Abstract
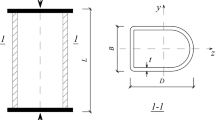
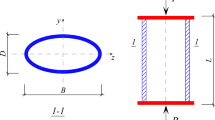
The steel oval hollow section (OHS) provides an aesthetic architecture and a greater local buckling strength. However, the existing design codes do not specify the effective width in calculating the load-bearing capacity of OHS members. This study aims to predict the axial compression capacity (ACC) of cold-formed steel OHS columns using artificial neural network (ANN) and adaptive neural fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) models. A total of 128 data sets collected from the literature were utilized to develop the ANN and ANFIS models. The performance of the two machine learning models was compared with three existing design codes. The results demonstrated that the developed ANN and ANFIS models predicted the ACC of steel OHS columns more accurately compared to the existing formulas. Specifically, the ANN model revealed a superior performance with the highest coefficient of determination and the smallest root means square errors. Moreover, the formulas based on ANN and ANFIS models, which accommodates all input parameters, were proposed to predict the ACC of cold-formed steel OHS columns. The thickness of the cross-section was the most influential parameter on the ACC of the OHS column. By contrast, the column length negatively affected the ACC value of the steel column. Finally, a graphical user interface tool was developed to readily calculate the ACC of the steel OHS columns.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abiodun, O. I., Jantan, A., Omolara, A. E., Dada, K. V., Mohamed, N. A., & Arshad, H. (2018). State-of-the-art in artificial neural network applications: A survey. Heliyon, 4(11), e00938.
Ahmadi, M., Naderpour, H., & Kheyroddin, A. (2014). Utilization of artificial neural networks to prediction of the capacity of CCFT short columns subject to short term axial load. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 14(3), 510–517.
AISC. (2010). Specification for structural steel buildings (ANSI/AISC 360–10). American Institute of Steel Construction. Chicago-Illinois, USA.
AISI. (2016). AISI-S100-16: North American specification for the design of cold-formed steel structural members. American Iron and Steel Institute, Washington, DC, USA.
AS/NZS. (2005). Australia/New Zealand standard AS/NZS 4600 cold-formed steel structures.
Chaabene, W. B., Flah, M., & Nehdi, M. L. (2020). Machine learning prediction of mechanical properties of concrete: Critical review. Construction and Building Materials, 260, 119889.
Chan, T.-M., Huai, Y.-M., & Wang, W. (2015). Experimental investigation on lightweight concrete-filled cold-formed elliptical hollow section stub columns. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 115, 434–444.
Chan, T. M., & Gardner, L. (2008). Bending strength of hot-rolled elliptical hollow sections. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 64(9), 971–986.
Chan, T. M., & Gardner, L. (2009). Flexural buckling of elliptical hollow section columns. Journal of Structural Engineering, 135(5), 546–557.
Chen, M.-T., & Young, B. (2018a). Cross-sectional behavior of cold-formed steel semi-oval hollow sections. Engineering Structures, 177, 318–330.
Chen, M.-T., & Young, B. (2018b). Experimental and numerical investigation on cold-formed steel semi-oval hollow section compression members. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 151, 174–184.
Chen, M.-T., & Young, B. (2019a). Behavior of cold-formed steel elliptical hollow sections subjected to bending. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 158, 317–330.
Chen, M.-T., & Young, B. (2019b). Material properties and structural behavior of cold-formed steel elliptical hollow section stub columns. Thin-Walled Structures, 134, 111–126.
Chen, M.-T., & Young, B. (2019c). Structural performance of cold-formed steel elliptical hollow section pin-ended columns. Thin-Walled Structures, 136, 267–279.
Chen, M.-T., & Young, B. (2020). Tests of cold-formed steel semi-oval hollow section members under eccentric axial load. Journal of Structural Engineering, 146(4), 04020027.
Chen, M.-T., & Young, B. (2021). Numerical analysis and design of cold-formed steel elliptical hollow sections under combined compression and bending. Engineering Structures, 241, 112417.
Dias, J. L. R., & Silvestre, N. (2011). A neural network based closed-form solution for the distortional buckling of elliptical tubes. Engineering Structures, 33(6), 2015–2024.
