Abstract
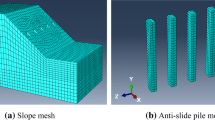
The double-row anti-slide pile is one of the main measures for treating medium and large-scale landslides. However, the pile–soil interaction mechanism and the influence of the row spacing and the pile spacing on the interaction are not very clear in the process of the load-caused landslide evolution. Based on the interaction model test of the double-row anti-slide pile and the load-caused landslide is carried out by using transparent soil model technology. The research results show that the transparent soil technology has advantages in capturing “wave-type” distribution of the displacement isoline and studying the pile–soil interaction and the soil arching effect in the landslide. The pile–soil interaction process can be divided into three stages, the initial deformation stage, the soil arch stability stage, and the deformation stage of the soil arch. With the increase in the row spacing, the reinforcement effect of the front pile to the rear pile is weakened. With the increase in the pile spacing, the phenomenon of soil flow around piles is more likely to happen. Pile spacing has a significant effect on landslide displacement control. And when the row spacing and the pile spacing are too large, there is no soil arch stability stage in the process of the landslide evolution. The conclusion has specific guiding significance for engineering practice.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data, models, and code generated or used during the study appear in the published article.
References
Fan, S.Y.; Song, Z.P.; Zhang, Y.W.; Liua, N.F.: Case study of the effect of rainfall infiltration on a tunnel underlying the roadbed slope with weak inter-layer. KSCE J. Civ. Eng 24(5), 1607–1619 (2020)
Singh, T.N.; Verma, A.K.; Sarkar, K.: Static and dynamic analysis of a landslide Geomatics. Nat. Hazards Risk 1(4), 323–338 (2010)
Kumar, N.; Verma, A.K.; Sardana, S.; Sarkar, K.; Singh, T.N.: Comparative analysis of limit equilibrium and numerical methods for prediction of a landslide. Bull. Eng. Geol. Env. 77(2), 595–608 (2018)
Usluogullari, O.F.; Temugan, A.; Duman, E.S.: Comparison of slope stabilization methods by three-dimensional finite element analysis. Nat. Hazards 81(2), 1027–1050 (2015)
Kang, G.C.; Song, Y.S.; Kim, T.H.: Behavior and stability of a large-scale cut slope considering reinforcement stages. Landslides 6(3), 263–272 (2009)
Tang, X.S.; Zheng, Y.R.; Xin, J.P.: Experimental study and numerical simulation on the large-sized models of micro anti-slide piles. Adv. Mater. Res. 919–921, 670–677 (2014)
Zhao, M.H.; Liu, D.P.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, C.: 3D finite element analysis on pile–soil interaction of passive pile group. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 15, 75–80 (2008)
Qiao, S.; Xu, P.; Teng, J.; Sun, X.: Numerical study of optimal parameters on the high filling embankment landslide reinforced by the portal anti-slide pile. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 24(5), 1460–1475 (2020)
Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.S.; Wang, Y.; Shen, T.; Zhai, Y.C.: Retaining mechanism and structural characteristics of h type anti-slide pile (hTP pile) and experience with its engineering application. Eng. Geol. 222, 29–37 (2017)
Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Sun, H.; Lu, Q.; Shang, Y.Q.: Robust optimization of the constructional time delay in the design of double-row stabilizing piles. Bull. Eng. Geol. Env. 79(1), 53–67 (2019)
Kourkoulis, R.; Gelagoti, F.; Anastasopoulos, I.; Gazetas, G.: Slope stabilizing piles and pile-groups: parametric study and design insights. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 137(7), 663–677 (2011)
He, G.F.; Li, Z.G.; Yuan, Y.; Li, X.H.; Hu, L.H.; Zhang, Y.: Optimization analysis of the factors affecting the soil arching effect between landslide stabilizing piles. Nat. Resour. Model. 31(2), e12148 (2018)
Li, C.; Wang. Z.; Ding, X.M.: Anti-sliding mechanism in soil–rock slope with transparent soil model tests and DEM. Int. J. Phys. Model. Geotech. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1680/jphmg.19.00027
Li, S.J.; Gao, H.; Xu, D.M.; Meng, F.Z.: Comprehensive determination of reinforcement parameters for high cut slope based on intelligent optimization and numerical analysis. J. Earth Sci. 23(2), 233–242 (2012)
Xiao, S.; Zeng, J.; Yan, Y.: A rational layout of double-row stabilizing piles for large-scale landslide control. Bull. Eng. Geol. Env. 76(1), 309–321 (2016)
