Abstract
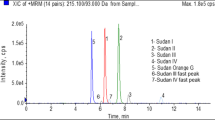
Para Red (PR) and Sudan dyes have been illegally used as colorants to adulterate certain foods by enhancing their red/orange colour. In addition, they are toxic and carcinogenic. This work presents the development of a simple flow injection chromatographic method combined with chemometric tools to perform the determination of PR, Sudan I (SI) and Sudan II (SII) in food samples. The flow chromatographic system consisted of a low-pressure manifold coupled to a reverse phase monolithic column. A Partial Least Square (PLS) model was applied to resolve overlapped absorption spectra registered for each dye at the corresponding retention time. The relative errors of calibration (RMSECV, %) were 0.49, 0.85 and 0.23, and the relative errors of prediction (RMSEP, %) were 1.12, 0.75 and 0.33 for PR, SI and SII, respectively. The residual predictive deviation (RPD) values obtained were higher than 3.00 for all analytes. The method was successfully applied to quantify the dyes in six different commercial spices samples. The results were compared with the HPLC reference method concluding that there were no significant differences at the studied confidence level (α = 0.05). The proposed method can be used to rapidly determine the analytes in a simple, reliable, low-cost and environmentally-friendly manner.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files. Datasets analysed by the PLS method are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Matlab software with PLS Toolbox 3.0; The Unscrumbler software.
References
Anzardi M, Arancibia J, Olivieri A (2021) Processing multi-way chromatographic data for analytical calibration, classification and discrimination: a successful marriage between separation science and chemometrics. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 134116128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.116128
AOAC (1998) Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Peer-Verified Methods Program: Manual on Policies and Procedures. AOAC International, Arlington VA.
ASTA (2005) American Spice Trade Association. http://www.astaspice.org/files/public/SudanWhitePaper.pdf. Accessed 02 April 2020.
Bos T, Knol W, Molenaar S, Niezen L, Schoenmakers P, Somsen G, Pirok B (2020) Recent applications of chemometrics in one- and two-dimensional chromatography. J Sep Sci 43:1678–1727. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.202000011
Chocholouš P, Gil R, Acebal C, Kubala V, Šatínský D, Solich P (2017) Multilayered particle-packed column: Evaluation and comparison with monolithic and core–shell particle columns for the determination of red azo dyes in Sequential Injection Chromatography. J Sep Sci 40(3):1225–1233. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201601224
European Commission (2005) Commission decision of 23 May 2005 on emergency measures regarding chilli, chilli products, curcuma and palm oil. 2005/402/EC. Off J Eur Commun L:34–35.
Duan HL, Mou ZL, Wang J, Ma SY, Zhan HY, Zhang ZQ (2019) Magnetically modified porous β-cyclodextrin polymers for dispersive solid-phase extraction high-performance liquid chromatography analysis of Sudan Dyes. Food Anal Methods 12:1429–1438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01476-w
Efenberger-Szmechtyk M, Nowak A, Kregiel D (2018) Implementation of chemometrics in quality evaluation of food and beverages. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 58:1747–1766. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2016.1276883
Esteki M, Shahsavari Z, Simal-Gandara J (2019) Food identification by high performance liquid chromatography fingerprinting and mathematical processing. Food Res Int 122:303–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2019.04.025
Fonovich T (2013) Sudan dyes: are they dangerous for human health? Drug Chem Toxicol 36(3):343–352
Fukuji T, Castro-Puyana M, Tavares M, Cifuentes A (2012) Sensitive and fast determination of Sudan dyes in chilli powder by partial-filling micellar electrokinetic chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 33(4):705–712. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201100272
Genualdi S, MacMahon S, Robbins K, Farris S, Shyong N, DeJager L (2016) Method development and survey of Sudan I-IV in palm oil and chilli spices in the Washington, DC, area. Food Addit Contam Part A 33(4):583–591. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2016.1147986
Gómez V, Miró M, Callao MP, Cerdà V (2007) Coupling of sequential injection chromatography with multivariate curve resolution-alternating least-squares for enhancement of peak capacity. Anal Chem 79(20):7767–7774. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac071202h
González H, Almirall I, Alpízar J, Montes de Oca R, Cerdà V (2020) Determination of Vitamin E in Spirulina Platensis extracts and photoprotective creams by multi-syringe Chromatography (MSC) and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). Anal Lett 53:2949–2959. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2020.1762629
Iammarino M, Mentana A, Centonze D, Palermo C, Mangiacotti M, Chiaravalle AE (2019) Simultaneous determination of twelve dyes in meat products: development and validation of an analytical method based on HPLC-UV-diode array detection. Food Chem 285:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.133
IARC, International Agency for Research on Cancer (1987) Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Lyon: World Health Organization. Supplement 7.
