Abstract
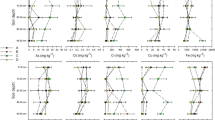
Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) was applied for analyzing the impact of earthquake on the elemental distribution of the soil, collected from the earthquake-stricken locations near Eurasian and Indian Tectonic Plates in the Kashmir Valley. The quantitative elemental analysis was carried out using an advanced calibration-free LIBS technique, assuming the establishment of optically thin plasma under the local thermodynamic equilibrium conditions. The results exhibited that the soil has nearly random concentration distribution of metallic elements such as Al, Na, and K, nonmetallic element P, micronutrients such as Fe and Si and secondary macronutrients such as Ca, S, and Mg, in and around the radius of 9 km from the epicenter of the earthquake. It is exhibited that the concentration of carbon in particular is the highest near the epicenter and declines systematically with the outward radial distance. The quantitative analysis by LIBS was confirmed and counter verified through the inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP–OES), and results achieved by both the techniques (LIBS and ICP–OES) are in good agreement.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gondal, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Yamani, Z.H.; Ahmed, Z.: Determination of toxic metals in petroleum, cultivated land and ore samples using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 78(3–4), 270–274 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-007-9141-7
Gondal, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Yamani, Z.H.; Baig, M.A.: Detection of heavy metals in Arabian crude oil residue using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Talanta 69(5), 1072–1078 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2005.11.023
Gondal, M.A.; Habibullah, Y.B.; Baig, U.; Oloore, L.E.: Direct spectral analysis of tea samples using 266 nm UV pulsed laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and cross validation of LIBS results with ICP–MS. Talanta 152, 341–352 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.02.030
Rehan, I.; Rehan, K.; Sultana, S.; ul Haq, M.O.; Niazi, M.Z.K.; Muhammad, R.: Spatial characterization of red and white skin potatoes using nano-second laser induced breakdown in air. EPJ Appl. Phys. 73(1), 10701 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1051/epjap/2015150453
Rehan, I.; Gondal, M.A.; Rehan, K.: Determination of lead content in drilling fueled soil using laser induced spectral analysis and its cross validation using ICP/OES method. Talanta 182, 443–449 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.02.024
Rehan, I.; Khan, M.Z.; Ali, I.; Rehan, K.; Sultana, S.; Shah, S.: Spectroscopic analysis of high protein nigella seeds (Kalonji) using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and inductively coupled plasma/optical emission spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. B 124(3), 49 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-018-6915-z
Rehan, I.; Khan, M.Z.; Rehan, K.; Abrar, S.U.; Farooq, Z.; Sultana, S.; Anwar, H.: Optimized laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for the determination of high toxic lead in edible colors. Appl. Opt. 57(21), 6033–6039 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.57.006033
Ali, A.; Khan, M.Z.; Rehan, I.; Rehan, K.; Muhammad, R.: Quantitative classification of quartz by laser induced breakdown spectroscopy in conjunction with discriminant function analysis. J. Spectrosc. 2016, 1835027 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1835027
Rehan, K.; Rehan, I.; Sultana, S.; Khan, M.Z.; Farooq, Z.; Mateen, A.; Humayun, M.: Determination of metals present in textile dyes using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and cross-validation using inductively coupled plasma/atomic emission spectroscopy. Int. J. Spectrosc. 2017, 9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1614654
Rehan, I.; Khan, M.Z.; Rehan, K.; Mateen, A.; Farooque, M.A.; Sultana, S.; Farooq, Z.: Determination of toxic and essential metals in rock and sea salts using pulsed nanosecond laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Appl. Opt. 57(2), 295–301 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.57.000295
Rehan, I.; Muhammad, R.; Rehan, K.; Karim, K.; Sultana, S.: Quantitative analysis of Shilajit using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy and inductively coupled plasma/optical emission spectroscopy. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 7, 1–9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9600.1000611
