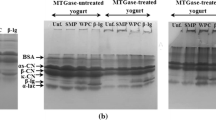
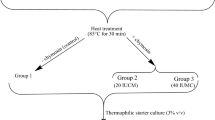
Abstract
Yogurt, produced by the lactic fermentation of milk base, is an important dairy product worldwide. One of the essential sensory properties of yogurt is the texture, and some textural defects such as weak gel firmness and syneresis likely occur in various types of yogurts, affecting consumer acceptance. In this regard, various strategies such as enrichment of milk-based with different additives and ingredients such as protein-based components (skimmed milk powder (SMP), whey protein-based powders (WP), casein-based powders (CP), and suitable stabilizers, as well as modification of processing conditions (homogenization, fermentation, and cooling), can be applied in order to reduce syneresis. The most effective proteins and stabilizers in syneresis reduction are CP and gelatin, respectively. Furthermore, yogurt's water holding capacity and syneresis can be affected by the type of starter cultures, the protolithic activity, production of extracellular polysaccharides, and inoculation rate. Moreover, optimizing the heat treatment process (85 °C/30 min and 95 °C/5 min), homogenization (single or dual-stage), incubation temperature (around 40 °C), and two-step cooling process can decrease yogurt syneresis. This review is aimed to investigate the effect of fortification of the milk base with various additives and optimization of process conditions on improving texture and preventing syneresis in yogurt.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SMP:
-
Skimmed milk powder
- WP:
-
Whey powder
- WPC:
-
Whey protein concentrates
- WPI:
-
Whey protein isolate
- WPH:
-
Whey protein hydrolysate
- CMC:
-
Carboxymethyl cellulose
- LBG:
-
Locust bean gum
- EPS:
-
Exopolysaccharides
References
Ahmed W, Rashid S (2019) Functional and therapeutic potential of inulin: a comprehensive review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2017.1355775
Akdeniz V, Akalın AS (2019) New approach for yoghurt and ice cream production: High-intensity ultrasound. Trends Food Sci Technol 86:392–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.02.046
Alakali JS, Unwiyi I, Ejiga O (2009) Effect of milk blends and temperature on the quality of thermized yoghurt. Elec J Environ Agricult Food Chem 8:676–684
Alimentarius FWC (2011) Milk and milk products. Codex Standard for Fermented Milk 6–616.
Altemimi AB (2018) Extraction and optimization of potato starch and its application as a stabilizer in yogurt manufacturing. Foods 7:14. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods7020014
Amalfitano N, Cipolat-Gotet C, Cecchinato A, Malacarne M, Summer A, Bittante G (2019) Milk protein fractions strongly affect the patterns of coagulation, curd firming, and syneresis. J Dairy Sci 102:2903–2917. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2018-15524
Amatayakul T, Sherkat F, Shah N (2006) Physical characteristics of set yoghurt made with altered casein to whey protein ratios and EPS-producing starter cultures at 9 and 14% total solids. Food Hydrocoll 20:314–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2005.02.015
Arab M, Razavi SH, Hosseini SM, Nayebzadeh K, Meybodi NM, Khanniri E, Mardi P, Mortazavian AM (2019a) Production and characterization of functional flavored milk and flavored fermented milk using microencapsulated canthaxanthin. LWT 114:108373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108373
Arab M, Sohrabvandi S, Khorshidian N, Mortazavian AM (2019b) Combined effects of salt-related variables on qualitative characteristics of probiotic fermented milk. Curr Nutr Food Sci 15:234–242. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573401314666180123151007
Aryana KJ, Olson DW (2017) A 100-year review: yogurt and other cultured dairy products. J Dairy Sci 100:9987–10013. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2017-12981
Bierzuńska P, Cais-Sokolińska D, Yiğit A (2019) Storage stability of texture and sensory properties of yogurt with the addition of polymerized whey proteins. Foods 8:548. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8110548
Bitaraf MS, Khodaiyan F, Hosseini SS (2018) Rheological properties of probiotic non-fat yogurt containing Lactobacillus reuteri: effects of inulin addition, inoculum level and fermentation temperature. J Food Bioprocess Eng 1:109–116
Célia JA, da Silva MAP, de Oliveira KB, Souza DG, de Moura Silva LC, Nicolau ES, Gonçalves JA (2017) Influence of heat treatment on physicochemical and rheological characteristics of natural yogurts. Semin Cienc Agrar 38:2489–2503
