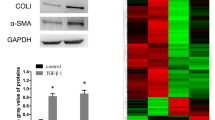
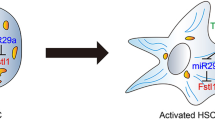
Abstract
E26 transformation specific or E twenty-six (ETS) protein family consists of 28 transcription factors, five of which, named ETS1/2, PU.1, ERG and EHF, are known to involve in the development of liver fibrosis, and are expected to become diagnostic markers or therapeutic targets of liver fibrosis. In recent years, some small molecule inhibitors of ETS protein family have been discovered, which might open up a new path for the liver fibrosis therapy targeting ETS. This article reviews the research progress of ETS family members in the development liver fibrosis as well as their prospect of clinical application.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Henderson NC, Rieder F, Wynn TA. Fibrosis: from mechanisms to medicines. Nature. 2020;587:555–66.
Kisseleva T, Brenner D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18(3):151–66.
Zhang CY, Yuan WG, He P, Lei JH, Wang CX. Liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cells: etiology, pathological hallmarks and therapeutic targets. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(48):10512–22.
Tsuchida T, Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;14(7):397–411.
Parola M, Pinzani M. Liver fibrosis: pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues. Mol Aspects Med. 2019;65:37–55.
Leprince D, Gegonne A, Coll J, de Taisne C, Schneeberger A, Lagrou C, Stehelin D. A putative second cell-derived oncogene of the avian leukaemia retrovirus E26. Nature. 1983;306(5941):395–7.
Seth A, Watson DK. ETS transcription factors and their emerging roles in human cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41(16):2462–78.
Gutierrez-Hartmann A, Duval DL, Bradford AP. ETS transcription factors in endocrine systems. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2007;18(4):150–8.
Sizemore GM, Pitarresi JR, Balakrishnan S, Ostrowski MC. The ETS family of oncogenic transcription factors in solid tumours. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17(6):337–51.
Pijuan-Sala B, Wilson NK, Xia J, Hou X, Hannah RL, Kinston S, Calero-Nieto FJ, Poirion O, Preissl S, Liu F, Gottgens B. Single-cell chromatin accessibility maps reveal regulatory programs driving early mouse organogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(4):487–97.
Craig MP, Sumanas S. ETS transcription factors in embryonic vascular development. Angiogenesis. 2016;19(3):275–85.
Adamo P, Ladomery MR. The oncogene ERG: a key factor in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2016;35(4):403–14.
Li Y, Luo H, Liu T, Zacksenhaus E, Ben-David Y. The ets transcription factor Fli-1 in development, cancer and disease. Oncogene. 2015;34(16):2022–31.
Chen Y, Sumardika IW, Tomonobu N, Kinoshita R, Inoue Y, Iioka H, Mitsui Y, Saito K, Ruma I, Sato H, Yamauchi A, Murata H, Yamamoto KI, Tomida S, Shien K, Yamamoto H, Soh J, Futami J, Kubo M, Putranto EW, Murakami T, Liu M, Hibino T, Nishibori M, Kondo E, Toyooka S, Sakaguchi M. Critical role of the MCAM-ETV4 axis triggered by extracellular S100A8/A9 in breast cancer aggressiveness. Neoplasia. 2019;21(7):627–40.
Hock H, Shimamura A. ETV6 in hematopoiesis and leukemia predisposition. Semin Hematol. 2017;54(2):98–104.
Hollenhorst PC, McIntosh LP, Graves BJ. Genomic and biochemical insights into the specificity of ETS transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011;80:437–71.
Kar A, Gutierrez-Hartmann A. Molecular mechanisms of ETS transcription factor-mediated tumorigenesis. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2013;48(6):522–43.
Slupsky CM, Gentile LN, Donaldson LW, Mackereth CD, Seidel JJ, Graves BJ, McIntosh LP. Structure of the Ets-1 pointed domain and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(21):12129–34.
Vivekanand P. Lessons from Drosophila pointed, an ETS family transcription factor and key nuclear effector of the RTK signaling pathway. Genesis. 2018;56(11–12): e23257.
