Abstract
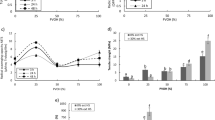
Common buckwheat starch modified by heat moisture treatment at different temperatures was analysed for functional, pasting, structural, thermal, gel textural and morphological properties. Heat moisture treatment decreased swelling power, solubility and oil absorption capacity while amplified water absorption capacity of buckwheat starch. Lower whiteness index with higher a* and b* values were observed for treated starches. Modified starches showed increased paste clarity and reduced syneresis. A declining order of paste clarity and freeze-thaw stability of native and treated starches was noticed during storage period. RVA analysis showed reduced viscosities (peak, trough, breakdown, final and setback viscosity) for hydrothermally treated starches. Increased gel hardness was observed for modified starches and starch sample treated at 85 °C produced the hardest gel. FTIR spectrums of native and treated starch samples showed peaks at similar wavenumbers. Micrographs revealed the polygonal shape of native starch granules with flat areas on surface. Increased agglomeration in heat moisture treated starch samples was noticed in scanned images of starches. X-ray diffraction analysis showed ‘A’ type crystalline pattern in native starch of common buckwheat and no alteration in crystalline pattern due to hydrothermal treatment was observed. Relative crystallinity of native buckwheat starch decreased during heat moisture treatment and the minimum value was recorded for starches treated at 85 °C. Differential scanning calorimetry showed raised gelatinisation temperatures (TO, TP and TC) and reduced ΔH values for hydrothermal treated starches.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali A, Wani TA, Wani IA, Masoodi FA (2016) Comparative study of the physico-chemical properties of rice and corn starches grown in Indian temperate climate. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 15:75–82
Balasubramanian S, Sharma R, Kaur J, Bhardwaj N (2014) Characterization of modified pearl millet (Pennisetum typhoides) starch. J Food Sci Technol 51:294–300
Cael JJ, Koenig JL, Blackwell J (1975) Infrared and Raman spectroscopy of carbohydrates. Part VI: normal coordinate analysis of V-amylose. Biopolymers 14:1885–1903
Chen Y, Yang Q, Xu X, Qi L, Dong Z, Luo Z, Lu X, Peng X (2017) Structural changes of waxy and normal maize starches modified by heat moisture treatment and their relationship with starch digestibility. Carbohydr Polym 177:232–240
Chi H, Xu K, Wu X, Chen Q, Xue D, Song C, Zhang W, Wang P (2008) Effect of acetylation on the properties of corn starch. Food Chem 106(3):923–928
Franco CM, Ciacco CF, Tavares DQ (1995) Effect of the heat-moisture treatment on the enzymatic susceptibility of corn starch granules. Starch-Stärke 47:223–228
Gunaratne A, Hoover R (2002) Effect of heat–moisture treatment on the structure and physicochemical properties of tuber and root starches. Carbohydr Polym 49:425–437
Hormdok R, Noomhorm A (2007) Hydrothermal treatments of rice starch for improvement of rice noodle quality. LWT-Food Sci Technol 40:1723–1731
Ige MM, Ogunsua AO, Oke OL (1984) Functional properties of the proteins of some Nigerian oilseeds: conophor seeds and three varieties of melon seeds. J Agric Food Chem 32:822–825
Jacobson MR, Obanni M, Bemiller JN (1997) Retrogradation of starches from different botanical sources. Cereal Chem 74:511–518
Jiranuntakul W, Puttanlek C, Rungsardthong V, Puncha-Arnon S, Uttapap D (2011) Microstructural and physicochemical properties of heat-moisture treated waxy and normal starches. J Food Eng 104:246–258
Khunae P, Tran T, Sirivongpaisal P (2007) Effect of heat-moisture treatment on structural and thermal properties of rice starches differing in amylose content. Starch-Stärke 59:593–599
Kumar R, Khatkar BS (2017) Thermal, pasting and morphological properties of starch granules of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) varieties. J Food Sci Technol 54(8):2403–2410