Chandan RC, O’Rell KR (2006) Manufacture of various types of yogurt. In: Chandan RC (ed) Manufacturing yogurt and fermented milks, 1st edn. Blackwell, New York, pp 211–236
Chandan RC, O’Rell K (2013) Principles of yogurt processing. In: Chandan RC, Kilara A (eds) Manufacturing yogurt and fermented milks, 2nd edn. Wiley-Blackwell, London, pp 239–262
Chua D, Deeth HC, Oh HE, Bansal N (2017) Altering the casein to whey protein ratio to enhance structural characteristics and release of major yoghurt volatile aroma compounds of non-fat stirred yoghurts. Int Dairy J 74:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2017.05.002
Clark S, Michael M, Schmidt KA (2019) Rheological properties of yogurt: effects of ingredients, processing and handling. In: Joyner SH (ed) Rheology of semisolid foods, 1st edn. Springer, Switzerland, pp 203–229
Dönmez Ö, Mogol BA, Gökmen V (2017) Syneresis and rheological behaviors of set yogurt containing green tea and green coffee powders. J Dairy Sci 100:901–907. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2016-11262
Duboc P, Mollet B (2001) Applications of exopolysaccharides in the dairy industry. Int Dairy J 11:759–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0958-6946(01)00119-4
El Bouchikhi S, Pagès P, El Alaoui Y, Ibrahimi A, Bensouda Y (2019) Syneresis investigations of lacto-fermented sodium caseinate in a mixed model system. BMC Biotechnol 19:57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-019-0539-1
Fang T, Shen X, Hou J, Guo M (2019) Effects of polymerized whey protein prepared directly from cheese whey as fat replacer on physiochemical, texture, microstructure and sensory properties of low-fat set yogurt. LWT 115:108268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108268
Fontes-Candia C, Ström A, Lopez-Sanchez P, López-Rubio A, Martínez-Sanz M (2020) Rheological and structural characterization of carrageenan emulsion gels. Algal Res 47:101873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2020.101873
Ghasempour Z, Kia EM, Golbandi S, Ehsani A (2019) Effects of mixed starters on quality attributes of probiotic yogurt using statistical design approach. Nutr Food Sci. https://doi.org/10.1108/NFS-11-2017-0255
Gilbert A, Rioux L-E, St-Gelais D, Turgeon SL (2020) Characterization of syneresis phenomena in stirred acid milk gel using low frequency nuclear magnetic resonance on hydrogen and image analyses. Food Hydrocoll 106:105907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105907
Gomez-Betancur AM, Carmona-Tamayo R, Martínez-Álvarez OL, Casanova-Yepes H, Torres-Oquendo JD (2020) Effect of fat substitution using long-chain inulin and fortification with microencapsulated calcium in the rheological and sensory properties of yogurt mousse. J Food Process Eng. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpe.13433
Guénard-Lampron V, St-Gelais D, Villeneuve S, Turgeon SLJJ (2019) Individual and sequential effects of stirring, smoothing, and cooling on the rheological properties of nonfat yogurts stirred with a technical scale unit. 102: 190–201. Doi:https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2018-14565
Gyawali R, Ibrahim SA (2016) Effects of hydrocolloids and processing conditions on acid whey production with reference to Greek yogurt. Trends Food Sci Technol 56:61–76
Hassan A, Ipsen R, Janzen T, Qvist K (2003) Microstructure and rheology of yogurt made with cultures differing only in their ability to produce exopolysaccharides. J Dairy Sci 86:1632–1638. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(03)73748-5
Iriondo-DeHond M, Iriondo-DeHond A, Herrera T, Fernández-Fernández AM, Sorzano COS, Miguel E, Castillo MDd (2020) Sensory acceptance, appetite control and gastrointestinal tolerance of yogurts containing coffee-cascara extract and inulin. Nutrients 12:627. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030627
Karam MC, Gaiani C, Hosri C, Burgain J, Scher J (2013) Effect of dairy powders fortification on yogurt textural and sensorial properties: a review. J Dairy Res 80:400–409
Kelly P (2019) Manufacture of whey protein products: concentrates, isolate, whey protein fractions and microparticulated. In: Deeth HC, Bansal N (eds) Whey proteins: from milk to medicine. Academic Press, New York, pp 97–122
Khanniri E, Sohrabvandi S, Arab SM, Shadnoush M, Mortazavian AM (2017) Effects of stabilizer mixture on physical stability of non-fat Doogh, an Iranian traditional drink. Koomesh 19:144–153