Foulds CE, Nelson ML, Blaszczak AG, Graves BJ. Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling activates Ets-1 and Ets-2 by CBP/p300 recruitment. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(24):10954–64.
Findlay VJ, LaRue AC, Turner DP, Watson PM, Watson DK. Understanding the role of ETS-mediated gene regulation in complex biological processes. Adv Cancer Res. 2013;119:1–61.
Mut M, Lule S, Demir O, Kurnaz IA, Vural I. Both mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular-signal-regulated kinases (ERK) 1/2 and phosphatidylinositide-3-OH kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathways regulate activation of E-twenty-six (ETS)-like transcription factor 1 (Elk-1) in U138 glioblastoma cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44(2):302–10.
Xu S, Ge J, Zhang Z, Zhou W. MiR-129 inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting ETS1 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in prostate cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;96:634–41.
Selvaraj N, Kedage V, Hollenhorst PC. Comparison of MAPK specificity across the ETS transcription factor family identifies a high-affinity ERK interaction required for ERG function in prostate cells. Cell Commun Signal. 2015;13:12.
Nelson ML, Kang HS, Lee GM, Blaszczak AG, Lau DK, McIntosh LP, Graves BJ. Ras signaling requires dynamic properties of Ets1 for phosphorylation-enhanced binding to coactivator CBP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(22):10026–31.
Teng Y, Cang B, Mao F, Chen W, Cheng P, Peng L, Luo P, Lu D, You N, Zou Q, Zhuang Y. Expression of ETS1 in gastric epithelial cells positively regulate inflammatory response in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis. Cell Death DIS. 2020;11(7):498.
Charlot C, Dubois-Pot H, Serchov T, Tourrette Y, Wasylyk B. A review of post-translational modifications and subcellular localization of Ets transcription factors: possible connection with cancer and involvement in the hypoxic response. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;647:3–30.
Ramachandran P, Dobie R, Wilson-Kanamori JR, Dora EF, Henderson B, Luu NT, Portman JR, Matchett KP, Brice M, Marwick JA, Taylor RS, Efremova M, Vento-Tormo R, Carragher NO, Kendall TJ, Fallowfield JA, Harrison EM, Mole DJ, Wigmore SJ, Newsome PN, Weston CJ, Iredale JP, Tacke F, Pollard JW, Ponting CP, Marioni JC, Teichmann SA, Henderson NC. Resolving the fibrotic niche of human liver cirrhosis at single-cell level. Nature. 2019;575(7783):512–8.
Knittel T, Kobold D, Dudas J, Saile B, Ramadori G. Role of the Ets-1 transcription factor during activation of rat hepatic stellate cells in culture. Am J Pathol. 1999;155(6):1841–8.
Marcher AB, Bendixen SM, Terkelsen MK, Hohmann SS, Hansen MH, Larsen BD, Mandrup S, Dimke H, Detlefsen S, Ravnskjaer K. Transcriptional regulation of hepatic stellate cell activation in NASH. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):2324.
Dittmer J. The role of the transcription factor Ets1 in carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015;35:20–38.
Whyte WA, Orlando DA, Hnisz D, Abraham BJ, Lin CY, Kagey MH, Rahl PB, Lee TI, Young RA. Master transcription factors and mediator establish super-enhancers at key cell identity genes. Cell. 2013;153(2):307–19.
Ghosh S, Basu M, Roy SS. ETS-1 protein regulates vascular endothelial growth factor-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 and matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in human ovarian carcinoma cell line SKOV-3. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(18):15001–15.
Taki M, Verschueren K, Yokoyama K, Nagayama M, Kamata N. Involvement of Ets-1 transcription factor in inducing matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression by epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human squamous carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 2006;28(2):487–96.
Koinuma D, Tsutsumi S, Kamimura N, Taniguchi H, Miyazawa K, Sunamura M, Imamura T, Miyazono K, Aburatani H. Chromatin immunoprecipitation on microarray analysis of Smad2/3 binding sites reveals roles of ETS1 and TFAP2A in transforming growth factor beta signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29(1):172–86.
