Abstract
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection-associated neurocognitive disorders is accompanied with brain atrophy. In these patients, impairment of adult neurogenesis and neurite outgrowth in the hippocampus may contribute to cognitive dysfunction. Although running exercises can enhance neurogenesis and normalize neurite outgrowth, the underlying molecular mechanisms are not well understood. The HIV envelope protein, gp120, has been shown to impair neurogenesis. Using a gp120 transgenic mouse model, we demonstrate that exercise stimulated neural progenitor cell (NPC) proliferation in the hippocampal dentate gyrus and increased the survival rate and generation of newborn cells. However, sustained exercise activity was necessary as the effects were reversed by detraining. Exercise also normalized dendritic outgrowth of neurons. Furthermore, it increased the expression of hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and normalized hyperactivation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5). Hyperactivated Cdk5 or gp120 treatment led to aberrant neurite outgrowth and BDNF treatment normalized the neurite outgrowth in NPC cultures. These results suggest that sustained exercise has trophic activity on the neuronal lineage which is mediated by Cdk5 modulation of the BDNF pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alirezaei M, Watry DD, Flynn CF, Kiosses WB, Masliah E, Williams BR, Kaul M, Lipton SA, Fox HS (2007) Human immunodeficiency virus-1/surface glycoprotein 120 induces apoptosis through RNA-activated protein kinase signaling in neurons. J Neurosci 27:11047–11055
Ang ET, Tai YK, Lo SQ, Seet R, Soong TW (2010) Neurodegenerative diseases: exercising toward neurogenesis and neuroregeneration. Front Aging Neurosci. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2010.00025
Bachis A, Avdoshina V, Zecca L, Parsadanian M, Mocchetti I (2012) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 alters brain-derived neurotrophic factor processing in neurons. J Neurosci 32:9477–9484
Bechara RG, Kelly AM (2013) Exercise improves object recognition memory and induces BDNF expression and cell proliferation in cognitively enriched rats. Behav Brain Res 245:96–100
Berchtold NC, Chinn G, Chou M, Kesslak JP, Cotman CW (2005) Exercise primes a molecular memory for brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein induction in the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 133:853–861
Chehrehasa F, Meedeniya AC, Dwyer P, Abrahamsen G, Mackay-Sim A (2009) EdU, a new thymidine analogue for labelling proliferating cells in the nervous system. J Neurosci Methods 177:122–130
Cheung ZH, Ip NY (2007) The roles of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 in dendrite and synapse development. Biotechnol J 2:949–957
Cheung R, Ravyn V, Wang L, Ptasznik A, Collman RG (2008) Signaling mechanism of HIV-1 gp120 and virion-induced IL-1beta release in primary human macrophages. J Immunol 180:6675–6684
Costa LM, Pereira JE, Filipe VM, Magalhaes LG, Couto PA, Gonzalo-Orden JM, Raimondo S, Geuna S, Mauricio AC, Nikulina E, Filbin MT, Varejao AS (2013) Rolipram promotes functional recovery after contusive thoracic spinal cord injury in rats. Behav Brain Res 243C:66–73
Couillard-Despres S, Winner B, Schaubeck S, Aigner R, Vroemen M, Weidner N, Bogdahn U, Winkler J, Kuhn HG, Aigner L (2005) Doublecortin expression levels in adult brain reflect neurogenesis. Eur J Neurosci 21:1–14
D'Hooge R, Franck F, Mucke L, De Deyn PP (1999) Age-related behavioural deficits in transgenic mice expressing the HIV-1 coat protein gp120. Eur J Neurosci 11:4398–4402
Duan X, Chang JH, Ge S, Faulkner RL, Kim JY, Kitabatake Y, Liu XB, Yang CH, Jordan JD, Ma DK, Liu CY, Ganesan S, Cheng HJ, Ming GL, Lu B, Song H (2007) Disrupted-in-schizophrenia 1 regulates integration of newly generated neurons in the adult brain. Cell 130:1146–1158
Ellis R, Langford D, Masliah E (2007) HIV and antiretroviral therapy in the brain: neuronal injury and repair. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:33–44
Ge S, Goh EL, Sailor KA, Kitabatake Y, Ming GL, Song H (2006) GABA regulates synaptic integration of newly generated neurons in the adult brain. Nature 439:589–593
Hawasli AH, Benavides DR, Nguyen C, Kansy JW, Hayashi K, Chambon P, Greengard P, Powell CM, Cooper DC, Bibb JA (2007) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 governs learning and synaptic plasticity via control of NMDAR degradation. Nat Neurosci 10:880–886