Khanniri E, Yousefi M, Khorshidian N, Sohrabvandi S, Mortazavian AM (2019) Development of an efficient stabiliser mixture for physical stability of nonfat unfizzy doogh. Int J Dairy Technol 72:8–14. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0307.12554
Khorshidian N, Yousefi M, Shadnoush M, Mortazavian AM (2018) An overview of β-glucan functionality in dairy products. Curr Nutr Food Sci 14:280–292. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573401313666170609092748
Kim SY, Hyeonbin O, Lee P, Kim Y-S (2020) The quality characteristics, antioxidant activity, and sensory evaluation of reduced-fat yogurt and nonfat yogurt supplemented with basil seed gum as a fat substitute. J Dairy Sci 103:1324–1336. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2019-17117
Kumar R, Chauhan SK, Shinde G, Subramanian V, Nadanasabapathi S (2018) Whey proteins: a potential ingredient for food industry—a review. J Dairy Foods Home Sci 37:283–290
Laiho S, Williams RP, Poelman A, Appelqvist I, Logan A (2017) Effect of whey protein phase volume on the tribology, rheology and sensory properties of fat-free stirred yoghurts. Food Hydrocoll 67:166–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.01.017
Lee WJ, Lucey JA (2004) Structure and physical properties of yogurt gels: effect of inoculation rate and incubation temperature. J Dairy Sci 87:3153–3164. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(04)73450-5
Lee W, Lucey J (2010) Formation and physical properties of yogurt. Asian-Aust J Anim Sci 23:1127–1136
Lesme H, Rannou C, Famelart M-H, Bouhallab S, Prost C (2020) Yogurts enriched with milk proteins: Texture properties, aroma release and sensory perception. Trends Food Sci Technol 98:140–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.02.006
Li J, Xu L, Su Y, Chang C, Yang Y, Gu L (2020) Flocculation behavior and gel properties of egg yolk/κ-carrageenan composite aqueous and emulsion systems: effect of NaCl. Food Res Int 132:108990. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2020.108990
Lucey JA, Singh H (1997) Formation and physical properties of acid milk gels: a review. Food Res Int 30:529–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0963-9969(98)00015-5
Madhubasani G, Prasanna P, Chandrasekara A, Gunasekara D, Senadeera P, Chandramali D, Vidanarachchi J (2020) Exopolysaccharide producing starter cultures positively influence on microbiological, physicochemical, and sensory properties of probiotic goats’ milk set-yoghurt. J Food Process Preserv 44:e14361. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.14361
Mahomud MS, Katsuno N, Nishizu T (2017) Formation of soluble protein complexes and yoghurt properties influenced by the addition of whey protein concentrate. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol 44:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2017.05.010
Mortazavian, A. M. and Sohrabvandi, S. (2004). Sensory characteristics of yogurt, A.M. Mortazavian (Ed.). Eta Publication, Iran [In Persian].
Mwizerwa H, Abong GO, Okoth MW, Ongol MP, Onyango C, Thavarajah P (2017) Effect of resistant cassava starch on quality parameters and sensory attributes of yoghurt. Curr Res Nutr Food Sci 5:353–367
Nagaoka S (2019) Yogurt Production. In: Kanauchi M (ed) Lactic Acid Bacteria: Methods and Protocols. Springer, New York, pp 45–54
Nguyen PT, Kravchuk O, Bhandari B, Prakash S (2017) Effect of different hydrocolloids on texture, rheology, tribology and sensory perception of texture and mouthfeel of low-fat pot-set yoghurt. Food Hydrocoll 72:90–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.05.035
Pakseresht S, Tehrani MM, Razavi SMA (2017) Optimization of low-fat set-type yoghurt: effect of altered whey protein to casein ratio, fat content and microbial transglutaminase on rheological and sensorial properties. J Food Sci Technol 54:2351–2360
Pang Z, Deeth H, Yang H, Prakash S, Bansal N (2017) Evaluation of tilapia skin gelatin as a mammalian gelatin replacer in acid milk gels and low-fat stirred yogurt. J Dairy Sci 100:3436–3447. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2016-11881
Pavlou A, Melikidou I, Petridis D, Panayiotou C, Ritzoulis C (2020) Winery by-product hydrocolloids as texture modifiers in yogurt formulations. J Culin Sci Technol 19:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/15428052.2020.1768996
Roefs SPFM, Van Vliet T (1990) Structure of acid casein gels 2. Dynamic measurements and type of interaction forces. Colloids Surf 50:161–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-6622(90)80260-B
Saha D, Bhattacharya S (2010) Hydrocolloids as thickening and gelling agents in food: a critical review. J Food Sci Technol 47:587–597