Liu D, Wang K, Li K, Xu R, Chang X, Zhu Y, Sun P, Han X. Ets-1 deficiency alleviates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via weakening TGF-beta1 signaling-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(6):458.
Gong J, Han J, He J, Liu J, Han P, Wang Y, Li M, Li D, Ding X, Du Z, Liao J, Tian D. Paired related homeobox protein 1 regulates PDGF-induced chemotaxis of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis. Lab Invest. 2017;97(9):1020–32.
Leask A, Chen S, Pala D, Brigstock DR. Regulation of CCN2 mRNA expression and promoter activity in activated hepatic stellate cells. J Cell Commun Signal. 2008;2(1–2):49–56.
Chen J, Fu Y, Day DS, Sun Y, Wang S, Liang X, Gu F, Zhang F, Stevens SM, Zhou P, Li K, Zhang Y, Lin RZ, Smith L, Zhang J, Sun K, Melero-Martin JM, Han Z, Park PJ, Zhang B, Pu WT. VEGF amplifies transcription through ETS1 acetylation to enable angiogenesis. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):383.
Ozaki I, Zhao G, Mizuta T, Ogawa Y, Hara T, Kajihara S, Hisatomi A, Sakai T, Yamamoto K. Hepatocyte growth factor induces collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase-1) via the transcription factor Ets-1 in human hepatic stellate cell line. J Hepatol. 2002;36(2):169–78.
Li J, Zhang J, Zhang B, Chen L, Chen G, Zhu D, Chen J, Duan L, Duan Y. rSjP40 inhibited the activity of collagen type I promoter via Ets-1 in HSCs. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9: 765616.
Liu X, Xu J, Rosenthal S, Zhang LJ, McCubbin R, Meshgin N, Shang L, Koyama Y, Ma HY, Sharma S, Heinz S, Glass CK, Benner C, Brenner DA, Kisseleva T. Identification of lineage-specific transcription factors that prevent activation of hepatic stellate cells and promote fibrosis resolution. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(6):1728–44.
Kodandapani R, Pio F, Ni CZ, Piccialli G, Klemsz M, McKercher S, Maki RA, Ely KR. A new pattern for helix-turn-helix recognition revealed by the PU.1 ETS-domain-DNA complex. Nature. 1996;380(6573):456–60.
Tang MS, Miraldi ER, Girgis NM, Bonneau RA, Loke P. Alternative activation of macrophages is accompanied by chromatin remodeling associated with lineage-dependent DNA shape features flanking PU.1 motifs. J Immunol. 2020;205(4):1070–83.
Pimenova AA, Herbinet M, Gupta I, Machlovi SI, Bowles KR, Marcora E, Goate AM. Alzheimer’s-associated PU1 expression levels regulate microglial inflammatory response. Neurobiol Dis. 2021;148:105217.
Feng R, Desbordes SC, Xie H, Tillo ES, Pixley F, Stanley ER, Graf T. PU.1 and C/EBPalpha/beta convert fibroblasts into macrophage-like cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(16):6057–62.
Minderjahn J, Schmidt A, Fuchs A, Schill R, Raithel J, Babina M, Schmidl C, Gebhard C, Schmidhofer S, Mendes K, Ratermann A, Glatz D, Nutzel M, Edinger M, Hoffmann P, Spang R, Langst G, Imhof A, Rehli M. Mechanisms governing the pioneering and redistribution capabilities of the non-classical pioneer PU.1. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):402.
Mullen AC, Orlando DA, Newman JJ, Loven J, Kumar RM, Bilodeau S, Reddy J, Guenther MG, DeKoter RP, Young RA. Master transcription factors determine cell-type-specific responses to TGF-beta signaling. Cell. 2011;147(3):565–76.
Bernard NJ. PU.1 pulls the strings in fibrotic disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(4):187.
