Abstract
To prepare a high-stability flexible sensor for body motion monitoring, a conductive warp-knitted fabric (CWKF) with a two-bar tricot structure coated with polyaniline(PANI) was prepared by in situ polymerization, and then a waterborne polyurethane-coated conductive warp-knitted fabric (WPU/CWKF) was prepared using a simple dip-and-dry method. The structure and properties of both CWKF and WPU/CWKF were analyzed, their strain-resistance sensing properties were investigated, and their application in body motion monitoring was discussed. The results indicate that conductive treatment of in situ polymerization can give the polyester warp-knitted fabric good electrical conductivity, with a resistivity of approximately 5 Ω cm. After coating with WPU, the resistivity of the WPU/CKWF increased to approximately 40 Ω cm. Both CKWF and WPU/CKWF showed good strain-resistance sensing performance, but CWKF was more sensitive than WPU/CKWF, whereas WPU/CKWF was more stable than CWKF. Both the CWKF and WPU/CKWF sensors could monitor body motion in real time. Similar to their base materials, the CWKF sensor demonstrated a higher sensitivity for human movement monitoring, whereas the WPU/CKWF sensor exhibited higher stability.
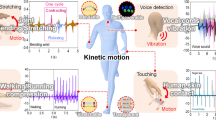
Graphic abstract
Conductive warp-knitted fabric (CWKF) with a two-bar tricot warp-knitted structure coated with polyaniline (PANI) was prepared by in situ polymerisation. After repeated reciprocal stretching, the structure of the PANI conductive layer on the CWKF surface broke down and its conductivity changed, especially under large strains. CWKF sensors enable real-time human motion monitoring with high sensitivity












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
J. Lee, H. Kwon, J. Seo, S. Shin, J.H. Koo, C. Pang, S. Son, J.H. Kim, Y.H. Jang, D.E. Kim, T. Lee, Conductive fiber-based ultrasensitive textile pressure sensor for wearable electronics. Adv. Mater. 27, 2433–2439 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201500009
M. Chen, Y. Ma, Y. Li, D. Wu, Y. Zhang, C.H. Youn, Wearable 2.0: enabling human-cloud integration in next generation healthcare systems. IEEE Commun. Mag. 55, 54–61 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2017.1600410CM
S. Ajami, F. Teimouri, Features and application of wearable biosensors in medical care. Res. Med. Sci 20, 1208–1215 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4103/1735-1995.172991
M. Chen, Y. Ma, J. Song, C.F. Lai, B. Hu, Smart clothing: connecting human with clouds and big data for sustainable health monitoring. Mob. Netw. Appl. 21, 825–845 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-016-0745-1
D. Kang, P.V. Pikhitsa, Y.W. Choi, C. Lee, S.S. Shin, L. Piao, B. Park, K.Y. Suh, T. Il Kim, M. Choi, Ultrasensitive mechanical crack-based sensor inspired by the spider sensory system. Nature 516, 222–226 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14002
S. Choi, H. Lee, R. Ghaffari, T. Hyeon, D.H. Kim, Recent advances in flexible and stretchable bio-electronic devices integrated with nanomaterials. Adv. Mater. 28, 4203–4218 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201504150
Y. Khan, A.E. Ostfeld, C.M. Lochner, A. Pierre, A.C. Arias, Monitoring of vital signs with flexible and wearable medical devices. Adv. Mater. 28, 4373–4395 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201504366
X. Zhou, C. Hu, X. Lin, X. Han, X. Zhao, J. Hong, Polyaniline-coated cotton knitted fabric for body motion monitoring, Sensors Actuators. A Phys. 321, 112591 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2021.112591
Z. Lei, Q. Wang, S. Sun, W. Zhu, P. Wu, A Bioinspired mineral hydrogel as a self-healable, mechanically adaptable ionic skin for highly sensitive pressure sensing. Adv. Mater. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201700321
J. Hong, Z. Pan, M. Zhewang, J. Yao, Y.Z. Chen, A large-strain weft-knitted sensor fabricated by conductive UHMWPE/PANI composite yarns. Sens. Actuat. A-phys. 238, 307–316 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2015.12.028
D. Lu, S. Liao, Q. Wei, X. Xiao, Q. Wang, Comparative study of different carbon materials for the preparation of knitted fabric sensors. Cellulose 29, 7431–7444 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04722-3
Q. Yu, J. Jiang, C. Su, Y. Huang, N. Chen, H. Shao, Ti3C2Tx MXene/polyvinyl alcohol decorated polyester warp knitting fabric for flexible wearable strain sensors. Text. Res. J. 92, 810–824 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1177/00405175211044163
A. Grassi, F. Cecchi, M. Maselli, M. Roling, C. Laschi, M. Cianchetti, Warp-knitted textile as a strain sensor: characterization procedure and application in a comfortable wearable goniometer. IEEE Sens. J. 17, 5927–5936 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2017.2736944
R. Xu, W. Wang, J. Sun, Y. Wang, C. Wang, X. Ding, Z. Ma, Y. Mao, D. Yu, A flexible, conductive and simple pressure sensor prepared by electroless silver plated polyester fabric. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 578, 123554 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.04.096