Li S, Ward R, Gao Q (2011) Effect of heat-moisture treatment on the formation and physicochemical properties of resistant starch from mung bean (Phaseolus radiatus) starch. Food Hydrocoll 25:1702–1709
Li W, Cao F, Fan J, Ouyang S, Luo Q, Zheng J, Zhang G (2014) Physically modified common buckwheat starch and their physicochemical and structural properties. Food Hydrocoll 40:237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.03.012
Liu H, Lv M, Peng Q, Shan F, Wang M (2014) Physicochemical and textural properties of tartary buckwheat starch after heat–moisture treatment at different moisture levels. Starch-Stärke 66:1–9
Liu H, Guo X, Li W, Wang X, Peng Q, Wang M (2015) Changes in physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of common buckwheat starch by heat-moisture treatment and annealing. Carbohydr Polym 132:237–244
Malik MA, Saxena DC (2016) Effect on physicochemical and thermal properties of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) starch by acid hydrolysis combined with heat moisture treatment. J Food Process Preserv 40:1352–1363
Perera C, Hoover R (1999) Influence of hydroxypropylation on retrogradation properties of native, defatted and heat-moisture treated potato starches. Food Chem 64:361–375
Sarkar S (2016) Influence of acetylation and heat-moisture treatment on physio-chemical, pasting and morphological properties of buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) starch. Asian J Dairy Food Res 35(4):298–303
Sindhu R, Khatkar BS (2018a) Amaranth starch isolation, oxidation, heat-moisture treatment and application in edible film formation. Intl J Adv Eng Res Sci 5(3):136–141. https://doi.org/10.22161/ijaers.5.3.17
Sindhu R, Khatkar BS (2018b) Development of edible films from native and modified starches of common buckwheat. Inl Adv Res J Sci Eng Technol 5(3):9–12. https://doi.org/10.17148/IARJSET.2018.532
Sindhu R, Khatkar BS, Rulahnia K (2018) Development of native and hydrothermally modified amaranth starch films. Int Adv Res J Sci Eng Technol 5(3):13–16. https://doi.org/10.17148/IARJSET.2018.533
Singh N, Inouchi N, Nishinari K (2006) Structural, thermal and viscoelastic characteristics of starches separated from normal sugary and waxy maize. Food Hydrocoll 20:923–935
Singh N, Nakaura Y, Inouchi N, Nishinari K (2007) Fine structure, thermal and viscoelastic properties of starches separated from Indica rice cultivars. Starch-Starke 59:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/star.200600527
Singh N, Kaur S, Kaur A, Isono N, Ichihashi Y, Noda T, Rana JC (2014) Structural, thermal, and rheological properties of Amaranthus hypochondriacus and Amaranthus caudatus starches. Starch-Stärke 66(5–6):457–467
Skrabanja V, Kreft I, Golob T, Modic M, Ikeda S, Ikeda K, Kreft S, Bonafaccia G, Knapp M, Kosmelj K (2004) Nutrient content in buckwheat milling fractions. Cereal Chem 81(2):172–176
Watcharatewinkul Y, Puttanlek C, Rungsardthong V, Uttapap D (2009) Pasting properties of a heat-moisture treated canna starch in relation to its structural characteristics. Carbohydr Polym 75(3):505–511
Zavareze E, Storck CR, de Castro LAS, Schirmer MA, Dias ARG (2010) Effect of heat-moisture treatment on rice starch of varying amylose content. Food Chem 121:358–365
Zavareze DRE, Pinto VZ, Klein B, Halal EISLM, Elias MC, Prentice-Hernández C, Dias ARG (2012) Development of oxidised and heat–moisture treated potato starch film. Food Chem 132(1):344–350
Zobel H (1964) X-ray analysis of starch granules. Methods in carbohydrate chemistry 4:109–113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sindhu, R., Devi, A. & Khatkar, B.S. Physicochemical, thermal and structural properties of heat moisture treated common buckwheat starches. J Food Sci Technol 56, 2480–2489 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03725-6
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-019-03725-6