Heaton RK, Franklin DR, Ellis RJ, McCutchan JA, Letendre SL, Leblanc S, Corkran SH, Duarte NA, Clifford DB, Woods SP, Collier AC, Marra CM, Morgello S, Mindt MR, Taylor MJ, Marcotte TD, Atkinson JH, Wolfson T, Gelman BB, McArthur JC, Simpson DM, Abramson I, Gamst A, Fennema-Notestine C, Jernigan TL, Wong J, Grant I (2011) HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders before and during the era of combination antiretroviral therapy: differences in rates, nature, and predictors. J Neurovirol 17:3–16
Hoke A, Morris M, Haughey NJ (2009) GPI-1046 protects dorsal root ganglia from gp120-induced axonal injury by modulating store-operated calcium entry. J Peripher Nerv Syst 14:27–35
Hopkins ME, Nitecki R, Bucci DJ (2011) Physical exercise during adolescence versus adulthood: differential effects on object recognition memory and brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels. Neuroscience 194:84–94
Ivy AS, Rodriguez FG, Garcia C, Chen MJ, Russo-Neustadt AA (2003) Noradrenergic and serotonergic blockade inhibits BDNF mRNA activation following exercise and antidepressant. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:81–88
Kaul M, Ma Q, Medders KE, Desai MK, Lipton SA (2007) HIV-1 coreceptors CCR5 and CXCR4 both mediate neuronal cell death but CCR5 paradoxically can also contribute to protection. Cell Death Differ 14:296–305
Kobilo T, Liu QR, Gandhi K, Mughal M, Shaham Y, van Praag H (2011) Running is the neurogenic and neurotrophic stimulus in environmental enrichment. Learn Mem 18:605–609
Kronenberg G, Bick-Sander A, Bunk E, Wolf C, Ehninger D, Kempermann G (2006) Physical exercise prevents age-related decline in precursor cell activity in the mouse dentate gyrus. Neurobiol Aging 27:1505–1513
Krucker T, Toggas SM, Mucke L, Siggins GR (1998) Transgenic mice with cerebral expression of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 coat protein gp120 show divergent changes in short- and long-term potentiation in CA1 hippocampus. Neuroscience 83:691–700
Lee MH, Wang T, Jang MH, Steiner J, Haughey N, Ming GL, Song H, Nath A, Venkatesan A (2011) Rescue of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in a mouse model of HIV neurologic disease. Neurobiol Dis 41:678–687
Lie DC, Colamarino SA, Song HJ, Desire L, Mira H, Consiglio A, Lein ES, Jessberger S, Lansford H, Dearie AR, Gage FH (2005) Wnt signalling regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Nature 437:1370–1375
Lindl KA, Marks DR, Kolson DL, Jordan-Sciutto KL (2010) HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder: pathogenesis and therapeutic opportunities. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 5:294–309
Lledo PM, Alonso M, Grubb MS (2006) Adult neurogenesis and functional plasticity in neuronal circuits. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:179–193
Lu Y, Christian K, Lu B (2008) BDNF: a key regulator for protein synthesis-dependent LTP and long-term memory? Neurobiol Learn Mem 89:312–323
Ma DK, Jang MH, Guo JU, Kitabatake Y, Chang ML, Pow-Anpongkul N, Flavell RA, Lu B, Ming GL, Song H (2009) Neuronal activity-induced Gadd45b promotes epigenetic DNA demethylation and adult neurogenesis. Science 323:1074–1077
Marlatt MW, Potter MC, Lucassen PJ, van Praag H (2012) Running throughout middle-age improves memory function, hippocampal neurogenesis, and BDNF levels in female C57BL/6J mice. Dev Neurobiol 72:943–952
Marzolini S, Oh P, McIlroy W, Brooks D (2013) The effects of an aerobic and resistance exercise training program on cognition following stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 27(5):392–402
Nath A (2002) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) proteins in neuropathogenesis of HIV dementia. J Infect Dis 186(Suppl 2):S193–S198
Nath S, Bachani M, Harshavardhana D, Steiner JP (2012) Catechins protect neurons against mitochondrial toxins and HIV proteins via activation of the BDNF pathway. J Neurovirol 18:445–455
Nattel S, Rangno RE, Van Loon G (1979) Mechanism of propranolol withdrawal phenomena. Circulation 59:1158–1164
Neeper SA, Gomez-Pinilla F, Choi J, Cotman CW (1996) Physical activity increases mRNA for brain-derived neurotrophic factor and nerve growth factor in rat brain. Brain Res 726:49–56
Nguyen MD, Lariviere RC, Julien JP (2001) Deregulation of Cdk5 in a mouse model of ALS: toxicity alleviated by perikaryal neurofilament inclusions. Neuron 30:135–147