EN1993-1-1. (2005). Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures-Part 1-1: General rules and rules for buildings. CEN, Brussels: European Committee for Standardization.
Falcone, R., Lima, C., & Martinelli, E. (2020). Soft computing techniques in structural and earthquake engineering: A literature review. Engineering Structures, 207, 110269.
Fang, Z., Roy, K., Chen, B., Sham, C.-W., Hajirasouliha, I., & Lim, J. B. (2021a). Deep learning-based procedure for structural design of cold-formed steel channel sections with edge-stiffened and un-stiffened holes under axial compression. Thin-Walled Structures, 166, 108076.
Fang, Z., Roy, K., Ma, Q., Uzzaman, A., & Lim, J. B. (2021b) Application of deep learning method in web crippling strength prediction of cold-formed stainless steel channel sections under end-two-flange loading. In Structures (Vol. 33, pp. 2903–2942). Elsevier.
Fang, Z., Roy, K., Mares, J., Sham, C.-W., Chen, B., & Lim, J. B. (2021c). Deep learning-based axial capacity prediction for cold-formed steel channel sections using Deep Belief Network. In Structures (Vol. 33, pp. 2792–2802). Elsevier.
Feng, D.-C., Liu, Z.-T., Wang, X.-D., Jiang, Z.-M., & Liang, S.-X. (2020). Failure mode classification and bearing capacity prediction for reinforced concrete columns based on ensemble machine learning algorithm. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 45, 101126.
Flood, I., & Kartam, N. (1998). Artificial neural networks for civil engineers: Advanced features and applications. ASCE Publications.
Gardner, L., & Chan, T. M. (2007). Cross-section classification of elliptical hollow sections. Steel and Composite Structures, 7(3), 185.
Gardner, L., & Ministro, A. (2005). Structural steel oval hollow sections. Structural Engineer, 83(21), 32–36.
Güneyisi, E. M., Gültekin, A., & Mermerdaş, K. (2016). Ultimate capacity prediction of axially loaded CFST short columns. International Journal of Steel Structures, 16(1), 99–114.
Hadi, M. N. (2003). Neural networks applications in concrete structures. Computers & Structures, 81(6), 373–381.
Hakim, S. J. S., & Razak, H. A. (2013). Adaptive neuro fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and artificial neural networks (ANNs) for structural damage identification. Structural Engineering and Mechanics: An International Journal, 45(6), 779–802.
Jang, J.-S. (1993). ANFIS: Adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 23(3), 665–685.
Kotsiantis, S. B., Zaharakis, I., & Pintelas, P. (2007). Supervised machine learning: A review of classification techniques. Emerging Artificial Intelligence Applications in Computer Engineering, 160(1), 3–24.
Le, L. M., Ly, H.-B., Pham, B. T., Le, V. M., Pham, T. A., Nguyen, D.-H., et al. (2019). Hybrid artificial intelligence approaches for predicting buckling damage of steel columns under axial compression. Materials, 12(10), 1670.
Le, T.-T. (2020a). Practical hybrid machine learning approach for estimation of ultimate load of elliptical concrete-filled steel tubular columns under axial loading. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2020, 1–19.
Le, T.-T. (2020b). Practical machine learning-based prediction model for axial capacity of square CFST columns. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376494.2020.1839608
Le, T.-T., Asteris, P. G., & Lemonis, M. E. (2021). Prediction of axial load capacity of rectangular concrete-filled steel tube columns using machine learning techniques. Engineering with Computers, 1–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-021-01461-0
Luat, N.-V., Lee, J., Lee, D. H., & Lee, K. (2020). GS-MARS method for predicting the ultimate load-carrying capacity of rectangular CFST columns under eccentric loading. Computers and Concrete, 25(1), 1–14.
Luat, N.-V., Shin, J., & Lee, K. (2020b). Hybrid BART-based models optimized by nature-inspired metaheuristics to predict ultimate axial capacity of CCFST columns. Engineering with Computers, 1–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01115-7
Ly, H.-B., Le, L. M., Duong, H. T., Nguyen, T. C., Pham, T. A., Le, T.-T., et al. (2019). Hybrid artificial intelligence approaches for predicting critical buckling load of structural members under compression considering the influence of initial geometric imperfections. Applied Sciences, 9(11), 2258.