A. Gurarslan, B. Özdemir, İH. Bayat, M.B. Yelten, G. Karabulut Kurt, Silver nanowire coated knitted wool fabrics for wearable electronic applications. J. Eng. Fiber Fabr. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1177/1558925019856222
S. Khadtare, E.J. Ko, Y.H. Kim, H.S. Lee, D.K. Moon, A flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator using conducting polymer and silver nanowire hybrid electrodes for its application in real-time muscular monitoring system. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 299, 111575 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2019.111575
C. Gao, S. He, L. Qiu, M. Wang, J. Gao, Q. Gao, Continuous dry–wet spinning of white, stretchable, and conductive fibers of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) and ATO@ TiO2 nanoparticles for wearable e-textiles. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 8, 8362–8367 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0tc01310b
F.S. da Luz, F. da Costa Garcia, M.-R. Filho, L.F. Cassiano Nascimento, W.A. Pinheiro, S.N. Monteiro, Graphene-incorporated natural fiber polymer composites: a first overview. Polymers (Basel) 12, 1601 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071601
G. Achagri, Y. Essamlali, O. Amadine, M. Majdoub, A. Chakir, M. Zahouily, Surface modification of highly hydrophobic polyester fabric coated with octadecylamine-functionalized graphene nanosheets. RSC Adv. 10, 24941–24950 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra02655g
L. Sun, F. Wang, J. Jiang, H. Liu, B. Du, M. Li, Y. Liu, M. Li, A wearable fabric strain sensor assemblied by graphene with dual sensing performance approach to practice application assisted by wireless bluetooth. Cellulose 27, 8923–8935 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03401-5
J. Zhou, Z. Zhao, R. Hu, J. Yang, H. Xiao, Y. Liu, M. Lu, Multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized silk fabrics for mechanical sensors and heating materials. Mater. Des. 191, 108636 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108636
C.R.S. de Oliveira, M.A. Batistella, S.M.A.G.U. de Souza, A.A.U. de Souza, Development of flexible sensors using knit fabrics with conductive polyaniline coating and graphite electrodes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 18, 134 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/app.44785
R. Hu, J. Zheng, Preparation of high strain porous polyvinyl alcohol/polyaniline composite and its applications in all-solid-state supercapacitor. J. Power. Sources 364, 200–207 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.08.022
X.H. Wang, Q. Tang, Y.H. Mu, C.Q. Li, Preparation of PANI–PVA composite conductive coatings doped with different acid. J. Adv. Polym. Technol. 36, 502–506 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/adv.21633
C.Y. Hu, R.W. Miao, X. Han, J.H. Hong, G.I.L. Ignacio, Effect of polyvinyl alcohol on the durability of polyaniline layer on poly(p-phenylene terephthamide) yarn surface. J. Text. Res. 41, 91–97 (2020)
R.W. Miao, X.R. Zhou, X.T. Wang, X. Han, J.H. Hong, Preparation and properties of highly durable J silk fibroin/polyaniline composite yarn. J. Silk. 58, 1–5 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3969/jissn.1001-7003.2021.04.001
B.C. Zhao, J.Q. Yan, F. Long, Q. Wu, G.Q. Meng, Z.C. Zeng, H. Wang, N.B. Lin, X.Y. Liu, Bioinspired conductive enhanced polyurethane ionic skin as reliable multifunctional sensors. J. Adv. Sci. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202300857
L. Wu, C. Xu, M.L. Fan, P. Tang, R. Zhang, S.T. Yang, L.J. Pan, Y.Z. Bin, Lotus root structure-inspired Ti3C2-MXene-based flexible and wearable strain sensor with ultra-high sensitivity and wide sensing range[J]. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 152, 106702 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2021.106702
R. Holm, Electric contacts theory and application. Journal of Handbook (1967), pp. 60–71
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Exploratory Public Welfare Project of the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LTGY24E030001) and Key Industrial Technology Research Projects of Keqiao District (Grant No. 2023JBGS110).
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Exploratory Public Welfare Project of the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LTGY24E030001), and Key Industrial Technology Research Projects of Keqiao District (Grant No. 2023JBGS110), Jianhan Hong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XY contributed to formal analysis, writing––original draft, and writing––review and editing. XW did formal analysis and provided software. XH and JH contributed to conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, and writing––review and editing.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, X., Wang, X., Han, X. et al. High-stability flexible body motion monitoring sensor based on waterborne polyurethane-coated conductive warp-knitted fabric. Macromol. Res. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-024-00258-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-024-00258-6