Xiao X, Zhou B et al (2022) LncRNA miR-17-92a-1 cluster host gene (MIR17HG) promotes neuronal damage and microglial activation by targeting the microRNA-153-3p/alpha-synuclein axis in Parkinson’s disease. Bioengineered 13(2):4493–4516
Zhu Z, Huang P, Sun R, Li X, Li W, Gong W (2022) A Novel long-noncoding RNA LncZFAS1 prevents MPP(+)-induced neuroinflammation through MIB1 activation. Mol Neurobiol 59(2):778–799
Zhu HB, Li B, Guo J, Miao YZ, Shen YT, Zhang YZ et al (2021) LncRNA MEG8 promotes TNF-alpha expression by sponging miR-454-3p in bone-invasive pituitary adenomas. Aging (Albany NY) 13(10):14342–14354
Tolosa E, Garrido A, Scholz SW, Poewe W (2021) Challenges in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 20(5):385–397
Lotankar S, Prabhavalkar KS, Bhatt LK (2017) Biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease: recent advancement. Neurosci Bull 33(5):585–597
Zhou Y, Zhao Z, Yan L, Yang J (2021) MiR-485-3p promotes proliferation of osteoarthritis chondrocytes and inhibits apoptosis via Notch2 and the NF-kappaB pathway. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 43(3):370–379
Sole C, Domingo S, Ferrer B, Moline T, Ordi-Ros J, Cortes-Hernandez J (2019) MicroRNA expression profiling identifies miR-31 and miR-485-3p as regulators in the pathogenesis of discoid cutaneous lupus. J Invest Dermatol 139(1):51–61
Koh HS, Lee S, Lee HJ, Min JW, Iwatsubo T, Teunissen CE et al (2021) Targeting microRNA-485-3p blocks Alzheimer’s disease progression. Int J Mol Sci 22(23):13136
Tsai M, Osman W, Adair J, ElMergawy R, Chafin L, Johns F et al (2022) The E3 ligase subunit FBXO45 binds the interferon-lambda receptor and promotes its degradation during influenza virus infection. J Biol Chem 298(12):102698
Saiga T, Fukuda T, Matsumoto M, Tada H, Okano HJ, Okano H et al (2009) Fbxo45 forms a novel ubiquitin ligase complex and is required for neuronal development. Mol Cell Biol 29(13):3529–3543
Tada H, Okano HJ, Takagi H, Shibata S, Yao I, Matsumoto M et al (2010) Fbxo45, a novel ubiquitin ligase, regulates synaptic activity. J Biol Chem 285(6):3840–3849
Na Y, Calvo-Jimenez E, Kon E, Cao H, Jossin Y, Cooper JA (2020) Fbxo45 binds SPRY motifs in the extracellular domain of N-cadherin and regulates neuron migration during brain development. Mol Cell Biol 40(14):e00539-e619
Cao T, Cui Y, Wang Y, Wu L, Yu K, Chen K et al (2022) CACNA1C-AS2 inhibits cell proliferation and suppresses cell migration and invasion via targeting FBXO45 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways in glioma. Apoptosis 27(11–12):979–991
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This study was funded by the Taizhou Social Development Science and Technology Plan Project (22ywb37).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL carried out the research design and conception; TT and XH analyzed and interpreted the data regarding; LM performed the examination of sample; LP and TT contributed essential reagents or tools; XL and LC authors wrote and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The experimental procedures were all in accordance with the guideline of the Ethics Committee of Taizhou Central Hospital (Taizhou University Hospital) and has approved by the Ethics Committee of Taizhou Central Hospital (Taizhou University Hospital). This study complies with the Declaration of Helsinki. A signed written informed consent was obtained from each patient.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, X., Tao, T., He, X. et al. LncRNA MEG8 ameliorates Parkinson’s disease neuro-inflammation through miR-485-3p/FBXO45 axis. Acta Neurol Belg 124, 549–557 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-023-02388-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13760-023-02388-7