Ly, H.-B., Pham, B. T., Le, L. M., Le, T.-T., Le, V. M., & Asteris, P. G. (2021). Estimation of axial load-carrying capacity of concrete-filled steel tubes using surrogate models. Neural Computing and Applications, 33(8), 3437–3458.
Mai, S. H., Seghier, M. E. A. B., Nguyen, P. L., Jafari-Asl, J., & Thai, D.-K. (2020). A hybrid model for predicting the axial compression capacity of square concrete-filled steel tubular columns. Engineering with Computers, 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-020-01104-w
Mathworks, I. (2018). MATLAB and statistics toolbox release 2018b. Natick (Massachusetts, United States).
Mirrashid, M., & Naderpour, H. (2020). Recent trends in prediction of concrete elements behavior using soft computing (2010–2020). Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 28, 3307–3327.
Naderpour, H., & Alavi, S. A. (2017). A proposed model to estimate shear contribution of FRP in strengthened RC beams in terms of Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System. Composite Structures, 170, 215–227.
Nguyen, D.-D., Tran, V.-L., Ha, D.-H., Nguyen, V.-Q., & Lee, T.-H. (2021a). A machine learning-based formulation for predicting shear capacity of squat flanged RC walls. Structures, 29, 1734–1747.
Nguyen, M.-S.T., Thai, D.-K., & Kim, S.-E. (2020). Predicting the axial compressive capacity of circular concrete filled steel tube columns using an artificial neural network. Steel and Composite Structures, 35(3), 415–437.
Nguyen, M.-S. T., Trinh, M.-C., & Kim, S.-E. (2021b). Uncertainty quantification of ultimate compressive strength of CCFST columns using hybrid machine learning model. Engineering with Computers, 1–20.
Nguyen, T.-H., Tran, N.-L., & Nguyen, D.-D. (2021c). Prediction of Critical Buckling Load of Web Tapered I-Section Steel Columns Using Artificial Neural Networks. International Journal of Steel Structures, 21(4), 1159–1181.
Nikbin, I. M., Rahimi, S., & Allahyari, H. (2017). A new empirical formula for prediction of fracture energy of concrete based on the artificial neural network. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 186, 466–482.
Reich, Y. (1997). Machine learning techniques for civil engineering problems. Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering, 12(4), 295–310.
Sadrmomtazi, A., Sobhani, J., & Mirgozar, M. A. (2013). Modeling compressive strength of EPS lightweight concrete using regression, neural network and ANFIS. Construction and Building Materials, 42, 205–216.
Seghier, M. E. A. B., Gao, X.-Z., Jafari-Asl, J., Thai, D.-K., Ohadi, S., & Trung, N.-T. (2021). Modeling the nonlinear behavior of ACC for SCFST columns using experimental-data and a novel evolutionary-algorithm. In Structures, 2021 (Vol. 30, pp. 692–709). Elsevier.
Siam, A., Ezzeldin, M., & El-Dakhakhni, W. (2019). Machine learning algorithms for structural performance classifications and predictions: Application to reinforced masonry shear walls. In Structures (Vol. 22, pp. 252–265). Elsevier.
Silvestre, N. (2008). Buckling behaviour of elliptical cylindrical shells and tubes under compression. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 45(16), 4427–4447.
Sugeno, M. (1985). An introductory survey of fuzzy control. Information Sciences, 36(1–2), 59–83.
Sun, H., Burton, H. V., & Huang, H. (2020). Machine learning applications for building structural design and performance assessment: state-of-the-art review. Journal of Building Engineering, 33, 101816.
Theofanous, M., Chan, T. M., & Gardner, L. (2009). Structural response of stainless steel oval hollow section compression members. Engineering Structures, 31(4), 922–934.
Tran, V.-L., Jang, Y., & Kim, S.-E. (2021). Improving the axial compression capacity prediction of elliptical CFST columns using a hybrid ANN-IP model. Steel and Composite Structures, 39(3), 319–335.