Nosheny RL, Bachis A, Acquas E, Mocchetti I (2004) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 glycoprotein gp120 reduces the levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in vivo: potential implication for neuronal cell death. Eur J Neurosci 20:2857–2864
Okamoto S, Kang YJ, Brechtel CW, Siviglia E, Russo R, Clemente A, Harrop A, McKercher S, Kaul M, Lipton SA (2007) HIV/gp120 decreases adult neural progenitor cell proliferation via checkpoint kinase-mediated cell-cycle withdrawal and G1 arrest. Cell Stem Cell 1:230–236
Ono K, Han J (2000) The p38 signal transduction pathway: activation and function. Cell Signal 12:1–13
Overstreet-Wadiche LS, Bromberg DA, Bensen AL, Westbrook GL (2006) Seizures accelerate functional integration of adult-generated granule cells. J Neurosci 26:4095–4103
Paoletti P, Vila I, Rife M, Lizcano JM, Alberch J, Gines S (2008) Dopaminergic and glutamatergic signaling crosstalk in Huntington's disease neurodegeneration: the role of p25/cyclin-dependent kinase 5. J Neurosci 28:10090–10101
Patrick C, Crews L, Desplats P, Dumaop W, Rockenstein E, Achim CL, Everall IP, Masliah E (2011) Increased CDK5 expression in HIV encephalitis contributes to neurodegeneration via tau phosphorylation and is reversed with Roscovitine. Am J Pathol 178:1646–1661
Perfettini JL, Castedo M, Nardacci R, Ciccosanti F, Boya P, Roumier T, Larochette N, Piacentini M, Kroemer G (2005) Essential role of p53 phosphorylation by p38 MAPK in apoptosis induction by the HIV-1 envelope. J Exp Med 201:279–289
Piatti VC, Davies-Sala MG, Esposito MS, Mongiat LA, Trinchero MF, Schinder AF (2011) The timing for neuronal maturation in the adult hippocampus is modulated by local network activity. J Neurosci 31:7715–7728
Pontifex MB, Saliba BJ, Raine LB, Picchietti DL, Hillman CH (2013) Exercise improves behavioral, neurocognitive, and scholastic performance in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Pediatr 162(3):543–551
Rao JS, Kim HW, Kellom M, Greenstein D, Chen M, Kraft AD, Harry GJ, Rapoport SI, Basselin M (2011) Increased neuroinflammatory and arachidonic acid cascade markers, and reduced synaptic proteins, in brain of HIV-1 transgenic rats. J Neuroinflammation 8:101
Schwartz L, Civitello L, Dunn-Pirio A, Ryschkewitsch S, Berry E, Cavert W, Kinzel N, Lawrence DM, Hazra R, Major EO (2007) Evidence of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of nestin-positive neural progenitors in archival pediatric brain tissue. J Neurovirol 13:274–283
Smith PD, Crocker SJ, Jackson-Lewis V, Jordan-Sciutto KL, Hayley S, Mount MP, O'Hare MJ, Callaghan S, Slack RS, Przedborski S, Anisman H, Park DS (2003) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 is a mediator of dopaminergic neuron loss in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:13650–13655
Snyder JS, Glover LR, Sanzone KM, Kamhi JF, Cameron HA (2009) The effects of exercise and stress on the survival and maturation of adult-generated granule cells. Hippocampus 19:898–906
Stranahan AM, Lee K, Becker KG, Zhang Y, Maudsley S, Martin B, Cutler RG, Mattson MP (2010) Hippocampal gene expression patterns underlying the enhancement of memory by running in aged mice. Neurobiol Aging 31:1937–1949
Toggas SM, Masliah E, Rockenstein EM, Rall GF, Abraham CR, Mucke L (1994) Central nervous system damage produced by expression of the HIV-1 coat protein gp120 in transgenic mice. Nature 367:188–193
Tran PB, Miller RJ (2003) Chemokine receptors: signposts to brain development and disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:444–455
Tyler WJ, Pozzo-Miller LD (2001) BDNF enhances quantal neurotransmitter release and increases the number of docked vesicles at the active zones of hippocampal excitatory synapses. J Neurosci 21:4249–4258
Veeranna, Shetty KT, Amin N, Grant P, Albers RW, Pant HC (1996) Inhibition of neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase-5 by staurosporine and purine analogs is independent of activation by Munc-18. Neurochem Res 21:629–636
Vivar C, Potter MC, van Praag H (2013) All about running: synaptic plasticity, growth factors and adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Curr Top Behav Neurosci15:189–210
Walter C, Murphy BL, Pun RY, Spieles-Engemann AL, Danzer SC (2007) Pilocarpine-induced seizures cause selective time-dependent changes to adult-generated hippocampal dentate granule cells. J Neurosci 27:7541–7552
Wang J, Liu S, Fu Y, Wang JH, Lu Y (2003) Cdk5 activation induces hippocampal CA1 cell death by directly phosphorylating NMDA receptors. Nat Neurosci 6:1039–1047
