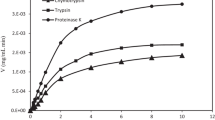
Abstract
Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors are widely used to control hypertension. In this study, protein hydrolysates from shiitake mushroom were hydrolyzed to prepare ACE-inhibitory peptides. Optimum process conditions for the hydrolysis of shiitake mushrooms using Alcalase were optimized using response surface methodology. Monitoring was conducted to check the degree of hydrolysis (DH) and ACE inhibitory activity. In the results, the optimum condition with the highest DH value of 28.88% was 50.2 °C, 3-h hydrolysis time, and 1.16 enzyme/substrate ratios. The highest ACE inhibitory activity (IC50 of 0.33 μg/mL) was under 47 °C, 3 h 28 min hydrolysis time, and 0.59 enzyme/substrate ratios. The highest activity was fractionated into 5 ranges of molecular weight, and the fraction below 0.65 kDa showed the highest activity with IC50 of 0.23 μg/mL. This fraction underwent purification using RP-HPLC, meanwhile the peak which offered a retention time of about 37 min showed high ACE inhibitory activity. Mass spectrometry identified the amino acid sequence of this peak as Lys-Ile-Gly-Ser-Arg-Ser-Arg-Phe-Asp-Val-Thr (KIGSRSRFDVT), with a molecular weight of 1265.43 Da. The synthesized variant of this peptide produced an ACE inhibitory activity (IC50) of 37.14 μM. The peptide KIGSRSRFDVT was shown to serve as a non-competitive inhibitor according to the Lineweaver–Burk plot findings. A molecular docking study was performed, which showed that the peptide binding occurred at an ACE non-active site. The findings suggest that peptides derived from shiitake mushrooms could serve either as useful components in pharmaceutical products, or in functional foods for the purpose of treating hypertension.
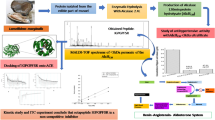
Graphic abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn CB, Jeon YJ, Kim YT, Je JY (2012) Angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from salmon. Process Biochem 47:2240–2245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150814077
Alexopoulos CJ, Minis CW, Blackwell M (1996) Introductory mycology, 4th edn. Wiley, New York, p 868
Asoodeh A, Tabrizi MH, Shabestarian H, Emtenani S, Emtenani S (2016) Biochemical characterization of a novel antioxidant and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from Struthio camelus egg white protein hydrolysis. J Food Drug Anal 24:332–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfda.2015.11.010
Auwal SM, Zarei M, Abdul-Hamid A, Saari N (2017) Optimization of bromelain-aided production of angiotensin I-coverting enzyme inhibitory hydrolysates from stone fish using response surface methodology. Mar Drugs 15:104. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15040104
Balti R, Arroume N, Bougatef A, Guillochon D, Nasri M (2010) Three novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) using digestive proteases. Food Res Int 43:1136–1143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2010.02.013
Bhagani S, Kapil V, Lobo MD (2018) Hypertension. Nat Rev Dis Prim 46:509–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mpmed.2018.06.009
Bhaskar B, Ananthanarayan L, Jamdar S (2019) Purification, identification, and characterization of novel angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from alcalase digested horse gram flour. LWT Food Sci Technol 103:155–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.12.059
Bisen PS, Baghel RK, Sanodiya BS, Thakur GS, Prasad GB (2010) Lentinus edodes: a macrofungus with pharmacological activities. Curr Med Chem 17:2419–2430. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986710791698495
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Chul KK, Lee DH, Kim JH, Yu HE, Par JS, Lee JS (2006) Production and characterization of antihypertensive angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitor from Pholiota adipose. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:757–763
El Sheikha AF, Hu DM (2018) How to trace the geographic origin of mushrooms? Trends Food Sci Technol 78:292–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.06.008
Elmastas M, Turkekul I, Ozturk L, Gulcin I et al (2006) Antioxidant activity of two wild edible mushrooms (Morchella vulgaris and Morchella esculanta) from North Turkey. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 9:443–448. https://doi.org/10.2174/138620706777698544
Erdmann K, Cheung BW, Schröder H (2008) The possible roles of food-derived bioactive peptides in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. J Nutr Biochem 19:643–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2007.11.010
Guo YX, Pan DD, Tanokura M (2009) Optimisation of hydrolysis conditions for the production of the angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from whey protein using response surface methodology. Food Chem 114:328–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.041
He JZ, Ru QM, Dong DD, Sun PL (2012) Chemical characteristics and antioxidant properties of crude water soluble polysaccharides from four common edible mushrooms. Molecules 17:4373–4387. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules17044373
Hibbett DS, Donoghue MJ (1996) Implications of phylogenetic studies for conservation of genetic diversity in Shiitake mushrooms. Conserv Biol 10:1321–1327. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1739.1996.10051321.x