Wohlfahrt T, Rauber S, Uebe S, Luber M, Soare A, Ekici A, Weber S, Matei AE, Chen CW, Maier C, Karouzakis E, Kiener HP, Pachera E, Dees C, Beyer C, Daniel C, Gelse K, Kremer AE, Naschberger E, Sturzl M, Butter F, Sticherling M, Finotto S, Kreuter A, Kaplan MH, Jungel A, Gay S, Nutt SL, Boykin DW, Poon G, Distler O, Schett G, Distler J, Ramming A. PU.1 controls fibroblast polarization and tissue fibrosis. Nature. 2019;566(7744):344–9.
Liu Q, Yu J, Wang L, Tang Y, Zhou Q, Ji S, Wang Y, Santos L, Haeusler RA, Que J, Rajbhandari P, Lei X, Valenti L, Pajvani UB, Qin J, Qiang L. Inhibition of PU.1 ameliorates metabolic dysfunction and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 2020;73(2):361–70.
Cooper L, Johnson C, Burslem F, Martin P. Wound healing and inflammation genes revealed by array analysis of “macrophageless” PU.1 null mice. Genome Biol. 2005;6(1):R5.
Wang Y, Welc SS, Wehling-Henricks M, Kong Y, Thomas C, Montecino-Rodriguez E, Dorshkind K, Tidball JG. Myeloid cell-specific mutation of Spi1 selectively reduces M2-biased macrophage numbers in skeletal muscle, reduces age-related muscle fibrosis and prevents sarcopenia. Aging Cell. 2022;21:e13690.
Tacke F. Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases. J Hepatol. 2017;66(6):1300–12.
Seidman JS, Troutman TD, Sakai M, Gola A, Spann NJ, Bennett H, Bruni CM, Ouyang Z, Li RZ, Sun X, Vu BT, Pasillas MP, Ego KM, Gosselin D, Link VM, Chong LW, Evans RM, Thompson BM, McDonald JG, Hosseini M, Witztum JL, Germain RN, Glass CK. Niche-specific reprogramming of epigenetic landscapes drives myeloid cell diversity in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Immunity. 2020;52(6):1057–74.
Liu Q, Zhang Y, Yang S, Wu Y, Wang J, Yu W, Liu Y. PU.1-deficient mice are resistant to thioacetamide-induced hepatic fibrosis: PU.1 finely regulates Sirt1 expression via transcriptional promotion of miR-34a and miR-29c in hepatic stellate cells. Biosci Rep. 2017;37(6).
Loughran SJ, Kruse EA, Hacking DF, de Graaf CA, Hyland CD, Willson TA, Henley KJ, Ellis S, Voss AK, Metcalf D, Hilton DJ, Alexander WS, Kile BT. The transcription factor Erg is essential for definitive hematopoiesis and the function of adult hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Immunol. 2008;9(7):810–9.
Lu TM, Houghton S, Magdeldin T, Duran J, Minotti AP, Snead A, Sproul A, Nguyen DT, Xiang J, Fine HA, Rosenwaks Z, Studer L, Rafii S, Agalliu D, Redmond D, Lis R. Pluripotent stem cell-derived epithelium misidentified as brain microvascular endothelium requires ETS factors to acquire vascular fate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021;118(8).
Moh-Moh-Aung A, Fujisawa M, Ito S, Katayama H, Ohara T, Ota Y, Yoshimura T, Matsukawa A. Decreased miR-200b-3p in cancer cells leads to angiogenesis in HCC by enhancing endothelial ERG expression. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):10418.
Lathen C, Zhang Y, Chow J, Singh M, Lin G, Nigam V, Ashraf YA, Yuan JX, Robbins IM, Thistlethwaite PA. ERG-APLNR axis controls pulmonary venule endothelial proliferation in pulmonary veno-occlusive disease. Circulation. 2014;130(14):1179–91.
Zhang X, Hu C, Yuan YP, Song P, Kong CY, Wu HM, Xu SC, Ma ZG, Tang QZ. Endothelial ERG alleviates cardiac fibrosis via blocking endothelin-1-dependent paracrine mechanism. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2021;37(6):873–90.