Wang Y, White MG, Akay C, Chodroff RA, Robinson J, Lindl KA, Dichter MA, Qian Y, Mao Z, Kolson DL, Jordan-Sciutto KL (2007) Activation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 by calpains contributes to human immunodeficiency virus-induced neurotoxicity. J Neurochem 103:439–455
Wu CW, Chang YT, Yu L, Chen HI, Jen CJ, Wu SY, Lo CP, Kuo YM (2008) Exercise enhances the proliferation of neural stem cells and neurite growth and survival of neuronal progenitor cells in dentate gyrus of middle-aged mice. J Appl Physiol 105:1585–1594
Zhang Y, Shi Y, Qiao L, Sun Y, Ding W, Zhang H, Li N, Chen D (2012) Sigma-1 receptor agonists provide neuroprotection against gp120 via a change in bcl-2 expression in mouse neuronal cultures. Brain Res 1431:13–22
Zhao CT, Li K, Li JT, Zheng W, Liang XJ, Geng AQ, Li N, Yuan XB (2009) PKCdelta regulates cortical radial migration by stabilizing the Cdk5 activator p35. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:21353–21358
Zheng YL, Amin ND, Hu YF, Rudrabhatla P, Shukla V, Kanungo J, Kesavapany S, Grant P, Albers W, Pant HC (2010) A 24-residue peptide (p5), derived from p35, the Cdk5 neuronal activator, specifically inhibits Cdk5-p25 hyperactivity and tau hyperphosphorylation. J Biol Chem 285:34202–34212
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Valerie Toodle for technical assistance. This work was supported by grants from the NIH (R01-DA024593; R01-NS039253) and NINDS intramural funds.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
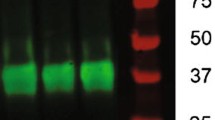
proBDNF expression was increased in the gp120 transgenic mice. a Shown are sample immunoreactive bands from Western blot analysis. Lysates from the hippocampus of the wild-type and gp120 transgenic mice were subjected to Western blot analysis for proBrain-derived neurotrophic factor (proBDNF; 34 kDa) and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH; as an internal control, 35 kDa). b The ratio of proBDNF/GAPDH was quantified. proBDNF expression was upregulated in the hippocampus of the gp120 transgenic mice. Values represent mean ± SEM (n = 3 animals in each group; *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan's test). (PDF 23 kb)
Fig. S2
Rolipram did not reinforce NPC proliferation and survival effect of exercise on newly generated cell. a Experimental design. To study the effect of the PDE4 inhibitor, rolipram on NPC proliferation, mice received rolipram (3 mg/kg) daily for ten consecutive days at 11 days after treatment (running or sedentary activity) for 10 days. Mice were administered a single dose of BrdU and killed 24 h later. b Rolipram treatment after 10 days of running failed to counteract the effect of detraining on NPC proliferation. Values represent mean ± SEM (n = 5 animals in each group; one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan's test). c Experimental design. For survival studies, mice were given 50 mg/kg of BrdU at 2-h intervals for 6 h. Rolipram (3 mg/kg) was administered to mice daily for ten consecutive days at 11 days after BrdU labeling. The mice were then killed either 1 or 21 days after the initial BrdU injection. d The survival rate was not increased by rolipram treatment after 10 days of running. Values represent mean ± SEM (n = 5 animals in each group; one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan's test). (PDF 91 kb)
Fig. S3
The effect of exercise on NPC proliferation was independent of NE signaling. a Experimental design. Mice were allowed free access to a running wheel for 10 days. Intraperitoneal injections of the β-adrenergic antagonist, propranolol at 5 mg/kg were given for the last 3 days of a 10-day period of exercise. All the animals were analyzed 24 h after BrdU injection. b Exercise increased proliferating NPCs both in the wild-type and gp120 transgenic mice, but propranolol failed to block exercise-induced increase in NPC proliferation. Values represent mean ± SEM (n = 5 animals in each group; one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan's test). (PDF 45 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, MH., Amin, N.D., Venkatesan, A. et al. Impaired neurogenesis and neurite outgrowth in an HIV-gp120 transgenic model is reversed by exercise via BDNF production and Cdk5 regulation. J. Neurovirol. 19, 418–431 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-013-0194-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13365-013-0194-6