Ibrahim HR, Ahmed AS, Miyata T (2017) Novel angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from caseins and whey proteins of goat milk. J Adv Res 8:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2016.12.002
Kim SK, Wijesekara I (2010) Development and biological activities of marine-derived bioactive peptides: a review. J Funct Foods 2:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2010.01.003
Ko SC, Lee JK, Byun HG, Lee SC, Jeon YJ (2012) Purification and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from enzymatic hydrolysates of Styela clava flesh tissue. Process Biochem 47:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2011.10.005
Largent DL, Johnson D, Watling R (1977) How to identify mushrooms to genus, III. Microscopic features. Mad River Press, Eureka
Lee JK, Jeon JK, Byun HG (2011) Effect of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide purified from skate skin hydrolysate. Food Chem 125:495–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.09.039
Li GH, Le GW, Shi YH (2004) Shrestha S, Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins and their physiological and pharmacological effects. Nutr Res 24:469–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0271-5317(04)00058-2
Moller NP, Scholz-Ahrens KE, Roos N, Schrezenmeir J (2008) Bioactive peptides and proteins from foods: indication for health effects. Eur J Clin Nutr 47:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-008-0710-2
Nawaz KA, David SM, Murugesh E, Thandeeswaran M, Kiran KG, Mahendran R, Palaniswamy M, Angayarkanni J (2017) Identification and in silico characterization of a novel peptide inhibitor of angiotensin converting enzyme from pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan). Phytomedicine 36:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2017.09.013
Nielsen PM, Petersen D, Dambmann C (2001) Improved method for determining food protein degree of hydrolysis. J Food Sci 66:642–646. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.2001.tb04614.x
Onuh JO, Aluko RE (2019) Metabolomics as a tool to study the mechanism of action of bioactive protein hydrolysates and peptides: a review of current literature. Trends Food Sci Technol 91:625–633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2019.08.002
Pan D, Cao J, Guo H, Zhao B (2012) Studies on purification and the molecular mechanism of a novel ACE inhibitory peptide from whey protein hydrolysate. Food Chem 130:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.07.011
Pan S, Wang S, Jing L, Yao D (2016) Purification and characterisation of a novel angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptide derived from the enzymatic hydrolysate of Enteromorpha clathrata protein. Food Chem 211:423–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.05.087
Rahman MA, Abdullah N, Aminudin N (2018) Lentinula edodes (shiitake mushroom): an assessment of in vitro anti-atherosclerotic bio-functionality. Saudi J Biol Sci 25:1515–1523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.01.021
Salampessy J, Reddy N, Phillps M, Kailasapathy K (2017) Isolation and characterization of nutraceutically potential ACE Inhibitory peptides from leatherjacket (Meuchenia sp.) protein hydrolysates. LWT Food Sci Technol 80:430–436. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2017.03.004
Sayer G, Bhat G (2014) The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and heart failure. Cardiol Clin 32:21–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccl.2013.09.002
Thetsrimuang C, Khammuang S, Chiablaem K, Srisomsap C, Sarnthima R (2011) Antioxidant properties and cytotoxicity of crude polysaccharides from Lentinus polychrous Lév. Food Chem 128:634–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.03.077
Turan D, Capanoglu E, Altay F (2015) Investigating the effect of roasting on functional properties of defatted hazelnut flour by response surface methodology (RSM). LWT Food Sci Technol 63:758–765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2015.03.061
Wang X, Chen H, Fu X, Li S, Wei J (2017) A novel antioxidant and ACE inhibitory peptide from rice bran protein: biochemical characterization and molecular docking study. LWT Food Sci Technol 75:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2016.08.047
Wu SG, Sun JH, Tong ZF, Lan XD, Zhao ZX, Liao DK (2012) Optimization of hydrolysis conditions for the production of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides and isolation of a novel peptide from lizard fish (Saurida elongata) muscle protein hydrolysate. Mar Drugs 10:1066–1080. https://doi.org/10.3390/md10051066
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Institute of Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering, Chulalongkorn University, for their support and providing access to their facilities. We acknowledge the financial support from the Grant for Research: The Research Assistantship Fund, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University (RAF_2561_009), and The Ratchadapisek Sompoch Endowment Fund (2019), Chulalongkorn University (762008) for providing the financial support for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paisansak, S., Sangtanoo, P., Srimongkol, P. et al. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from the shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes). J Food Sci Technol 58, 85–97 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04517-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-020-04517-z