Rodriguez, J.; Ustin, S.; Sandoval-Solis, S.; O’Geen, A.T.: Food, water, and fault lines: remote sensing opportunities for earthquake-response management of agricultural water. Sci. Total Environ. 565, 1020–1027 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.05.146
Yuce, G.; Fu, C.C.; D’Alessandro, W.; Gulbay, A.H.; Lai, C.W.; Bellomo, S.; Yang, T.F.; Italiano, F.; Walia, V.İV.E.K.: Geochemical characteristics of soil radon and carbon dioxide within the Dead Sea Fault and Karasu Fault in the Amik Basin (Hatay), Turkey. Chem. Geol. 469, 129–146 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.01.003
Cui, P.; Lin, Y.M.; Chen, C.: Destruction of vegetation due to geo-hazards and its environmental impacts in the Wenchuan earthquake areas. Ecol. Eng. 44, 61–69 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2012.03.012
Lin, Y.; Deng, H.; Du, K.; Rafay, L.; Zhang, G.S.; Li, J.; Wu, C.; Lin, H.; Yu, W.; Fan, H.; Ge, Y.: Combined effects of climate, restoration measures and slope position in change in soil chemical properties and nutrient loss across lands affected by the Wenchuan Earthquake in China. Sci. Total Environ. 596, 274–283 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.04.034
Lin, Y.; Deng, H.; Du, K.; Li, J.; Lin, H.; Chen, C.; Fisher, L.; Wu, C.; Hong, T.; Zhang, G.: Soil quality assessment in different climate zones of China’s Wenchuan earthquake affected region. Soil Tillage Res. 165, 315–324 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2016.09.009
Colon, C.; Hatem, G.; Verdugo, E.; Ruiz, P.; Campos, J.: Measurement of the Stark broadening and shift parameters for several ultraviolet lines of singly ionized aluminum. J. Appl. Phys. 73(10), 4752–4758 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.353839
Harilal, S.S.; Bindhu, C.V.; Issac, R.C.; Nampoori, V.P.N.; Vallabhan, C.P.G.: Electron density and temperature measurements in a laser produced carbon plasma. J. Appl. Phys. 82(5), 2140–2146 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.366276
Rehan, I.; Khan, M.A.; Muhammad, R.; Khan, M.Z.; Hafeez, A.; Nadeem, A.; Rehan, K.: Operational and spectral characteristics of a Sr–Ne glow discharge plasma. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44(1), 561–568 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3439-0
Cristoforetti, G.; De Giacomo, A.; Dell’Aglio, M.; Legnaioli, S.; Tognoni, E.; Palleschi, V.; Omenetto, N.: Local thermodynamic equilibrium in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy: beyond the McWhirter criterion. Spectrochim. Acta B 65(1), 86–95 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2009.11.005
Hahn, D.W.; Omenetto, N.: Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS), part I: review of basic diagnostics and plasma–particle interactions: still-challenging issues within the analytical plasma community. Appl. Spectrosc. 64(12), 335A-366A (2010). https://doi.org/10.1366/000370210793561691
Xu, L.; Yang, H.; Chen, K.; Tan, Q.; He, Q.; Jin, G.: Resolution enhancement by combination of subpixel and deconvolution in miniature spectrometers. Appl. Opt. 46(16), 3210–3214 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.46.003210
Ralchenko, Y.: NIST atomic spectra database. Memorie della Societa Astronomica Italiana Supplementi, v8, 96. http://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/ASD/index.html (2005)
Burakov, V.S.; Kiris, V.V.; Naumenkov, P.A.; Raikov, S.N.: Calibration-free laser spectral analysis of glasses and copper alloys. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 71, 740–746 (2004)
Ciucci, A.; Corsi, M.; Palleschi, V.; Rastelli, S.; Salvetti, A.; Tognoni, E.: New procedure for quantitative elemental analysis by laser induced plasma spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 53(1999), 960–964 (1999)
Ishikawa, T.; Hirono, T.; Matsuta, N.: Geochemical and mineralogical characteristics of fault gouge in the median tectonic line, Japan: evidence for earthquake slip. Earth Planets Space 66(1), 36 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/1880-5981-66-36
Young, S.; Balluz, L.; Malilay, J.: Natural and technologic hazardous material releases during and after natural disasters: a review. Sci. Total Environ. 322(1–3), 3–20 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00446-7
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals for supporting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rehan, I., Gondal, M.A., Sultana, S. et al. Elemental Compositions of Earthquake-Stricken Soil from the Vicinity of the Epicenter at Eurasian and Indian Tectonic Plates Using Calibration Free Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 6101–6108 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05503-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05503-z