Saleh A, Mohamed AA, Alamri MS, Hussain S, Qasem AA, Ibraheem MA (2020) Effect of different starches on the rheological, sensory and storage attributes of non-fat set yogurt. Foods 9:61. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods9010061
Sánchez L, Pérez MD, Parrón JA (2020) HPP in dairy products: impact on quality and applications. In: Barba F, Tonello-Samson C, Puértolas E, Lavilla M (eds) Present and future of high pressure processing, 1st edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 245–272
Shaker RR, Jumah RY, Abu-Jdayil B (2000) Rheological properties of plain yogurt during coagulation process: impact of fat content and preheat treatment of milk. J Food Eng 44:175–180
Snoeren T, Damman A, Klok H (1982) The viscosity of skim-milk concentrate. Neth Milk Dairy J 36:305–316
Sodini I, Montella J, Tong PS (2005) Physical properties of yogurt fortified with various commercial whey protein concentrates. J Sci Food Agric 85:853–859. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2037
Tamime AY, Robinson RK (1999) Yoghurt: science and technology, 2end edn. CRC Press, New York
Tamime AY, Robinson RK (2007) 5-Traditional and recent developments in yoghurt production and related products. In: Tamime AY, Robinson RK (eds) Tamime and Robinson’s Yoghurt, 3rd edn. CRC Press, New York, pp 348–467
Tang M-X, Zhu Y-D, Li D, Adhikari B, Wang L-J (2019) Rheological, thermal and microstructural properties of casein/κ-carrageenan mixed systems. LWT 113:108296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108296
Tribst AAL, Falcade LTP, Carvalho NS, de Oliveira MM (2020) Using stirring and homogenization to improve the fermentation profile and physicochemical characteristics of set yogurt from fresh, refrigerated and frozen/thawed sheep milk. LWT 130:109557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109557
Wang X, Kristo E, LaPointe G (2019) The effect of apple pomace on the texture, rheology and microstructure of set type yogurt. Food Hydrocoll 91:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.01.004
Wherry B, Barbano DM, Drake MA (2019) Use of acid whey protein concentrate as an ingredient in nonfat cup set-style yogurt. J Dairy Sci 102:8768–8784. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2019-16247
Yemenicioğlu A, Farris S, Turkyilmaz M, Gulec S (2020) A review of current and future food applications of natural hydrocolloids. Int J Food Sci Technol 55:1389–1406. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijfs.14363
Yildiz F (2010) Development and manufacture of yogurt and other functional dairy products. CRC Press/Taylor & Francis, New York
Yousefi M, Jafari SM (2019) Recent advances in application of different hydrocolloids in dairy products to improve their techno-functional properties. Trends Food Sci Technol 88:468–483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.04.015
Yousefi M, Khorshidian N, Hosseini H (2018) An overview of the functionality of inulin in meat and poultry products. Nutr Food Sci 48:819–835. https://doi.org/10.1108/NFS-11-2017-0253
Zamberlin Š, Samaržija D (2017) The effect of non-standard heat treatment of sheep’s milk on physico-chemical properties, sensory characteristics, and the bacterial viability of classical and probiotic yogurt. Food Chem 225:62–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.01.001
Żbikowska A, Szymańska I, Kowalska M (2020) Impact of inulin addition on properties of natural yogurt. Appl Sci 10:4317. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10124317
Zhao L, Wang X, Tian Q, Mao X (2016) Effect of casein to whey protein ratios on the protein interactions and coagulation properties of low-fat yogurt. J Dairy Sci 99:7768–7775. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2015-10794
Acknowledgements
Support for this study provided by Shahid Sadoughi University of medical sciences is gratefully acknowledged.
Funding
Not Applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA and NM designed the study. MY, VQ and NM collected the data. EK and MA wrote the initial draft. MY, MA and VQ revised the initial draft and finally all the autohrs approved the final version of manuscript for the submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arab, M., Yousefi, M., Khanniri, E. et al. A comprehensive review on yogurt syneresis: effect of processing conditions and added additives. J Food Sci Technol 60, 1656–1665 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05403-6
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05403-6