Tran, V.-L., & Kim, S.-E. (2020a). Efficiency of three advanced data-driven models for predicting axial compression capacity of CFDST columns. Thin-Walled Structures, 152, 106744.
Tran, V.-L., & Kim, S.-E. (2020b). A practical ANN model for predicting the PSS of two-way reinforced concrete slabs. Engineering with Computers, 37, 2303–2327.
Tran, V.-L., Thai, D.-K., & Kim, S.-E. (2019a). Application of ANN in predicting ACC of SCFST column. Composite Structures, 228, 111332.
Tran, V.-L., Thai, D.-K., & Kim, S.-E. (2019b). A new empirical formula for prediction of the axial compression capacity of CCFT columns. Steel and Composite Structures, 33(2), 181–194.
Tran, V.-L., Thai, D.-K., & Nguyen, D.-D. (2020). Practical artificial neural network tool for predicting the axial compression capacity of circular concrete-filled steel tube columns with ultra-high-strength concrete. Thin-Walled Structures, 151, 106720.
Vakhshouri, B., & Nejadi, S. (2018). Prediction of compressive strength of self-compacting concrete by ANFIS models. Neurocomputing, 280, 13–22.
Vu, Q.-V., Truong, V.-H., & Thai, H.-T. (2021). Machine learning-based prediction of CFST columns using gradient tree boosting algorithm. Composite Structures, 259, 113505.
Worden, K., & Manson, G. (2007). The application of machine learning to structural health monitoring. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society a: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 365(1851), 515–537.
Xu, Y., Zheng, B., & Zhang, M. (2021). Capacity prediction of cold-formed stainless steel tubular columns using machine learning methods. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 182, 106682.
Zarringol, M., Thai, H.-T., & Naser, M. (2021). Application of machine learning models for designing CFCFST columns. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 185, 106856.
Zhou, Q., Zhu, F., Yang, X., Wang, F., Chi, B., & Zhang, Z. (2017). Shear capacity estimation of fully grouted reinforced concrete masonry walls using neural network and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system models. Construction and Building Materials, 153, 937–947.
Zhu, J.-H., Su, M.-N., Zhu, X., Daniels, J., & Young, B. (2021). Flexural behaviour of cold-formed steel oval hollow section beams. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 180, 106605.
Zhu, J.-H., & Young, B. (2011). Cold-formed-steel oval hollow sections under axial compression. Journal of Structural Engineering, 137(7), 719–727.
Zhu, J.-H., & Young, B. (2012). Design of cold-formed steel oval hollow section columns. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 71, 26–37.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix: Database used in developing ANN and ANFIS models
Appendix: Database used in developing ANN and ANFIS models
\(D\) (mm) | \(W\) (mm) | \(t\) (mm) | \(h/t\) | \(L\) (mm) | \(E\) (MPa) | \(\sigma_{u}\) (MPa) | \(\varepsilon_{f}\) (%) | \(\sigma_{0.2}\) (MPa) | \(P_{Test}\) (kN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
120 | 48 | 2 | 36 | 360 | 202 | 403 | 18 | 359 | 181.2 |
120 | 48 | 2 | 36 | 360 | 202 | 403 | 18 | 359 | 185.9 |
120 | 48 | 2 | 36 | 600 | 202 | 403 | 18 | 359 | 196 |
120 | 48 | 2 | 36 | 1200 | 202 | 403 | 18 | 359 | 190.3 |
120 | 48 | 2 | 36 | 1200 | 202 | 403 | 18 | 359 | 188.5 |
120 | 48 | 2 | 36 | 1800 | 202 | 403 | 18 | 359 | 183.9 |
120 | 48 | 2 | 36 | 2400 | 202 | 403 | 18 | 359 | 173.1 |
120 | 48 | 2 | 36 | 3000 | 202 | 403 | 18 | 359 | 157.7 |
42 | 21 | 2.8 | 7.5 | 126 | 200 | 456 | 20 | 443 | 144.1 |
42 | 21 | 2.8 | 7.5 | 300 | 200 | 456 | 20 | 443 | 122.3 |
42 | 21 | 2.8 | 7.5 | 600 | 200 | 456 | 20 | 443 | 111 |
42 | 21 | 2.8 | 7.5 | 900 | 200 | 456 | 20 | 443 | 96.8 |
42 | 21 | 2.8 | 7.5 | 900 | 200 | 456 | 20 | 443 | 92.8 |
42 | 21 | 2.8 | 7.5 | 1200 | 200 | 456 | 20 | 443 | 64.6 |
42 | 21 | 2.8 | 7.5 | 1500 | 200 | 456 | 20 | 443 | 51.5 |
115 | 38 | 2 | 38.5 | 345 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 163.3 |
115 | 38 | 2 | 38.5 | 600 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 156.2 |
115 | 38 | 2 | 38.5 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 146.6 |
115 | 38 | 2 | 38.5 | 1800 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 131.6 |
115 | 38 | 2 | 38.5 | 2400 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 118.8 |
115 | 38 | 2 | 38.5 | 3000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 103.5 |
30 | 15 | 1.6 | 9.4 | 90 | 199 | 454 | 21 | 432 | 58.4 |