Xiong, X.; Shi, Z.M.; Xiong, Y.L.; Peng, M.; Ma, X.L.; Zhang, F.: Unsaturated slope stability around the Three Gorges Reservoir under various combinations of rainfall and water level fluctuation. Eng. Geol. 261, 105231 (2019)
Chatra, A.S.; Dodagoudar, G.R.; Maji, V.B.: Numerical modelling of rainfall effects on the stability of soil slopes. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 13(5), 425–437 (2017)
Tang, H.M.; Hu, X.L.; Xu, C.; Li, C.D.; Yong, R.; Wang, L.Q.: A novel approach for determining landslide pushing force based on landslide-pile interactions. Eng. Geol. 182, 15–24 (2014)
Allersma, H.: Photo-elastic stress analysis and strains in simple shear. In: Proceeding of the Iutam Symposium on Deformation and Failure of Granular Materials. Rotterdam: A. A. Balkema, pp. 345–353 (1982)
Bathurst, R.J.; Ezzein, F.M.: Geogrid and soil displacement observations during pullout using a transparent granular soil. Geotech. Test. J. 38(5), 673–685 (2015)
Iskander, M.; Bathurst, R.; Omidvar, M.: Past, present, and future of transparent soils. Geotech. Test. J. 28(5), 557–573 (2015)
Ding, X.M.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.L.: Model test on the soil arching effect of pile-supported embankments using transparent soil. Geotech. Test. J. 44(3), 20190347 (2021)
Liu, J.Y.; Iskander, M.G.: Modelling capacity of transparent soil. Can. Geotech. J. 47(4), 451–460 (2010)
Zhou, D.; Liu, H.L.; Zhang, W.G.; Ding, X.M.; Yang, C.Y.: Transparent soil model test on displacement field of soils around single passive pile. Rock Soil Mech. 40(7), 2686–2694 (2019)
Hu, X.D.; Zhang, H.; Mei, H.B.; Xiao, D.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, M.D.: Landslide susceptibility mapping using the stacking ensemble machine learning method in Lushui, Southwest China. Appl. Sci. Basel 10(11), 4016 (2020)
Tan, F.L.; Hu, X.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wu, S.S.; Pan, Y.H.: Loading method research in model test of a landslide. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 21(9), 3007–3022 (2016)
Liu, D.Z.; Hu, X.L.; Zhou, C.; Xu, C.; He, C.C.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.: Deformation mechanisms and evolution of a pile-reinforced landslide under long-term reservoir operation. Eng. Geol. 275, 105747 (2020)
Zou, Z.X.; Yan, J.b.; Tang, H.M.; Wang, S.H.; Xiong, C.G.; Hu, X.L.: A shear constitutive model for describing the full process of the deformation and failure of slip zone soil, Engineering Geology 276 (2020)
Iskander, M.G.; Liu, J.Y.; Sadek, S.: Optical measurement of deformation using transparent silica gel to model sand. Int. J. Phys. Model. Geotech. 2(4), 13–26 (2002)
Kong, G.Q.; Cao, Z.H.; Zhou, H.; Sun, X.J.: Analysis of piles under oblique pullout load using transparent-soil models. Geotech. Test. J. 38(5), 725–738 (2015)
Zhang, W.G.; Zhong, H.Y.; Xiang, Y.Z.; Wu, D.F.; Zeng, Z.K.; Zhang, Y.M.: Visualization and digitization of model tunnel deformation via transparent soil testing technique. Undergr. Space (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.undsp.2020.05.004
Ding, X.M.; Wu, Q.; Huang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.L.: Model test on the soil arching effect of pile-supported embankments using transparent soil. Geotech. Test. J. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20190347
Li, S.J.; Chen, J.; Lian, C.: Mechanical model of soil arch for interaction of piles and slope and problem of pile spacing. Rock Soil Mech. 31(5), 1352–1358 (2010). (in Chinese)
Chen, G.F.; Zou, L.C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.D.: Pile-spacing calculation of anti-slide pile based on soil arching effect. Adv. Civil Eng. 2020, 7149379 (2020)
Hu, X.L.; Zhou, C.; Xu, C.; Liu, D.Z.; Wu, S.S.; Li, L.X.: Model tests of the response of landslide-stabilizing piles to piles with different stiffness. Landslides 16(11), 2187–2200 (2019)
Terzaghi, K.: Theoretical Soil Mechanics. Wiley, New York (1943)
Bosscher, P.J.; Gray, D.H.: Soil arching in sandy slopes. J. Geotech. Eng. 112(6), 626–645 (1986)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51779021, 51008319) and the Key Laboratory of New Technology for Construction of Cities in Mountain Area (LNTCCMA-20200103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Q., Cao, Z., Shi, X. et al. Model Test of Interaction Between Load-Caused Landslide and Double-Row Anti-slide Piles by Transparent Soil Material. Arab J Sci Eng 46, 4841–4856 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05256-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05256-1