Dufton NP, Peghaire CR, Osuna-Almagro L, Raimondi C, Kalna V, Chauhan A, Webb G, Yang Y, Birdsey GM, Lalor P, Mason JC, Adams DH, Randi AM. Dynamic regulation of canonical TGFbeta signalling by endothelial transcription factor ERG protects from liver fibrogenesis. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):895.
Stolzenburg LR, Yang R, Kerschner JL, Fossum S, Xu M, Hoffmann A, Lamar KM, Ghosh S, Wachtel S, Leir SH, Harris A. Regulatory dynamics of 11p13 suggest a role for EHF in modifying CF lung disease severity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(15):8773–84.
Swahn H, Sabith EJ, Lamar KM, Yin S, Kerschner JL, NandyMazumdar M, Coppola C, Mendenhall EM, Leir SH, Harris A. Coordinate regulation of ELF5 and EHF at the chr11p13 CF modifier region. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(11):7726–40.
Ramnath D, Irvine KM, Lukowski SW, Horsfall LU, Loh Z, Clouston AD, Patel PJ, Fagan KJ, Iyer A, Lampe G, Stow JL, Schroder K, Fairlie DP, Powell JE, Powell EE, Sweet MJ. Hepatic expression profiling identifies steatosis-independent and steatosis-driven advanced fibrosis genes. JCI Insight. 2018;3(14).
Jie Y, Liu G, Mingyan E, Li Y, Xu G, Guo J, Li Y, Rong G, Li Y, Gu A. Novel small molecule inhibitors of the transcription factor ETS-1 and their antitumor activity against hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021;906:174214.
Erkizan HV, Kong Y, Merchant M, Schlottmann S, Barber-Rotenberg JS, Yuan L, Abaan OD, Chou TH, Dakshanamurthy S, Brown ML, Uren A, Toretsky JA. A small molecule blocking oncogenic protein EWS-FLI1 interaction with RNA helicase A inhibits growth of Ewing’s sarcoma. NAT MED. 2009;15(7):750–6.
Rahim S, Beauchamp EM, Kong Y, Brown ML, Toretsky JA, Uren A. YK-4-279 inhibits ERG and ETV1 mediated prostate cancer cell invasion. PLoS ONE. 2011;6(4): e19343.
Schafer CM, Gurley JM, Kurylowicz K, Lin PK, Chen W, Elliott MH, Davis GE, Bhatti F, Griffin CT. An inhibitor of endothelial ETS transcription factors promotes physiologic and therapeutic vessel regression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(42):26494–502.
Mohamed AA, Xavier CP, Sukumar G, Tan SH, Ravindranath L, Seraj N, Kumar V, Sreenath T, McLeod DG, Petrovics G, Rosner IL, Srivastava M, Strovel J, Malhotra SV, LaRonde NA, Dobi A, Dalgard CL, Srivastava S. Identification of a small molecule that selectively inhibits ERG-positive cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 2018;78(13):3659–71.
Butler MS, Roshan-Moniri M, Hsing M, Lau D, Kim A, Yen P, Mroczek M, Nouri M, Lien S, Axerio-Cilies P, Dalal K, Yau C, Ghaidi F, Guo Y, Yamazaki T, Lawn S, Gleave ME, Gregory-Evans CY, McIntosh LP, Cox ME, Rennie PS, Cherkasov A. Discovery and characterization of small molecules targeting the DNA-binding ETS domain of ERG in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(26):42438–54.
Chenoweth DM, Dervan PB. Allosteric modulation of DNA by small molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(32):13175–9.
Szymczyna BR, Arrowsmith CH. DNA binding specificity studies of four ETS proteins support an indirect read-out mechanism of protein-DNA recognition. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(37):28363–70.
Pham TH, Minderjahn J, Schmidl C, Hoffmeister H, Schmidhofer S, Chen W, Langst G, Benner C, Rehli M. Mechanisms of in vivo binding site selection of the hematopoietic master transcription factor PU.1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(13):6391–402.
Munde M, Wang S, Kumar A, Stephens CE, Farahat AA, Boykin DW, Wilson WD, Poon GM. Structure-dependent inhibition of the ETS-family transcription factor PU.1 by novel heterocyclic diamidines. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(2):1379–90.