Kalinowska K, Bystrzanowska M, Tobiszewski M (2021) Chemometrics approaches to green analytical chemistry procedure development. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 30:100498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2021.100498
Khalikova M, Šatínský D, Šmidrkalová T, Solich P (2014) On-line SPE–UHPLC method using fused core columns for extraction and separation of nine illegal dyes in chilli-containing spices. Talanta 130:433–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.07.038
Mejia E, Yongsheng D, Mora M, Garcia C (2007) Determination of banned sudan dyes in chili powder by capillary electrophoresis. Food Chem 102(4):1027–1033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.06.038
Mishra KK, Dixi S, Purshottam SK, Pandey RC, Das M, Khanna SK (2007) Exposure assessment to Sudan dyes through consumption of artificially coloured chilli powders in India. Int J Food Sci Tech 42(11):1363–1366. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2006.01356.x
Olivieri A (2018) Introduction to multivariate calibration: A practical approach. Springer Nature Switzerland AG, Cham
Périat A, Bieri S, Mottier N (2019) SWATH-MS screening strategy for the determination of food dyes in spices by UHPLC-HRMS. Food Chem 1:100009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fochx.2019.100009
Pochivalov A, Davletbaeva P, Cherkashina K, Lezov A, Vakh C, Bulatov A (2018) Surfactant-mediated microextraction approach using switchable hydrophilicity solvent: HPLC-UV determination of Sudan dyes in solid food samples. J Mol Liq 271:807–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.09.072
Rebane R, Leito I, Yurchenko S, Herodes K (2010) A review of analytical techniques for determination of Sudan I-IV dyes in food matrixes. J Chromatogr A 1217(17):2747–2757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2010.02.038
Santos J, Rangel A (2015) Development of a chromatographic low pressure flow injection system using amperometric detection: Application to the analysis of niacin in coffee. Food Chem 187:52–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.04.093
Šatínsky D, Huclová J, Solich P, Karlíček R (2003) Reversed-phase porous silica rods, an alternative approach to high-performance liquid chromatographic separation using the sequential injection chromatography technique. J Chromatogr A 1015(1–2):239–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9673(03)01239-1
Sebaei AS, Youssif MI, Ghazi AA-M (2019) Determination of seven illegal dyes in Egyptian spices by HPLC with gel permeation chromatography clean up. J Food Compos Anal 84:103304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2019.103304
Sousa M, Santos J, Almeida P, Rodrigues J (2018) Low pressure ion pair chromatography with amperometric detection for the determination of trigonelline in coffee samples. Food Res Int 114:223–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.07.068
Tripathi M, Khanna S, Das M (2007) Surveillance on use of synthetic colours in eatables vis a vis Prevention of Food Adulteration Act of India. Food Control 18(3):211–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2005.09.016
Yuan Z, Zhou W, Chen Z (2020) Flower-like layered double hydroxide-modified stainless-steel fibers for online in-tube solid-phase microextraction of Sudan Dyes. J Sep Sci 43:1316–1322. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201900831
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge to CONICET and the financial support of Universidad Nacional del Sur (PGI 24/ZQ17). This work was also supported by the STARSS project (Reg. No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/15_003/0000465) co-funded by ERDF.
Funding
PGI 24/ZQ17 and STARSS project (Reg. No. CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/15_003/0000465).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LN performed the optimization of the FIAC method and analysis of the samples; NL performed the validation by the reference HPLC method; PC conceived the idea, supervised the work and revised the MS; MSR revised the MS; HS conceived the idea, revised and edited the MS; PS supervised the work and revised the MS; CDA: performed the PLS analysis, wrote and revised the MS; CA conceived the idea, performed optimization of the method and, wrote, revised and edited the MS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Consent to participate
All authors are aware and approved the manuscript and this submission.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nussbaum, L., Llamas, N., Chocholouš, P. et al. A simple method to quantify azo dyes in spices based on flow injection chromatography combined with chemometric tools. J Food Sci Technol 59, 2764–2775 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05299-8
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-021-05299-8