30 | 15 | 1.6 | 9.4 | 300 | 199 | 454 | 21 | 432 | 51.1 |
30 | 15 | 1.6 | 9.4 | 600 | 199 | 454 | 21 | 432 | 38.9 |
30 | 15 | 1.6 | 9.4 | 900 | 199 | 454 | 21 | 432 | 30.4 |
30 | 15 | 1.6 | 9.4 | 900 | 199 | 454 | 21 | 432 | 28.4 |
30 | 15 | 1.6 | 9.4 | 1200 | 199 | 454 | 21 | 432 | 19 |
30 | 15 | 1.6 | 9.4 | 1500 | 199 | 454 | 21 | 432 | 12.7 |
300 | 60 | 2 | 120 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 223.4 |
300 | 60 | 2 | 120 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 205 |
300 | 60 | 2 | 120 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 202.3 |
300 | 60 | 2 | 120 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 178.3 |
300 | 60 | 2 | 120 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 171.7 |
300 | 60 | 2.4 | 100 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 299.9 |
300 | 60 | 2.4 | 100 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 273.3 |
300 | 60 | 2.4 | 100 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 267.1 |
300 | 60 | 2.4 | 100 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 237.7 |
300 | 60 | 2.4 | 100 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 227.3 |
300 | 60 | 3 | 80 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 429.4 |
300 | 60 | 3 | 80 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 395.9 |
300 | 60 | 3 | 80 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 380.7 |
300 | 60 | 3 | 80 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 355.7 |
300 | 60 | 3 | 80 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 326.5 |
300 | 60 | 4 | 60 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 700.6 |
300 | 60 | 4 | 60 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 658.5 |
300 | 60 | 4 | 60 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 626.3 |
300 | 60 | 4 | 60 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 598.5 |
300 | 60 | 4 | 60 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 562.8 |
300 | 60 | 10 | 24 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2350.6 |
300 | 60 | 10 | 24 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2279.6 |
300 | 60 | 10 | 24 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2133.6 |
300 | 60 | 10 | 24 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 1994.4 |
300 | 60 | 10 | 24 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 1826.2 |
300 | 75 | 1.9 | 118.4 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 237.5 |
300 | 75 | 1.9 | 118.4 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 231.1 |
300 | 75 | 1.9 | 118.4 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 220.6 |
300 | 75 | 1.9 | 118.4 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 212.8 |
300 | 75 | 1.9 | 118.4 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 182.1 |
300 | 75 | 2.2 | 102.3 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 286 |
300 | 75 | 2.2 | 102.3 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 284.8 |
300 | 75 | 2.2 | 102.3 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 266.2 |
300 | 75 | 2.2 | 102.3 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 263.1 |
300 | 75 | 2.2 | 102.3 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 245.7 |
300 | 75 | 2.8 | 80.4 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 415.5 |
300 | 75 | 2.8 | 80.4 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 406.2 |
300 | 75 | 2.8 | 80.4 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 387.8 |
300 | 75 | 2.8 | 80.4 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 373.2 |
300 | 75 | 2.8 | 80.4 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 348.9 |
300 | 75 | 3.8 | 59.2 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 678.9 |
300 | 75 | 3.8 | 59.2 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 648.1 |
300 | 75 | 3.8 | 59.2 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 621.9 |
300 | 75 | 3.8 | 59.2 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 603.4 |
300 | 75 | 3.8 | 59.2 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 579.7 |
300 | 75 | 10 | 22.5 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2433.9 |
300 | 75 | 10 | 22.5 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2380.1 |
300 | 75 | 10 | 22.5 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2266.4 |
300 | 75 | 10 | 22.5 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2147.8 |
300 | 75 | 10 | 22.5 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2016.8 |
300 | 100 | 1.7 | 117.6 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 228.3 |