Antony-Debre I, Paul A, Leite J, Mitchell K, Kim HM, Carvajal LA, Todorova TI, Huang K, Kumar A, Farahat AA, Bartholdy B, Narayanagari SR, Chen J, Ambesi-Impiombato A, Ferrando AA, Mantzaris I, Gavathiotis E, Verma A, Will B, Boykin DW, Wilson WD, Poon GM, Steidl U. Pharmacological inhibition of the transcription factor PU.1 in leukemia. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(12):4297–313.
Paine MF, Wang MZ, Generaux CN, Boykin DW, Wilson WD, De Koning HP, Olson CA, Pohlig G, Burri C, Brun R, Murilla GA, Thuita JK, Barrett MP, Tidwell RR. Diamidines for human African trypanosomiasis. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2010;11(8):876–83.
Shao L, Tekedereli I, Wang J, Yuca E, Tsang S, Sood A, Lopez-Berestein G, Ozpolat B, Ittmann M. Highly specific targeting of the TMPRSS2/ERG fusion gene using liposomal nanovectors. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(24):6648–57.
Wang X, Qiao Y, Asangani IA, Ateeq B, Poliakov A, Cieslik M, Pitchiaya S, Chakravarthi B, Cao X, Jing X, Wang CX, Apel IJ, Wang R, Tien JC, Juckette KM, Yan W, Jiang H, Wang S, Varambally S, Chinnaiyan AM. Development of peptidomimetic inhibitors of the ERG gene fusion product in prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. 2017;31(4):532–48.
Liu B, Bashkin JK, Poon G, Wang S, Wang S, Wilson WD. Modulating DNA by polyamides to regulate transcription factor PU.1-DNA binding interactions. Biochimie. 2019;167:1–11.
Shen S, Wu Y, Chen J, Xie Z, Huang K, Wang G, Yang Y, Ni W, Chen Z, Shi P, Ma Y, Fan S. CircSERPINE2 protects against osteoarthritis by targeting miR-1271 and ETS-related gene. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(6):826–36.
Brenner JC, Ateeq B, Li Y, Yocum AK, Cao Q, Asangani IA, Patel S, Wang X, Liang H, Yu J, Palanisamy N, Siddiqui J, Yan W, Cao X, Mehra R, Sabolch A, Basrur V, Lonigro RJ, Yang J, Tomlins SA, Maher CA, Elenitoba-Johnson KS, Hussain M, Navone NM, Pienta KJ, Varambally S, Feng FY, Chinnaiyan AM. Mechanistic rationale for inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in ETS gene fusion-positive prostate cancer. Cancer Cell. 2011;19(5):664–78.
Wang S, Kollipara RK, Srivastava N, Li R, Ravindranathan P, Hernandez E, Freeman E, Humphries CG, Kapur P, Lotan Y, Fazli L, Gleave ME, Plymate SR, Raj GV, Hsieh JT, Kittler R. Ablation of the oncogenic transcription factor ERG by deubiquitinase inhibition in prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(11):4251–6.
Nguyen LT, Tretiakova MS, Silvis MR, Lucas J, Klezovitch O, Coleman I, Bolouri H, Kutyavin VI, Morrissey C, True LD, Nelson PS, Vasioukhin V. ERG activates the YAP1 transcriptional program and induces the development of age-related prostate tumors. Cancer Cell. 2015;27(6):797–808.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81670555). This work was also supported by State Key Laboratory Special Fund (2060204), Health commission of Hubei Province scientific research project (WJ2019H533), and The Opening Foundation of Hubei Key Laboratory of Tumor Microenvironment and Immunotherapy (2022KZL2-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L-YZ wrote this manuscript. Y-RN designed the work and revised it critically for important intellectual content. YT and X-JL designed the figure and table. J-FW substantively revised the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no competing interests and approved the final manuscript.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, LY., Tan, Y., Luo, XJ. et al. The roles of ETS transcription factors in liver fibrosis. Human Cell 36, 528–539 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-022-00848-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-022-00848-5