300 | 100 | 1.7 | 117.6 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 226.3 |
300 | 100 | 1.7 | 117.6 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 222.4 |
300 | 100 | 1.7 | 117.6 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 216.8 |
300 | 100 | 1.7 | 117.6 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 208.8 |
300 | 100 | 2 | 100 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 283.7 |
300 | 100 | 2 | 100 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 282.4 |
300 | 100 | 2 | 100 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 278.1 |
300 | 100 | 2 | 100 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 271.8 |
300 | 100 | 2 | 100 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 261.3 |
300 | 100 | 2.5 | 80 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 385.9 |
300 | 100 | 2.5 | 80 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 384.1 |
300 | 100 | 2.5 | 80 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 376.7 |
300 | 100 | 2.5 | 80 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 369.5 |
300 | 100 | 2.5 | 80 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 356.4 |
300 | 100 | 3.3 | 60.6 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 578 |
300 | 100 | 3.3 | 60.6 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 574 |
300 | 100 | 3.3 | 60.6 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 560.6 |
300 | 100 | 3.3 | 60.6 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 550.9 |
300 | 100 | 3.3 | 60.6 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 535.7 |
300 | 100 | 10 | 20 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2514.8 |
300 | 100 | 10 | 20 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2487.9 |
300 | 100 | 10 | 20 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2422.6 |
300 | 100 | 10 | 20 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2338.4 |
300 | 100 | 10 | 20 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2234 |
300 | 150 | 1.3 | 115.4 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 211.5 |
300 | 150 | 1.3 | 115.4 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 208.5 |
300 | 150 | 1.3 | 115.4 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 206.6 |
300 | 150 | 1.3 | 115.4 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 204.3 |
300 | 150 | 1.3 | 115.4 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 203.5 |
300 | 150 | 1.5 | 100 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 255.9 |
300 | 150 | 1.5 | 100 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 253.3 |
300 | 150 | 1.5 | 100 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 252.1 |
300 | 150 | 1.5 | 100 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 249.4 |
300 | 150 | 1.5 | 100 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 240 |
300 | 150 | 1.8 | 83.3 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 325.3 |
300 | 150 | 1.8 | 83.3 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 322.7 |
300 | 150 | 1.8 | 83.3 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 318 |
300 | 150 | 1.8 | 83.3 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 313.9 |
300 | 150 | 1.8 | 83.3 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 307.8 |
300 | 150 | 2.5 | 60 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 499.5 |
300 | 150 | 2.5 | 60 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 482.1 |
300 | 150 | 2.5 | 60 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 479.5 |
300 | 150 | 2.5 | 60 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 473.5 |
300 | 150 | 2.5 | 60 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 466.8 |
300 | 150 | 10 | 15 | 500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2788.1 |
300 | 150 | 10 | 15 | 1200 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2755.4 |
300 | 150 | 10 | 15 | 2000 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2694.9 |
300 | 150 | 10 | 15 | 2700 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2638.7 |
300 | 150 | 10 | 15 | 3500 | 202 | 387 | 27 | 359 | 2566.9 |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, TH., Tran, NL. & Nguyen, DD. Prediction of Axial Compression Capacity of Cold-Formed Steel Oval Hollow Section Columns Using ANN and ANFIS Models. Int J Steel Struct 22, 1–26 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-021-00557-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13296-021-00557-z